Utah Snowpack Spring Runoff: Top 7 Management Tips
“Utah’s snowpack provides up to 80% of the state’s annual water supply, crucial for agriculture and forestry.”
Introduction: Understanding Utah Snowpack & Spring Runoff
When it comes to understanding Utah snowpack levels and springtime runoff, we’re delving into the lifeblood of Utah’s water system. Snowpack acts as a vast, natural reservoir: in the heart of winter, snow accumulates on Utah’s mountainous slopes, only to begin its gradual transformation into river and reservoir water as spring temperatures rise.
The spring runoff in Utah nourishes everything from agricultural crops to forestry systems and even the daily needs of our communities. But the dynamics of this process are anything but simple. Snowpack quantity, the speed of snowmelt, and year-to-year variations all have significant consequences for water supplies, soil moisture, crop health, forest ecosystems, and overall sustainability in the state.
Our goal in this comprehensive guide is to explain the most effective water management strategies—tips, tools, and technologies that empower us to address both opportunities and challenges that arise from variable snowmelt patterns in Utah.
“Spring runoff in Utah can release over 10 million acre-feet of water, impacting water management and sustainability efforts.”
The Role of Snowpack in Utah’s Water System
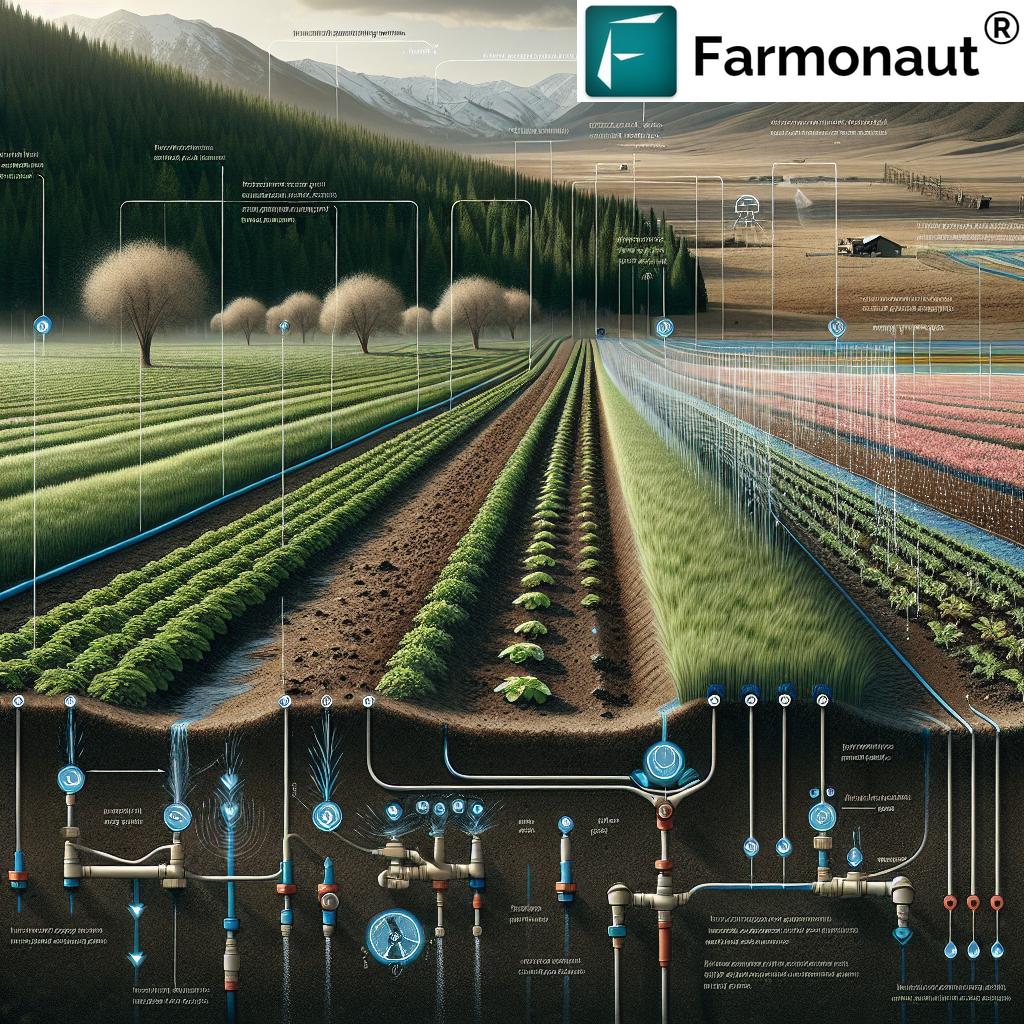
Let’s start with the basics: Snowpack forms when winter precipitation accumulates as snow in Utah’s mountainous regions. This snow becomes a natural reservoir—holding vast supplies of water until warmer spring months trigger melting. As the snow melts, it releases water which flows down rivers, streams, and into reservoirs, replenishing supplies for the dry summer months.
- Timing, volume, and rate of snowmelt are the keys affecting water availability for agriculture and forestry in Utah.
- An early or rapid melt can mean flooding, erosion, and water losses to evaporation.
- Delayed or reduced runoff results in water shortages for irrigation, livestock, and forest growth.
Therefore, understanding snowpack dynamics—how much snow accumulates, how quickly it melts, and how it’s routed through the landscape—is essential for agricultural water availability in Utah, for forest ecosystem health, and for the broader sustainability of water supplies.
Recent Trends in Utah’s Snowpack & Spring Runoff Patterns
Over the past few years, we’ve observed significant variability in Utah snowpack levels. For example, in early 2025, Utah’s overall snowpack measured about 93% of average, but some southern basins fell below 50% of the typical snow water equivalent (SWE).
These low snowpack levels are particularly concerning for agriculture and forestry sectors. Reduced spring runoff directly threatens irrigation water supplies, soil moisture for crops, forest health, and ecosystem resilience. In contrast, an exceptionally snowy winter can result in a rapid snowmelt, potentially causing flooding, soil erosion, and damage to both crops and forests.
- The Great Salt Lake Basin and southern Utah (especially southwestern Utah) have recently seen a return of extreme drought conditions, as recent as March 2023-2025 (Utah Water Conditions Update).
- Even normal snow years may result in insufficient supplies if timing and rate of snowmelt do not align with cropping and growing seasons.
These variable patterns demand robust monitoring, planning, and adaptive management strategies—not just for today’s needs, but for adapting to future changes driven by climate and regional development.
Agricultural Impacts: Snowmelt and Crops
Agriculture in Utah—from alfalfa and wheat to corn and orchards—is intricately linked to the availability of water delivered during spring runoff. Farmers must carefully track both the quantity and timing of water released by snowpack to meet the needs of growing crops and livestock.
- Insufficient runoff leads to reduced irrigation, forcing farmers to tap into limited and expensive groundwater resources. This can increase production costs and harm long-term sustainability.
- Excessive or early runoff can damage crops through flooding, disrupt planting schedules, and lead to erosion / soil degradation.
Snowmelt impacts on crops are apparent in variable yields, increased risks, and seasonal uncertainties. For this reason, monitoring snowpack, tracking soil moisture, and implementing efficient irrigation systems are fundamental for sustainable agricultural water availability in Utah.
- Planning ahead—using weather data, snowpack maps, and resource forecasts—enables farmers to adjust irrigation timing, conserve water, and avoid over-tapping resources
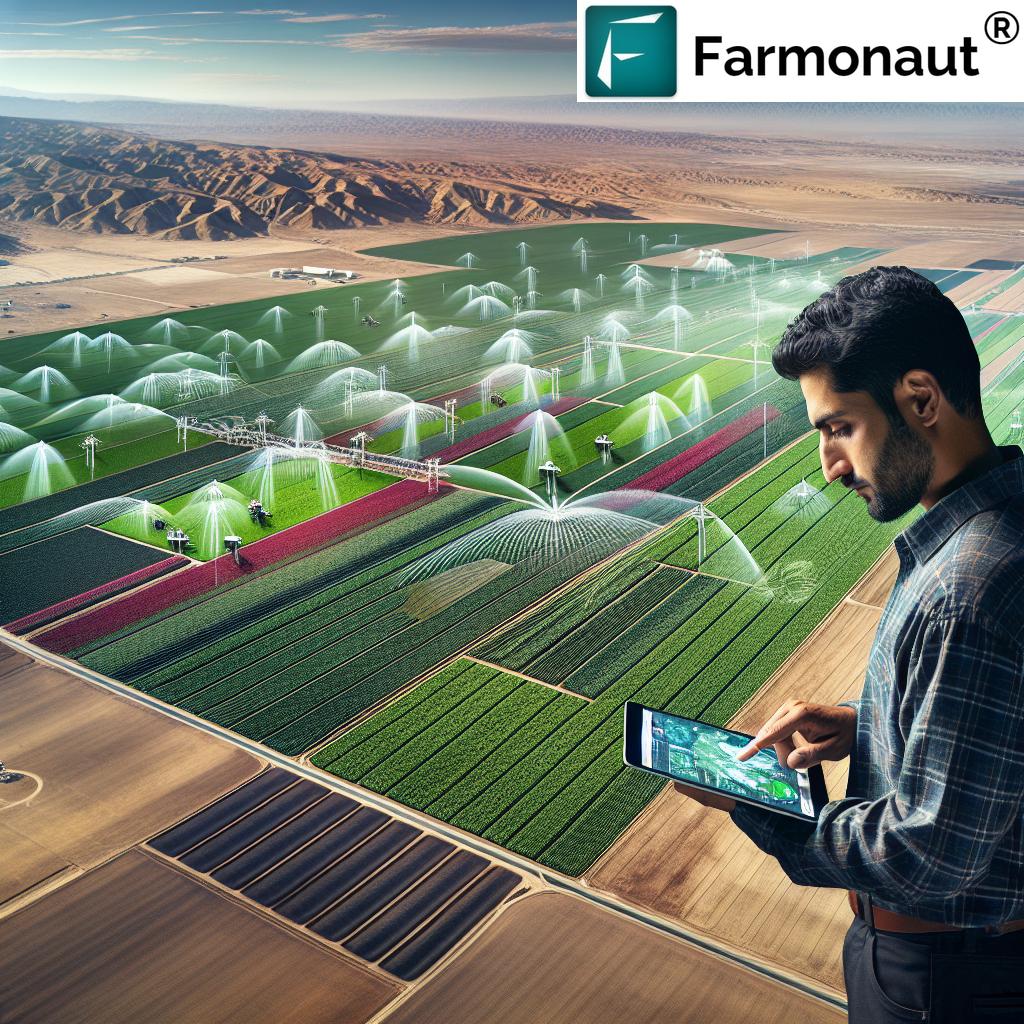
- Efficient irrigation systems like drip irrigation maximize water use efficiency while protecting both soil and crop health during variable runoff conditions
The dynamics of agriculture and water in Utah are influenced both by average snowpack levels and their year-to-year variability. Approaches that combine technology, data-driven planning, and conservation practices are critical to thriving amidst these challenges.
Forestry Impacts: Water for Forest Health and Ecosystems
Our state’s forests depend on a reliable pulse of water from spring snowmelt. Healthy tree growth, robust wildlife habitats, and stable soils all stem from well-timed, ample runoff. But as runoff patterns become more variable, forest health and water supply face new pressures.
- Early snowmelt due to higher temperatures can mean reduced soil moisture during critical growth phases. Trees and undergrowth are more vulnerable to stress and drought.
- Rapid runoff increases the risk of flooding, landslides, and erosion. These impacts can degrade forest structure, reduce tree health, and disrupt sensitive ecosystems.
- Long-term droughts can exacerbate fire risk and threaten the regeneration of pine, fir, and aspen forests across Utah.
To protect forest health, we must track snowpack, implement soil conservation, adopt adaptive forest practices, and develop water management strategies that buffer against variable runoff and climate extremes.
Using advanced geospatial solutions, such as Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop plantation and forest advisory tool, can help landowners and forestry professionals monitor tree health, moisture trends, and predict stress before critical damage occurs.
Climate Change and Utah Agriculture
Climate change and Utah agriculture are now inseparably linked. As average temperatures rise, snow accumulates later and melts earlier. This means:
- Reduced total snowpack, especially in lower-elevation zones
- Earlier runoff peaks, which disrupt irrigation and crop scheduling
- Increased evaporation rates, further lowering water availability during the crucial summer growing season
Scientific studies in the Great Salt Lake basin warn that climate warming could cause a 71% reduction in snow water equivalent and a 20% decrease in runoff (Source: MDPI Study).
For both the agricultural and forestry sectors, these changes will result in increased risks of drought, crop failure, and ecosystem decline. Our water management strategies must now include adaptation to these shifting patterns, through a mix of technology-enabled monitoring, infrastructure upgrades, conservation, and drought-resistant species.
Soil moisture monitoring—through advanced sensors, satellite data, or technologies like Farmonaut’s platform—is vital for optimizing irrigation and resource use in an era of rapid variability.
Learn how you can integrate near real-time weather and soil data into your operations using Farmonaut’s robust satellite and weather data API for custom applications and in-depth farm analytics. Check out the detailed developer documentation for integration guidance!
Top 7 Utah Snowpack Spring Runoff Management Tips
It’s time to break down the most effective, sustainable water management strategies for dealing with Utah snowpack levels and spring runoff. Here are the top 7 actionable tips for farmers, landowners, and forest managers:
-
1. Proactive Snowpack and Soil Moisture Monitoring
Use resources like the SNOTEL (Snow Telemetry Network) and Farmonaut’s satellite-driven monitoring to get real-time data on snowpack levels, soil moisture, and SWE.
- Improves forecasting of runoff quantity and timing
- Enables early warning for risks like drought or flooding
- Supports informed resource management and irrigation planning
For precision insights, Farmonaut’s mobile and web app offers crop health and moisture mapping at field scale, empowering smarter decisions throughout the season.
-
2. Implement Efficient Irrigation Systems
Water conservation starts at the field level. Upgrade to modern, efficient irrigation systems such as:
- Drip irrigation: direct water to roots, reduce evaporation
- Sprinkler systems: can be optimized for low-flow conditions
- Soil moisture sensors: only irrigate when and where needed
Efficient irrigation not only reduces water waste but builds resilience against variable runoff and helps maintain crop health.
Explore Farmonaut’s solutions for smart irrigation, field-level monitoring, and digital advisory to maximize your yields. -
3. Diversify Water Sources and Storage
Don’t rely solely on spring runoff. Develop alternative water sources:
- Rainwater harvesting systems
- Small-scale water reservoirs or on-farm ponds for seasonal storage
- Recycled/reused water for non-potable farm or forestry needs
Increasing storage capacity provides a critical buffer during periods of low snowpack or drought.
-
4. Adopt Soil Conservation and Erosion Control Practices
To prevent damage from both runoff-driven flooding and depleted moisture:
- Use cover crops, mulching, and crop residue to protect soil surface
- Practice contour farming and terracing on slopes to slow runoff and promote infiltration
- Install buffer strips alongside streams and ditches
These techniques reduce soil loss, promote moisture retention, and benefit both agriculture and forestry.
-
5. Integrate Technology & Data-Driven Decision Making
Use satellite imagery, AI advisory tools, and digital field mapping to identify trends and adjust management proactively.
Farmonaut provides real-time crop health, soil moisture, and irrigation advisory—empowering us to optimize every drop with confidence. Use their advanced large-scale farm management solutions for enterprise operations. -
6. Plan for Droughts and Early Season Risks
Expect variability. Build contingency plans:
- Stagger or diversify crop planting schedules
- Plant drought-resistant varieties
- Monitor and manage livestock water needs closely during dry spells
- Utilize satellite-based crop insurance options for risk protection
Proactive drought management is fundamental for long-term sustainability and stability.
-
7. Enhance Resource Traceability and Sustainability Monitoring
Track not just your water, but also resource use, crop inputs, and supply chain sustainability. This includes:
- Implementing blockchain-based traceability for crops and forestry products.
- Carbon footprint tracking (learn more here) to monitor environmental impact and qualify for sustainability programs.
- Transparent fleet and equipment management for large-scale farm or forestry business (fleet management platform).
These practices support resource stewardship, build trust with buyers and regulators, and prepare us for the sustainable future of Utah agriculture and forestry.
Comparative Management Strategies Impact Table
| Strategy | Estimated Water Savings (acre-feet/year) | Agricultural Benefit (Crop Yield Improvement %) | Forestry Impact (Erosion Reduction Estimate) | Sustainability Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proactive Snowpack & Soil Moisture Monitoring | 400-900 | 10–16% | Up to 8% less erosion from timely interventions | High |
| Efficient Irrigation Systems (e.g., drip) | 600-1200 | 12–20% | 4% less erosion due to reduced runoff | High |
| Diversified Water Sources and Storage | 200-700 | 6–14% | Water buffer reduces soil stress by 5% | Moderate–High |
| Soil Conservation & Erosion Control | 100-300 | 4–8% | Up to 15% less erosion and nutrient loss | High |
| Technology & Data-Driven Decisions | 400-1500 (when integrated annually) | 15–22% | Optimizes response; up to 12% less loss | Very High |
| Drought/Early Risk Planning | 200-800 | 8–14% | 8% less stress/erosion in dry periods | High |
| Traceability & Sustainability Monitoring | Indirect | 6–10% | Verification aids regulatory soil protection | Very High |
Farmonaut Solutions for Water & Resource Management in Utah
Embracing technology and data is now at the forefront of effective runoff management in Utah. Farmonaut is an agricultural technology leader providing advanced, satellite-based solutions accessible via Android, iOS, web/browser app, and API.
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Use dynamic, multispectral imagery for real-time tracking of vegetation health, soil moisture, and stress. Know when and where to act to minimize water loss and maximize yield.
- AI-Driven Farm Advisory (Jeevn AI): Get custom recommendations on irrigation timing, weather risks, and precise input applications.
- Fleet and Resource Management: Efficiently track, deploy, and manage equipment—optimizing resource use across farms, ranches, and forestry operations. Explore fleet solutions here.
- Product Traceability and Blockchain: Track your product from field to market for transparency and sustainability compliance. Learn about the benefits of blockchain traceability.
- Carbon Footprinting: Monitor and reduce your environmental impact with field-specific carbon analytics. Assess your farm’s sustainability footprint here.
- Satellite-based Crop Loan & Insurance Assistance: Support for agricultural financing and insurance—verify fields remotely and reduce risk. Farmonaut’s insurance solutions.
With affordable subscriptions, scalable features, and a user-friendly interface, Farmonaut democratizes access to precision agriculture in Utah. Powerful digital tools—once reserved for mega-farms—are now within reach of every Utah farmer, rancher, forester, and land steward.
Conclusion: Adapting for the Future
Utah’s agricultural and forestry sectors are inextricably linked to the state’s snowpack and spring runoff dynamics. Variable snowmelt patterns are increasingly the “new normal”—requiring vigilance, smarter planning, and innovation at every level of water management.
- Proactive monitoring, efficient systems, diversified water sources, and sustainable practices form the bedrock of resilience against droughts, floods, and climate-induced resource fluctuations.
- Advanced technologies—like those available through Farmonaut—offer real-time insights, resource tracking, carbon footprinting, and adaptive advisory so we can continually improve our stewardship of Utah’s precious water, soil, and forests.
- By implementing these top seven management tips, we safeguard the productivity, health, and longevity of Utah agriculture and forestry for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the average Utah snowpack level, and why is it important?
On average, Utah snowpack supplies up to 80% of the state’s annual water, acting as a natural reserve to nourish crops, sustain livestock, and maintain healthy forests. Without sufficient snowpack, water supplies for agriculture, forestry, and communities are at risk.
How does spring runoff in Utah impact irrigation and crops?
The timing and volume of spring runoff determine agricultural water availability statewide. Too little runoff leads to shortages and stressed crops; too much, or a very rapid runoff, can cause flooding, erosion, and planting disruption.
What are the signs of drought affecting Utah farming?
Early warning indicators include below-average snow water equivalent (SWE), rapid snowmelt, low stream and reservoir levels, and declining soil moisture. Crop yields, planting schedules, and irrigation costs are all negatively impacted.
What are the most efficient irrigation systems for Utah farms?
Drip irrigation systems are optimal for water conservation, followed by well-tuned sprinkler setups. These systems deliver water directly to plant roots, reduce evaporation loss, and help manage limited runoff efficiently.
How can I use technology to improve snowpack and runoff management?
Utilize satellite monitoring tools, AI advisory systems, fleet/resource management platforms, and traceability/blockchain solutions to monitor trends, schedule irrigation, track moisture, and optimize operational efficiency. Farmonaut provides a unified platform for all these needs.
How do I start with Farmonaut’s solutions for Utah agriculture and forestry?
Download the Farmonaut mobile/web app or explore their API integration options. Affordable subscriptions, dedicated support, and real-time analytics make it accessible for Utah farmers and forest managers of all sizes.