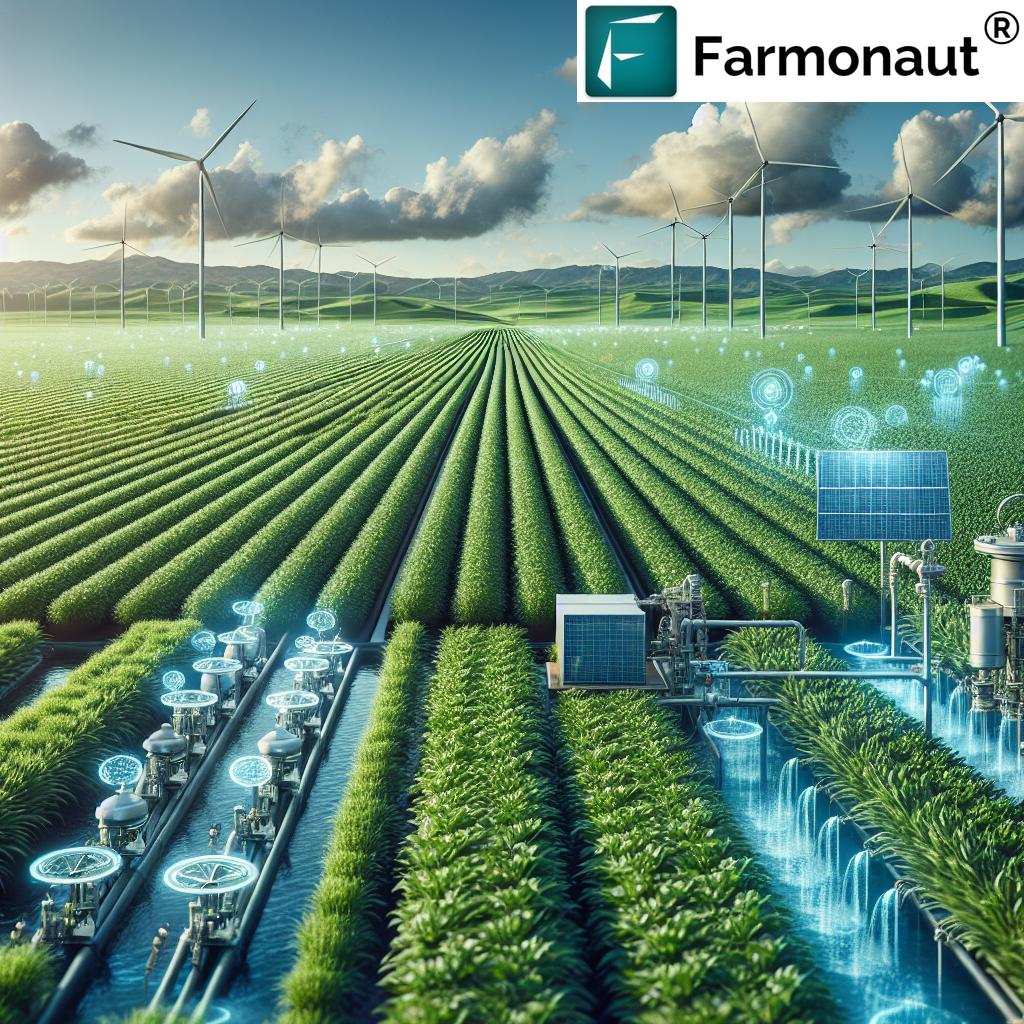
Utility and Agricultural Advances: 7 Farming Innovations Transforming Productivity & Sustainability
- Introduction: The Role of Utility Integration in Agriculture
- 7 Farming Innovations Elevating Agriculture
- Farmonaut’s Contribution to Precision Agriculture
- Comparative Benefits Table
- Challenges in Integrating Utilities in Agriculture
- Policy, Support Mechanisms & Educational Extension
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Introduction: The Role of Utility Integration in Agriculture
Agriculture, the backbone of human civilization, extends far beyond just farming and forestry. It is foundational in providing essential resources—food, fiber, and raw materials—and supporting economies across the globe. Yet, with growing populations, climate volatility, and diminishing water reserves, traditional methods are now challenged to keep pace.
The answer? The integration of advanced utility services—notably water supply, electricity, and telecommunications—into modern agricultural practices. This fusion is reshaping how farmers access and manage critical resources, optimize operations, foster sustainability, and boost efficiency for improved crop productivity.
This comprehensive guide explores the multidimensional role of utilities in agriculture, innovative technologies like smart irrigation systems, agricultural data analytics, integrated renewable energy, and much more. We will also examine challenges, policy support, and the future of sustainable, connected farming.
7 Farming Innovations Elevating Agriculture
The integration of technology and utility services in agriculture has given rise to seven key innovations that are redefining sustainable farming practices, enhancing crop yield, and improving environmental outcomes. Below, we explore each innovation, with a close look at their technologies, impact, and how they are rapidly becoming global standards.
1. Advanced Water Management in Agriculture
Effective water management in agriculture is the linchpin of both food production and environmental sustainability. It goes beyond simply supplying water; it is about optimizing resource usage and ensuring a resilient ecosystem in the face of climate-induced rainfall variability.
- Critical Resource: Water is pivotal for crop growth, impacting every stage from seed germination to harvest.
- Irrigation Systems: In arid regions or areas with insufficient rainfall, irrigation systems deliver water—often powered by electricity and managed via sensors—to targeted crops.
- Techniques: Modern irrigation methods, including drip and sprinkler systems, reduce waste, minimize surface runoff, and prevent soil degradation.
- Environmental Balance: Sustainable water management ensures a balance between farmers’ needs, conservation efforts, and natural resource renewal.
Farmers now rely on advanced digital monitoring tools and automation to determine exactly when and how much water to apply. This minimizes usage, saves energy, and supports increased yields. Tools such as soil moisture sensors or satellite imagery allow for real-time adjustments, helping reduce water scarcity concerns.
Learn how Farmonaut’s Large Scale Farm Management solutions enable advanced water monitoring and smart scheduling to help optimize every drop for your plantation or cooperative.
2. Smart Irrigation Systems – A Leap Toward Precision and Sustainability
Modern agriculture harnesses smart irrigation systems to achieve remarkable efficiency in water usage. These systems combine sensors, weather data, and even satellite imagery to adjust irrigation in real-time according to actual soil conditions, crop needs, and predicted precipitation.
- Data-Driven Application: Smart irrigation measures soil moisture, weather, and plant health to provide exactly the water plants require—no more, no less.
- Resource Optimization: Reduces overwatering, prevents runoff and waste, and ensures the crop yield is never compromised.
- Automation: These systems are often powered by renewable energy sources (like solar panels), further amplifying their sustainable footprint.
Smart irrigation systems are especially vital in water-scarce regions and in climates where rainfall patterns are increasingly unpredictable. The adaptability and precision drastically enhance efficiency and crop productivity, forming the bedrock of next-generation agricultural practices.
3. Renewable Energy Integration in Agriculture
As agriculture intensifies, energy demand grows—for powering pumps, machinery, climate control, and more. Integrating renewable energy in agriculture through solar, wind, or bioenergy not only reduces carbon footprints but also insulates farmers from rising electricity costs and unreliable grid access.
- Solar-Powered Irrigation Pumps: Directly harness solar energy to supply water, slashing operational costs and bringing sustainable power to rural, off-grid locations.
- Wind-Powered Operations: Wind energy is used for mechanical and electrical processes, like running grain mills or powering water pumps.
- Bioenergy: Organic farm waste is converted to biogas or biofuels, closing material loops and cutting emissions.
These solutions help in reducing greenhouse gas emissions, enhancing resilience to grid outages, and providing reliable, cost-effective energy for agricultural operations.
Read more about Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting service, which enables tracking and reduction of CO2 emissions using real-time agricultural data for sustainable operations.
4. Agricultural Data Analytics & Precision Farming
We are living in an era of precision agriculture technologies, where data analytics drives every key decision—from sowing to harvest. By collecting and analyzing massive amounts of data from sensors, satellites, machines, and weather stations, farmers gain actionable insights that optimize resource allocation and enhance productivity.
- Monitoring Soil, Crop, and Weather Conditions: Data from remote sensors and satellites enables hyper-local recommendations, powering targeted irrigation, fertilization, and disease management.
- Predictive Analytics: Advanced algorithms forecast crop yield, pest outbreaks, or nutrient needs, supporting efficient, proactive management.
- Resource Efficiency: Inputs—water, fertilizers, pesticides—are applied with utmost precision, reducing waste and environmental impact.
As a result, farms enjoy increased yields, improved sustainability, and lower input costs. Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI Advisory System is a prime example, providing real-time personalized recommendations based on satellite imagery and environmental data.
5. IoT & Sensor Deployment in Agricultural Operations
The Internet of Things (IoT) continues to create ripples across farming by enabling enormous connectivity and automation. Networks of sensors monitor vital conditions such as soil moisture, plant health, weather changes, and machinery status—feeding real-time data to centralized farm management systems.
- Continuous Monitoring: Soil, water, and crop health are constantly tracked, providing rapid response to environmental and crop stressors.
- Remote Operation: Farmers can remotely manage irrigation, fertilization, and even pest control systems via smartphone apps or web platforms.
- Data Centralization: Integrating all sensor data allows optimum adjustment of agricultural inputs and machinery, raising overall efficiency.
With IoT, not only do we optimize water usage, but we also minimize input wastage, reduce operational labor, and streamline the management of large or dispersed farms.
For seamless integration and automation, Farmonaut’s Fleet and Resource Management tools can help coordinate vehicles, machinery, and logistics for optimal efficiency and cost savings.
6. Electrification of Farm Operations
Modern farm operations are increasingly reliant on a stable and efficient supply of electricity. From lighting and climate control systems in greenhouses to automated machinery—electric-powered equipment is transforming farming by decreasing manual labor and elevating productivity.
- Automated Monitoring: Electric sensors and control systems are at the heart of precision agriculture.
- Climate Adaptation: Electric HVAC and misting systems in protected cultivation (like greenhouses) enable year-round crop growth, buffering unpredictable weather.
- Processing and Handling: Post-harvest equipment powered by electricity (sorting, packaging, cooling) helps maintain food quality and extends shelf-life.
The combination of electrification and smart automation ensures optimal resource use, improved consistency, and scalability across different farming sizes and locations.
7. Blockchain-Based Product Traceability in Agriculture
Transparent supply chains are a growing consumer and regulatory demand—especially for food, fiber, and raw materials. Blockchain-based product traceability now allows every stage of agricultural production, processing, and distribution to be securely recorded and viewable.
- Fraud Reduction: Cryptographically secure ledgers ensure authenticity of both origin and journey across the value chain.
- Consumer Trust: Customers can verify product origins, methods, and certifications, enabling informed choices and fostering brand loyalty.
- Compliance: Assists with governmental and industry regulations by automatically generating auditable histories.
Explore the benefits of Farmonaut’s Blockchain Traceability Solutions which provide instant and tamper-proof tracking from farm to fork.
Farmonaut’s Contribution to Precision Agriculture & Sustainability
At Farmonaut, we understand that the farming landscape is evolving at an unprecedented pace. We’ve dedicated ourselves to providing affordable, accessible, and advanced agricultural technology platforms for farmers, agribusinesses, governments, and institutions worldwide. Our mission is to empower the transformation towards sustainable farming practices—backed by precision agriculture technologies spanning satellite-based crop monitoring, AI/ML analytics, blockchain traceability, and carbon footprinting.
Through web, Android, iOS, and API interfaces, our solutions deliver:
- Real-time Crop Health Monitoring: Multispectral satellite imagery revealing invisible stress, moisture, and disease factors.
- AI-Based Advisory: Our Jeevn AI analyzes sensor, weather, and satellite data for actionable recommendations that improve farm productivity.
- Blockchain Traceability: End-to-end transparency for food safety and brand value.
- Fleet and Resource Management: Efficient logistics coordination, automated farm equipment tracking, and safety controls.
- Carbon Footprinting: Monitor and proactively reduce your environmental impact.
Our mobile apps and API make integration seamless. For institutional use, check the Fleet Management and Large-Scale Farm Management platform—perfect for cooperatives, agribusinesses, and government agencies.
Ready to join the precision farming revolution?
Start with our flexible subscription plans or see our open developer documentation: Farmonaut API Developer Docs.
Comparative Benefits Table: The 7 Farming Innovations
| Innovation Name | Core Technology | Estimated Water Savings (%) | Increase in Crop Yield (%) | Efficiency Improvement (%) | Environmental Benefit | Utility Integration Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Water Management | Sensor & Satellite Monitoring | 25–50% | 10–20% | 15–25% | Prevents soil degradation and reduces water overuse | Automated |
| Smart Irrigation Systems | IoT Sensors, Data Platforms | 20–30% | 10–15% | 18–30% | Minimizes runoff & optimizes fresh water usage | Automated |
| Renewable Energy Integration | Solar, Wind, Bioenergy | 10–18% | 5–12% | 10–15% | Lowered CO2 emissions and green energy adoption | Hybrid Automated/Manual |
| Agricultural Data Analytics | AI & ML, Satellites | 12–22% | 15–20% | 20–28% | Reduced input waste and improved soil conservation | Automated |
| IoT & Sensor Deployment | Connected Sensors (IoT) | 18–28% | 8–15% | 15–25% | Optimized energy and material use | Automated |
| Electrification of Farm Operations | Electric Powered Equipment | 5–12% | 7–15% | 15–22% | Supports decarbonization and energy-efficient production | Automated |
| Blockchain-Based Traceability | Blockchain Secure Ledgers | 5–10% | 3–6% | 10–18% | Reduces supply chain fraud and enhances trust | Automated |
These figures represent weighted industry-wide estimates where deployment is optimized. Actual savings and improvements may vary based on farm scale, geography, and crop types.
Challenges in Integrating Utilities in Agriculture
1. Infrastructure Limitations
A major challenge for rural agriculture globally is limited infrastructure. Many farmers face unreliable electricity supply or lack high-speed internet, restricting the adoption of smart technologies and real-time data transmission. Upgrading local and national infrastructure is vital to widen access to transformative agricultural systems.
2. Cost Implications
The shift towards integrating modern utility services and advanced technologies can involve high up-front investments. Small and medium-sized farmers often find the initial costs prohibitive, threatening to deepen access gaps. Subsidies, financing solutions, and scalable, modular payments (e.g., subscriptions) are essential in promoting equitable adoption.
For instance, Farmonaut’s subscription-based pricing model helps lower the financial barrier, making precision farming truly accessible for farms of every size.
3. Environmental Concerns
While utility integration enhances productivity, it can also contribute to new environmental challenges in farming. Excessive irrigation depletes water tables and salinizes soil; high energy use spikes carbon emissions. Practicing sustainable water management in agriculture, switching to renewables, and leveraging analytical tools (like those provided by Farmonaut) are necessary to mitigate these risks.
4. Data Security & Privacy
The broad deployment of internet-enabled systems means that safeguarding farmers’ data (crop, soil, climate, operations) is paramount. Solutions using encryption, blockchain, and robust authentication protocols help protect sensitive information and build trust in the digital agricultural revolution.
Policy, Support Mechanisms & Educational Extension
The integration of utilities in agriculture is not just a technological challenge, but a policy and educational one. Effective frameworks from both government and industry play an essential role in ensuring that the benefits of these innovations are universal and lasting.
- Government Incentives: Direct subsidies, infrastructure investments, research grants, and low-interest financing encourage the adoption of smart irrigation systems, renewable energy, and digital management tools.
- Education & Extension Services: Agricultural extension programs disseminate best practices, train in the use of precision agriculture technologies, and support farmers with troubleshooting. Digital platforms such as Farmonaut offer ongoing advice and community support.
- Smart Regulations: Policy can set standards for data privacy, environmental protection, and resource use, promoting sustainability at scale.
For additional transparency and compliance, Farmonaut’s Crop Loan and Insurance verification tools support financial institutions and farmers alike with satellite-based farm assessment, making access to credit and insurance fairer and less prone to fraud.
Conclusion: Toward a Smarter, Sustainable Future in Agriculture
Integrating key utility services—from water management in agriculture and smart irrigation systems to agricultural data analytics and renewable energy in agriculture—has delivered unprecedented advancements for farmers, agribusinesses, and policy-makers. These technologies drive improved efficiency, lower costs, greater crop productivity, and foster sustainable farming practices that safeguard our environmental future.
Challenges remain—particularly in infrastructure, up-front costs, and environmental management. Yet, through innovation, data-driven decision-making, sound policy, and accessible platforms like Farmonaut, the global agricultural community is better equipped than ever to build resilient, efficient, and sustainable food systems.
Our belief is simple: Connected, data-driven agriculture is the root of global food security, climate resilience, and rural prosperity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What is the biggest benefit of ‘water management in agriculture’?
A: Effective water management ensures optimal crop yield while conserving water resources and maintaining soil health, significantly reducing environmental impact and operational costs. -
Q: How do smart irrigation systems improve farm productivity?
A: Smart irrigation systems primarily utilize real-time data from sensors and weather platforms to adjust water delivery, minimizing waste and ensuring crops receive the right amount of moisture, which can increase yields by up to 15%. -
Q: Why is renewable energy integration important in agriculture?
A: Renewable energy reduces reliance on traditional, fossil-fuel-powered grids, lowers CO2 emissions, and provides reliable, cost-effective energy critical for rural and off-grid farm operations. -
Q: What is ‘precision agriculture’ and how does data analytics contribute?
A: Precision agriculture leverages data from sensors, satellites, and analytics to optimize input application (such as water, fertilizers, pesticides) which improves efficiency, reduces costs, and enhances environmental stewardship. -
Q: How does blockchain-based product traceability benefit farmers and consumers?
A: Blockchain ensures every stage in the agricultural supply chain is documented and tamper-proof, building transparency, preventing fraud, and giving consumers data-backed trust in product authenticity. -
Q: Can small farms adopt these advanced farming innovations?
A: Yes! Flexible pricing, modular service plans, and cloud-based tools (like those from Farmonaut) make advanced agricultural innovations accessible and scalable for small and medium-sized farms.
Ready to optimize your farm’s water use, enhance crop monitoring, and join the precision agriculture movement?
Start with Farmonaut or integrate our developer-friendly API for seamless data-driven farming.