Technology for Farm: 7 Shocking Innovations Revealed!
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Tech Revolution in Agriculture
- Fun Fact: AI’s Yield Power
- 7 Shocking Innovations Transforming Modern Farming
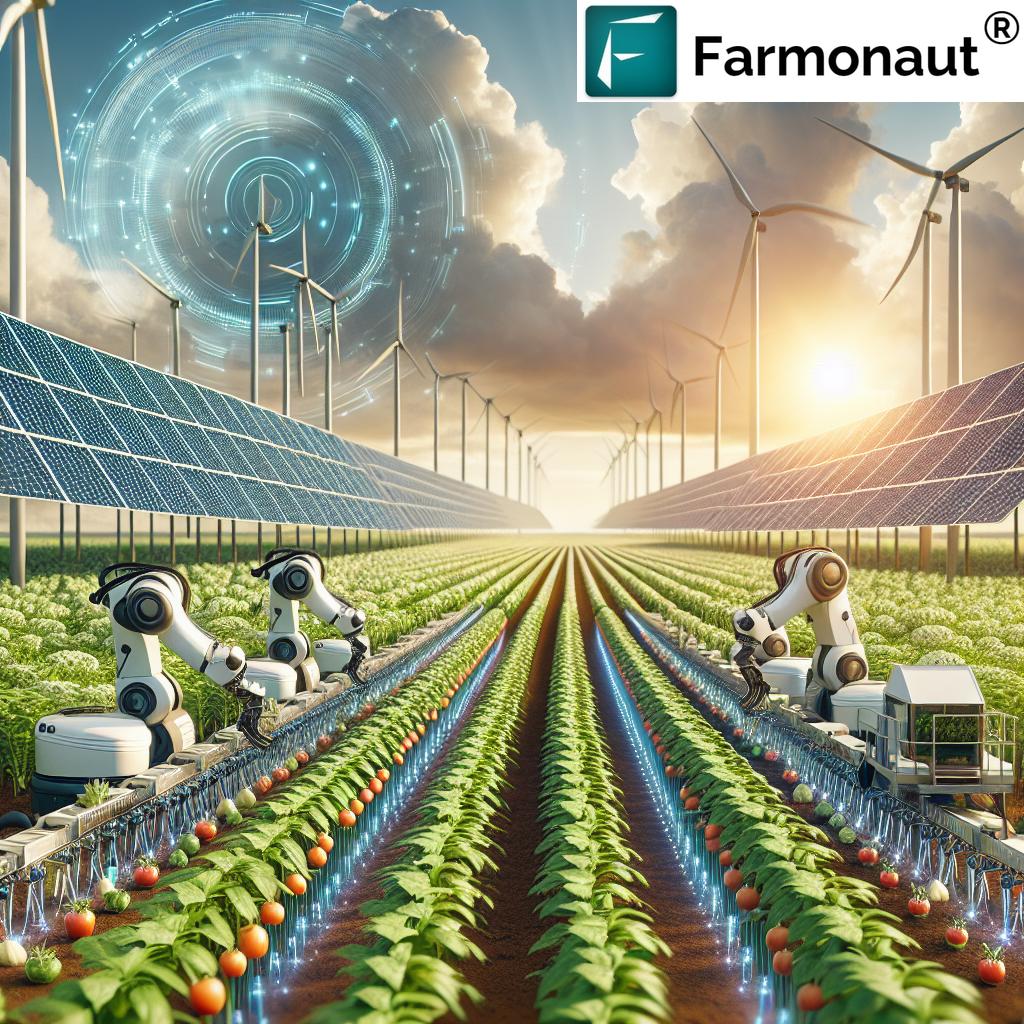
- 1. Agricultural Automation & Robotics
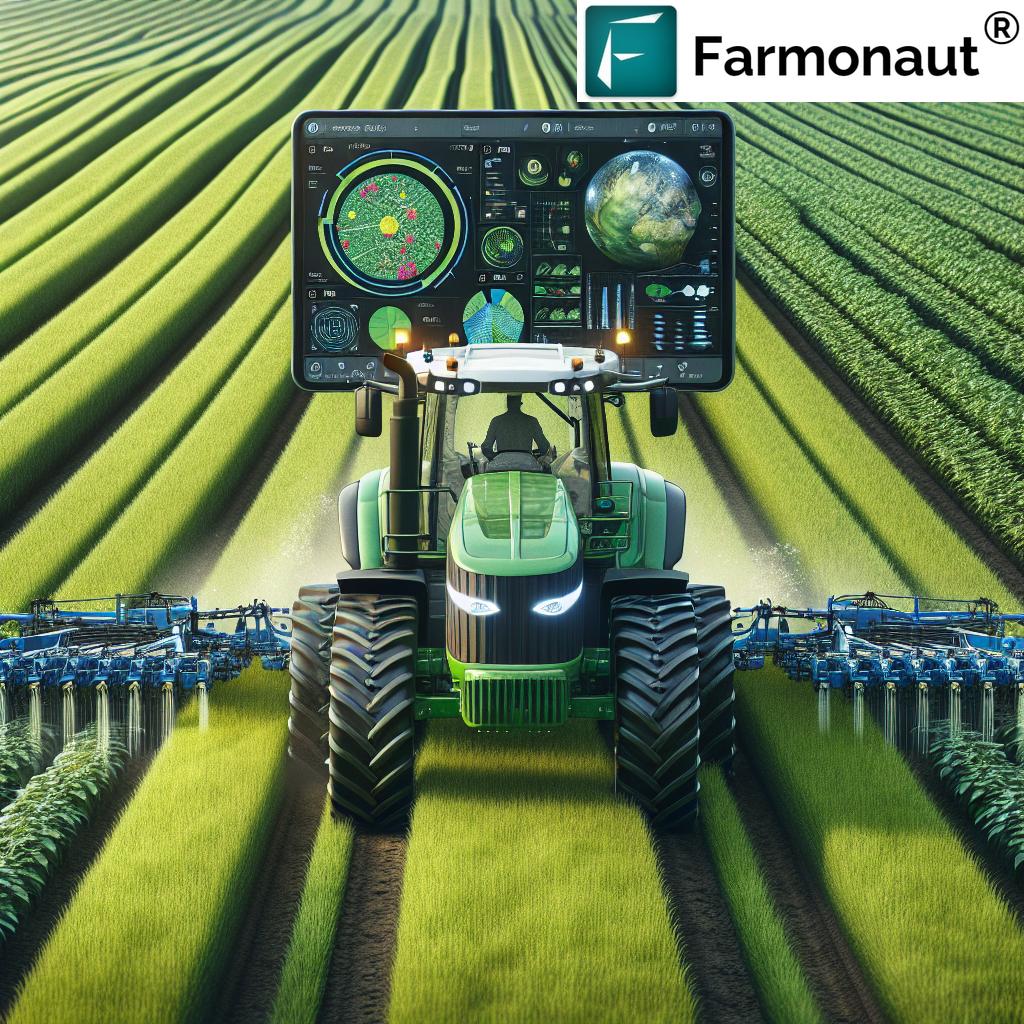
- 2. AI in Agriculture & Data Analytics
- 3. Smart Farming Technologies: IoT & Connectivity
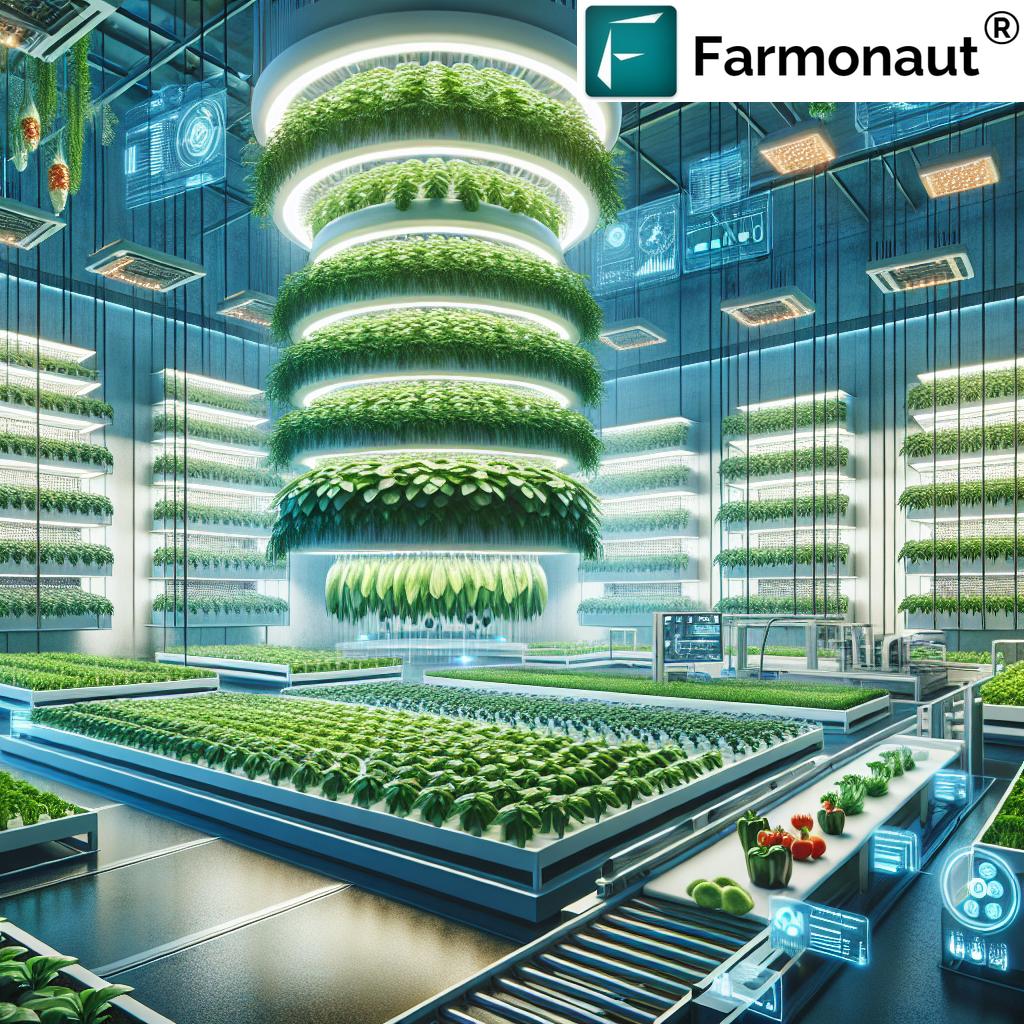
- 4. Vertical Farming Methods & Controlled Environment Agriculture
- 5. Renewable Energy in Agriculture: Agrivoltaics & Sustainability
- 6. Farmonaut: Satellite-Based Farm Management for Precision
- 7. Blockchain & Advanced Traceability in Agriculture
- Comparison Table of Farming Technologies and Their Impact
- Fun Fact: Automation and Labor
- Challenges and Key Considerations
- Farmonaut Subscription Packages
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion: The Future of Agriculture is Here
Introduction: The Tech Revolution in Agriculture
The intersection of technology and agriculture is rapidly rewriting the future of global food systems, forestry, and land management. Thanks to automation, AI in agriculture, smart farming technologies, and other innovative methods, farmers and agribusinesses achieve unprecedented efficiency, sustainability, and productivity.
Today, we stand at the brink of the most significant transformation in farming history. Traditional practices are giving way to data-driven decisions, advanced sensors, renewable energy adoption, and climate-adaptive solutions. Whether you care about boosting crop yields, slashing costs, conserving water, or reducing environmental footprints, these advances deliver shockingly positive impacts at every stage in the agricultural value chain.
Join us as we delve into the top 7 innovations shaking up global farming landscapes. Along the way, discover how companies like Farmonaut make cutting-edge solutions accessible for all — helping both smallholders and large-scale farming operations achieve a healthier, more resilient future.
“AI-driven precision farming can increase crop yields by up to 30% compared to traditional methods.”
7 Shocking Innovations Transforming Modern Farming
1. Agricultural Automation & Robotics
Agricultural automation is revolutionizing how we handle labor-intensive tasks. From robotic harvesters that pick fruits, vegetables, and grains at peak ripeness to automated mechanical weeders like those developed by FarmWise, the future is here. These smart machines reduce manual labor, minimize food waste, and slash operational costs, transforming both the economics and sustainability of modern farming.
- Robotic harvesters: Use computer vision and AI to accurately pick crops, ensuring minimal mechanical damage and optimal quality.
- Automated weeders: Employ AI to identify and remove weeds with surgical precision, reducing the need for chemicals and promoting sustainable farming practices.
Advanced precision irrigation systems also fall within the automation umbrella. Smart irrigation controllers analyze real-time weather and soil data to create optimal watering schedules. By delivering water directly to the roots based on soil moisture sensors and weather forecasts, they conserve water, boost yields, and help farmers adapt to climate change and resource scarcity.
We see the most dramatic benefits in large-scale agricultural operations, where automated machinery reduces labor costs by nearly 50%.
Managing agricultural machinery is seamless with Farmonaut’s Fleet Management Tools. Monitor your mobile assets, optimize routes, and enhance field operations to reduce fuel usage and improve crop productivity.
2. AI in Agriculture & Crop Yield Analytics
Artificial intelligence has redefined farming as a dynamic, data-driven discipline. In today’s AI-powered agricultural landscape, software solutions expertly analyze weather forecasts, satellite images, soil data, and historical harvest records to predict yields, anticipate pest threats, and optimize resource allocation.
- Yield Prediction: By analyzing a variety of parameters (weather, soil moisture, NDVI, past crop records), AI-powered systems generate actionable insights for long-term planning and supply chain management.
- Pest & Disease Control: AI and sensors monitor patterns in pest behavior, recommend targeted treatments, and reduce reliance on blanket pesticides, supporting both healthier crops and lower input costs.
Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI Advisory System puts these tools in your hands, delivering personalized crop management insights, weather updates, and actionable farming strategies directly to mobile or web. Real-time crop health monitoring helps us make rapid, informed decisions — driving up yields while keeping input costs in check.
For climate-smart farming, try Carbon Footprinting Solutions. Track your emissions in real time, set sustainability goals, and comply with environmental regulations using satellite-based tools from Farmonaut.
3. Smart Farming Technologies: IoT in Agriculture & Connectivity
The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) in agriculture has fundamentally transformed connectivity and control in farming. Today, smart sensors are embedded everywhere, from field soil to machinery dashboards, collecting real-time data on every critical parameter:
- Soil health monitoring: Sensors deliver up-to-the-minute information on moisture, pH, nutrient levels, and temperature.
- Weather tracking: Weather stations feed analytics engines, allowing for precise irrigation, fertilizer scheduling, and risk mitigation.
- Livestock health: Wearable IOT devices reveal stress, movement, and health trends among herds for proactive intervention.
- Connected irrigation systems: These manage watering schedules with maximum precision, directly addressing climate variability and water scarcity.
Central control dashboards allow us to analyze data from all our devices — improving productivity, efficiency, and resource allocation. This connectivity also supports seamless integration with weather and satellite data, bringing us closer to truly autonomous farm management.
Use Farmonaut’s satellite weather and IoT data APIs or check out the API Developer Docs to bring smart farming capability to your agricultural business.
4. Vertical Farming Methods & Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA)
Spatial efficiency and environmental control are at the heart of vertical farming methods and controlled environment agriculture (CEA). Urban and peri-urban areas, facing severe land constraints, now cultivate a wide range of crops in vertically stacked layers using hydroponics, aquaponics, and aeroponics.
- Vertical farming: Stacks plants to maximize usage of limited space, greatly reducing the need for traditional arable land.
- Hydroponics: Delivers nutrients and water directly to roots, improving growth rate while minimizing water waste.
- CEA facilities/plant factories: Allow precise management of temperature, humidity, light, and CO₂, supporting year-round production and minimizing crop losses due to unpredictable weather or pests.
- Food miles reduction: Proximity to consumers slashes transportation costs and environmental impact.
CEA and vertical farming are especially promising for sustainable food production in urbanized regions and areas with harsh climates or poor soil quality.
For expansive, plantation-level insight, leverage the Farmonaut Large Scale Farm Management Platform to manage multiple farms or facilities using real-time data, crop health maps, and performance analytics.
5. Renewable Energy in Agriculture: Agrivoltaics & On-Farm Sustainability
Another shocking innovation is the dual integration of renewable energy sources with agricultural production, especially through agrivoltaics. Here, solar panels and wind turbines are co-located with crops or livestock, enabling dual land use and maximizing economic and environmental returns.
- Solar-powered irrigation, machinery, and cold storage: Slashes emissions and reduces operational costs by tapping into abundant, clean energy.
- Agrivoltaic systems: Solar panels offer partial shading, which can boost yields in certain arid regions while producing farm-scale electricity and supporting grazing livestock beneath panels.
- Wind energy: For windy areas, onsite turbines further increase renewable energy resilience for farms.
This integration of renewables exemplifies the shift toward carbon neutrality in agriculture. Farms not only minimize their own environmental footprint but also become power generators for their local grid.
6. Farmonaut: Satellite-Based Smart Farming & Precision Agriculture
At the frontier of affordable farm innovation stands Farmonaut — a platform blending satellite imagery, AI, and blockchain with deep agricultural domain knowledge. Let’s explore how Farmonaut empowers farmers, agribusinesses, and institutions worldwide:
- Satellite crop health monitoring: Multispectral images provide weekly, field-level insights into vegetation health (NDVI), soil moisture, and stress signals — enabling timely interventions for improved yields.
- Jeevn AI Advisory System: Personalizes advice for irrigation schedules, fertilizer application, and pest/disease alerts, incorporating satellite and on-ground data.
- Fleet and resource management tools: Optimize logistical efficiency (fleet vehicles, operational timelines, load routes), minimizing transportation costs and carbon emissions.
- Carbon Footprinting: Real-time emissions tracking for compliance and actionable sustainability improvements at any scale.
Access the Farmonaut App on web/mobile, or integrate satellite data via API into your agribusiness workflow!
Simplify secure farm financing with satellite-based crop loan & insurance verification. Reduce risks and fraud for lenders and insurers, making financing more accessible for all.
7. Blockchain & Advanced Traceability in Food Supply Chains
Trust and transparency are more essential than ever in today’s food supply chain. Blockchain technology in agriculture delivers ironclad product traceability, documenting each stage from planting to harvest to shelf. What does it mean for agriculture?
- Enhanced food safety: Contamination or fraud events can be traced and contained in real-time.
- Supply chain transparency: Boosts consumer trust and supports brand value for food and textile companies.
Learn more about blockchain-based traceability solutions by Farmonaut — ensure every batch is tracked, safe, and delivered with integrity.
Comparison Table of Farming Technologies and Their Impact
| Innovation Name | Technology Type | Main Function | Estimated Boost in Crop Yield (%) | Estimated Resource Savings | Sustainability Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agricultural Automation & Robotics | Automation, Robotics, Computer Vision | Automated harvesting, weed removal, labor savings | 10–20% | 50% labor, 15% reduced waste | Minimized chemical use, lower carbon emissions |
| AI in Agriculture & Analytics | Artificial Intelligence, Data Analytics | Yield prediction, pest/disease forecasting, decision support | 15–30% | 20% input cost, optimized fertilizer | Fewer pesticides, efficient water use |
| Smart Farming Technologies (IoT) | IoT Sensors, Automation | Real-time monitoring, precision irrigation, livestock tracking | 8–18% | 30% water, 15% fuel | Resource conservation, better farm health |
| Vertical Farming & CEA | Controlled Environment Agriculture | Indoor crop production in stacked layers | 25–50% | Up to 90% water, 50% less land | Urban food supply, reduced transport, year-round harvest |
| Renewable Energy & Agrivoltaics | Solar, Wind, Energy Management | Power generation, dual land use, shade for crops | 5–10% | 100% renewable, 15% higher soil moisture | Huge carbon reductions, land maximization |
| Satellite Farm Management (Farmonaut) | Satellites, AI, App/API | Crop health, advisories, fleet tracking | 10–30% | 25% fertilizer, 40% water | Scalable, equitable tech, lower inputs |
| Blockchain Traceability | Blockchain, Digital Ledger | End-to-end product tracing, fraud prevention | ▼ (Indirect) | 10% admin cost, reduced recalls | Food safety, consumer trust |
“Automated machinery reduces farm labor costs by nearly 50% in large-scale agricultural operations.”
Challenges and Key Considerations in Farming Technology Adoption
Barriers to Adoption
- Initial investment costs: Robotics, advanced hardware, and data-providing services require upfront spending that can strain smaller operations.
- Technical expertise and training: Farmers and staff need support to operate, interpret, and maintain emerging systems.
- Digital divide: Rural areas may lack robust internet for seamless IoT in agriculture deployment.
- Data privacy and cybersecurity concerns: As connectivity increases, so do worries about secure data handling.
- Labor market impacts: Automation can displace manual workers; this requires strategic workforce reskilling and policy support.
Sustainability & Access
- Ensuring equitable access: All farmers deserve access to precision agriculture regardless of field size or resources.
- Environmental and social impact: Our choices of technologies must align with sustainable farming practices and support rural communities.
In navigating these barriers, innovators like Farmonaut prove vital by offering cost-effective SaaS and API platforms, enabling affordable entry into satellite-guided, AI-empowered farm management.
For forestry and leafy crop producers, access tailored crop plantation and forest advisory solutions via Farmonaut’s crop advisory system.
Farmonaut Subscription Packages
Choose between web, mobile, or API access. Packages scale to individual smallholders, cooperatives, agribusinesses, or government agencies seeking large-area, multi-farm analytics and sustainable growth. Learn more below!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the main benefit of automation in agriculture?
Automation streamlines repetitive and labor-intensive tasks such as crop harvesting, weeding, and irrigation. It dramatically reduces manual labor, minimizes waste, and ensures crops are picked at optimal ripeness for the best yields.
How does AI in agriculture improve productivity?
AI analyzes vast datasets—including weather patterns, soil conditions, and crop health indicators—to deliver actionable insights. It enables prediction of optimal planting schedules, targeted pest control, and precise application of resources, boosting both crop yields and cost efficiency.
What are precision irrigation systems and why are they important?
Precision irrigation systems use sensors and weather data to deliver water only where and when it’s needed. This technology conserves water, prevents overwatering, and enhances plant health, particularly crucial in drought-prone regions.
Why is vertical farming becoming popular in urban areas?
Vertical farming methods optimize limited urban space by growing crops in stacked layers. They ensure a consistent food supply, use less water and land, and can reduce transportation emissions by bringing production closer to consumers.
How does renewable energy in agriculture contribute to sustainability?
Solar panels, wind turbines, and agrivoltaic systems on farms provide clean, renewable energy. This reduces reliance on fossil fuels, drives down operational costs, and decreases the carbon footprint associated with traditional farming practices.
What makes Farmonaut’s platform different from other precision agriculture solutions?
Farmonaut combines real-time satellite imaging, artificial intelligence, blockchain, and resource management into an affordable, user-friendly platform. It delivers actionable data and insights to all types and sizes of farms, supporting truly sustainable growth.
Conclusion: The Future of Agriculture is Here
The latest technological advancements are not just transforming farming—they are redefining what’s possible in crop production, sustainability, and food security. Automation, robotics, AI, IoT-enabled smart farming technologies, and renewable energy integration all offer clear, measurable benefits: higher yields, lower costs, and smaller environmental footprints.
In particular, Farmonaut stands out by making real-time data, precision insights, and blockchain-backed traceability accessible and affordable to every stakeholder in the agricultural value chain. Its user-first design, scalability, and data-driven approach empower us to manage farms smartly, sustainably, and profitably—no matter the size or geography.
The agricultural revolution is underway and ready for your participation. Let’s embrace these changes, address the remaining challenges, and build a truly sustainable food system for the future.