Agro Based Industries in Nigeria, Cassava Nigeria Trends 2025
“**In 2023, Nigeria produced over 63 million metric tons of cassava, making it the world’s largest cassava producer.**”
Introduction
Agro based industries in Nigeria, especially those focused on cassava Nigeria, are set for unprecedented growth and transformation in 2025 and beyond. As the world’s largest producer of cassava, Nigeria stands at the center of an agricultural evolution that is impacting food security, rural employment, industrial development, and the overall economic structure of the nation. This article explores the latest trends, growth indicators, challenges, and breakthroughs that define the current and future landscape of agro based industries in Nigeria, with a special focus on cassava.
Through detailed analysis, factual insights, and real data, we investigate how cassava’s strategic importance, production trends, value chains, and technological innovations are contributing to rural development and economic diversification. This educational blog post offers a comprehensive overview for policymakers, entrepreneurs, investors, farmers, and enthusiasts seeking to understand—and participate in—the ever-evolving agri-industrial sector of Nigeria.
Agro Based Industries in Nigeria: An Overview
Nigeria is recognized as one of Africa’s largest agricultural hubs, with agro based industries playing a crucial role in the nation’s economy. The country’s vast land mass, fertile soils, diverse ecological zones, and climatic adaptability position it uniquely among global producers of a wide array of crops. Yet, among the various staples, cassava stands out due to its high yield, versatility, resilience, and its capacity to generate sustainable value across multiple industries. As the sector continues to demonstrate significant potential, it is important to examine the elements that contribute to its growth and transformation in 2025 and beyond:
- Role in Economic Diversification: Agro based industries in Nigeria act as a counterweight to oil dependency, driving diversification for a more robust national economy.
- Employment Generation: Agriculture and related processing industries provide livelihoods for millions—particularly in rural communities, supporting both gender inclusion and youth empowerment.
- Industrialization and Value Addition: Processing of agricultural products like cassava into various industrial and food commodities adds considerable value and reduces post-harvest losses.
- Import Substitution: An increase in locally processed agriculture products has cut down Nigeria’s reliance on food imports—helping to bolster national food security.
Cassava Production in Nigeria: The Heart of Agricultural Hubs
Cassava is Nigeria’s most significant staple crop in terms of volume, adaptability, and economic impact. According to the latest estimates, Nigeria produces over 40 million tonnes of cassava annually, with some 2023 projections already surpassing 63 million metric tonnes, firmly establishing the country as the world’s largest producer.
Cassava thrives across the southern rainforest and northern savannah belt regions, owing to its ability to adapt to diverse soil types and climates. This adaptability ensures that cassava is accessible to millions of smallholder farmers, supporting their food needs and providing a steady source of income and employment.
Key characteristics and usage patterns that solidify cassava’s role in Nigeria’s development include:
- Versatility: Cassava can be processed into various products, including garri, fufu, starch, flour, animal feed, bioethanol, and even biodegradable plastics.
- Climate Resilience: The crop’s ability to survive under drought conditions and marginal soils boosts food security and helps minimize hunger in rural areas.
- Economic Impact: With cassava Nigeria trends indicating rising domestic and export demand, the sector remains a major pillar in both food consumption and industrial production.
- Empowerment of Rural Women and Youth: A significant portion of cassava processing and trading activities is managed by women and youth, promoting inclusivity and socio-economic stability.
Agro Processing and Industrialization: Driving Economic Growth
The evolution from traditional to modern processing methods marks one of the most critical trends in agro based industries in Nigeria. While cassava has been a staple in Nigerian diets for centuries, recent government policies, investments, and emerging technologies have fueled the growth of processing infrastructure, increasing the sector’s efficiency, product quality, and economic impact.
- Factory Expansion: The number of modern cassava processing plants continues to rise, offering advanced facilities capable of producing higher-grade products for local and international markets.
- Import Substitution: The expansion reduces Nigeria’s historical reliance on imported food products, especially starch-based and processed foods.
- Industrial-Scale Value Addition: Cassava is now a source for food, industrial starch, ethanol, and biodegradable plastics, contributing directly to Nigeria’s non-oil GDP.
- Employment Creation: Industrial processing facilities have cultivated new job opportunities in rural areas, with government figures indicating millions employed across the sector in 2025.
Agro Based Industries in Nigeria, Cassava Nigeria Trends 2025: Comparative Table
| Year | Cassava Production (million tonnes, estimated) | Number of Processing Facilities (estimated) | Employment in Cassava Sector (thousand, estimated) | Export Value (USD million, estimated) | Projected Growth Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 42 | 135 | 1,360 | 93 | 3.8 |
| 2023 | 63 | 180 | 1,700 | 120 | 5.6 |
| 2025* | 70 (projected) | 210 (projected) | 2,100 (projected) | 160 (projected) | 7.1 (projected) |
*2025 values are projections based on current trends and industry reports.
“**By 2025, agro-based cassava processing in Nigeria is projected to create over 1.5 million new rural jobs.**”
Cassava Value Chains, Products, and Industrial Opportunities
As the cassava Nigeria sector continues to evolve, the value chain extends from smallholder cultivation to advanced industrial processing, offering a wide spectrum of employment, investment, and export possibilities. Notably, cassava’s multiple uses are foundational to its enduring economic and social significance. Let us break down the primary value-added products and their industrial implications:
Key Cassava Products and Uses
- Garri (Cassava Granules): A fermented, dried product integral to the typical Nigerian diet; garri serves as a major source of carbohydrates with both local consumption and export significance.
- Fufu: Cassava-based dough-like staple popular in Southern Nigeria, used as a meal accompaniment.
- Industrial Starch: Used in food processing, pharmaceuticals, textiles, and paper manufacturing, the demand for cassava starch is sharply rising in both domestic and international markets.
- Animal Feed: Processed, dried cassava peels and chips are used as energy-rich feed for livestock—reducing waste in the value chain.
- Flour: High-quality cassava flour is now a substitute or partial replacement for wheat flour in bread and pastries, supporting Nigeria’s gluten-free movement.”
- Bioethanol and Biodegradable Plastics: Cassava-based bioethanol is gaining traction as a renewable energy source. Production of biodegradable plastics from cassava starch is also on the rise, spurred by sustainability mandates.
Industrial Opportunities in 2025 and Beyond
- Food Security: As a staple, cassava acts as a food reserve and a buffer against supply shocks, offering households sustained nutrition options.
- Economic Empowerment: Cassava-based industries create jobs in agriculture, logistics, processing, and distribution, with the ripple effect fueling rural income and consumption.
- Export Growth: Ongoing market expansions—especially for high-quality starch and ethanol—are projected to boost export earnings and position Nigeria in global value chains.
- Support for SDGs: Agro based cassava industries align with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, particularly SDG 2 (Zero Hunger), SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth), and SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production).
Challenges Facing Agro Based Cassava Industries & Emerging Solutions
Despite Nigeria’s advantages in cassava production, the road to maximizing its development potential is dotted with persistent challenges that warrant collective action and innovative solutions:
- Limited Access to Modern Inputs: Many farmers still grapple with a lack of certified seed varieties, fertilizers, and mechanized tools, which limits productivity and yields.
- Inadequate Infrastructure: Poor rural road networks, irregular electric power supply, and weak cold chain systems amplify post-harvest losses and limit market access.
- Access to Financing: Small and medium agro-processors face difficulty in securing affordable credit to invest in expansion, modernization, or risk mitigation.
- Knowledge Gaps: Many smallholder farmers rely on traditional methods, missing out on breakthroughs in sustainability, pest control, or high-yield varieties.
- Fluctuating Market Prices: Market volatility and periodic gluts or shortages can undermine stable incomes for growers and processors alike.
Emerging Solutions for 2025 and Beyond
- Technological Innovations: New, pest-resistant cassava varieties, mechanized harvesting tools, and improved processing technologies are being widely adopted.
- Digital Platforms: Farmer-to-market linkage apps and platforms have begun to bridge information gaps and unlock transparent, efficient product flows.
- Investments in Rural Infrastructure: Ongoing government initiatives aim to upgrade rural roads, electrification, and storage facilities—already showing promising impact by 2025.
- Extension Services: Expanded outreach programs are providing smallholders with training on sustainable, climate-smart, and profitable farming and processing methods.
Technology & Innovation: The Role of Digital Tools and Satellite Monitoring
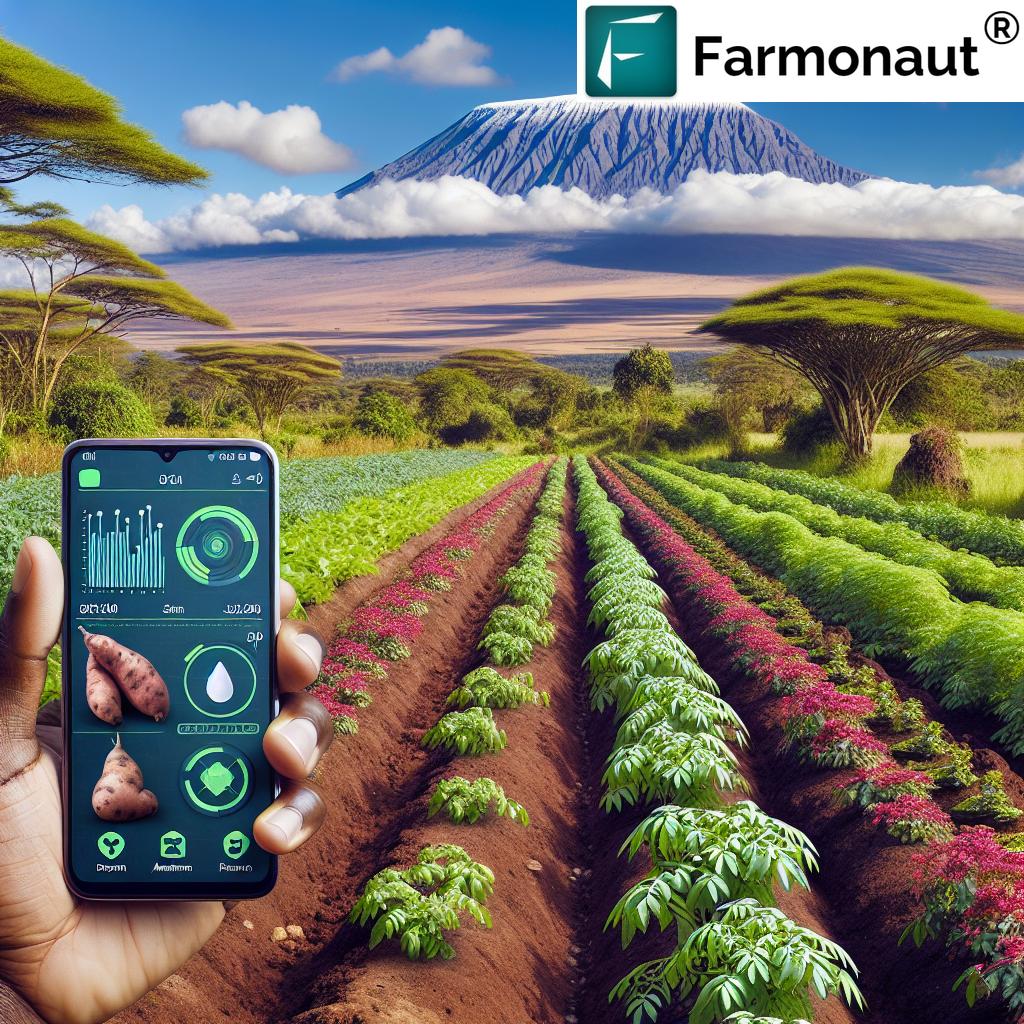
The integration of advanced technology is redefining agro based industries in Nigeria. In particular, satellite-based solutions, artificial intelligence (AI), and digital advisory platforms are now critical drivers for increased productivity, resilience, and sustainability in cassava and other staple crops.
Farmonaut, as a leading satellite technology company, leverages multispectral satellite imagery, blockchain, and machine learning to provide actionable agricultural insights across Nigeria and beyond. Our tools empower farmers, businesses, and policymakers to access real-time data on crop health, monitor environmental impact, and ensure supply chain transparency—a foundation for smarter rural development.
- Satellite-Based Monitoring: Helping agri-operators remotely track cassava crop health, soil moisture, pest infestation, and yield trends, enabling timely interventions and higher output.
- AI Advisory: Farmonaut’s AI-based advisory systems deliver real-time recommendations, weather forecasts, and yield-boosting strategies directly to users, strengthening their capacity for sustainable decision-making.
- Blockchain Traceability: By integrating blockchain for supply chain traceability, Farmonaut enhances market trust and provides end-to-end security—from farm to final consumer.
- Fleet and Resource Management: With dedicated fleet and resource management solutions, operators can optimize their logistics, track movement, and reduce costs throughout the value chain.
- API Integration: Farmonaut offers easy integration via APIs and developer documentation for businesses seeking to internalize satellite and data insights into their platforms.
Interested users can experience Farmonaut’s web and mobile platform by downloading from the links below:
- Large Scale Farm Management: This all-in-one dashboard empowers farm managers, agribusinesses, and government agencies to monitor multiple fields, optimize resource utilization, and improve coordination at scale.
- Carbon Footprinting: Farmonaut assists agro-industries in tracking and mitigating their carbon emissions, helping to align with green policies and sustainability goals that are increasingly important for export compliance and eco-conscious investment.
- Crop Loan and Insurance: Satellite-driven verification supports easier, faster, and more secure access to agricultural loans and insurance products, lowering risk for both financial institutions and rural farmers.
Cassava, Climate Resilience & Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Cassava’s resilience is one of its greatest strengths, especially as climate change creates instability in Nigeria’s traditional food systems. By thriving on marginal soils and withstanding drought, cassava helps farmers sustain their livelihoods and food supplies during unpredictable weather or pest outbreaks.
- Food Security: Cassava’s ability to be stored underground for extended periods enables food supply management, smoothing out the impact of seasonal fluctuations.
- Rural Prosperity: The stable nature of cassava farming under unpredictable climate conditions supports millions of rural families, safeguarding their income and consumption needs.
- Sustainable Chains: Agro-based cassava industries in Nigeria actively support SDG 2, SDG 8, and SDG 12 by reducing waste, improving value retention in rural areas, and encouraging responsible consumption.
- Environmental Impact Monitoring: With Farmonaut’s carbon footprint monitoring tools, businesses can proactively manage and report their environmental impact in line with global sustainability standards.
Policy Frameworks & The Role of the Government for 2025 and Beyond
Policy and institutional support remain critical for the continued advancement of agro based industries in Nigeria. The Nigerian government, recognizing the sector’s transformative potential, is committed to a blend of initiatives designed to cement cassava’s status as a springboard for industrialization and rural upliftment.
- Agriculture Promotion Policy (APP) 2025: Fosters increased investment, reduced import dependencies, and diversification.
- Agro-Industrial Hubs: These specialized zones cluster processing, storage, and distribution. By 2025, several such hubs are operational, improving the efficiency and profitability of the entire cassava value chain.
- Public and Private Sector Synergy: Although investments and capacity building continue to surge, the role of transparent market regulations, tax incentives, and infrastructural upgrades will be more pivotal going forward.
Additionally, new policy instruments are targeting:
- Expanded access to high-yielding, disease-resistant cassava varieties
- Increased support for rural extension workers and vocational training programs
- Incentives for export-oriented processing and certification
- Greater digital inclusion for market and weather information services
Future Opportunities: Export, Rural Development, and Economic Diversification
Looking forward, the future of agro based industries in Nigeria, cassava Nigeria trends in 2025 and beyond hinge on three axes: expansion of export markets, comprehensive rural development, and sustained economic diversification.
Export Expansion: Nigeria on the Global Stage
- Growing demand for industrial starch, food-grade flour, animal feed, and bioethanol is accelerating Nigeria’s export revenues.
- Efforts to meet global quality standards and traceability requirements are opening up new international markets, particularly in Europe and Asia.
Rural Development: Inclusive Growth
- With a projected 1.5–2 million new rural jobs by 2025, cassava industries are a major force in reducing urban migration and poverty.
- Women and youth are central to these developments, benefiting from targeted vocational programs and digital platforms connecting producers to processors.
Economic Diversification and Sustainable Growth
- Cassava continues to be the bridge between traditional agriculture and industrialization, serving as a strategic anchor for ecosystem-wide transformation.
- Investments in technology, innovation, and policy reform promise to solidify Nigeria’s leadership in sustainable agro-industrial growth.
Farmonaut Subscriptions & Data Solutions
Experience advanced monitoring, AI-driven insights, and sustainability solutions with Farmonaut. Our tiered subscription plans ensure affordability and scalability for everyone—from smallholder farms to enterprise and government users.
Useful Links & Farmonaut Solutions
- Farmonaut Web System and API: Access the web platform here or integrate Farmonaut API into your business.
- API Documentation: Get technical details via our API developer documentation.
- Mobile Apps: Download the Farmonaut app on Android or iOS to manage your cassava fields on the go.
- Product Solutions: Large scale farm management, carbon footprinting, traceability, crop loan and insurance, fleet management
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What are agro based industries in Nigeria?
Agro based industries refer to industries that use agricultural products as raw materials. In Nigeria, this includes processing crops like cassava into food, animal feed, starch, bioethanol, and industrial products—providing large-scale employment and contributing to economic growth. -
Why is cassava significant for Nigeria’s economy?
Cassava is Nigeria’s staple crop, serving millions and acting as a source for food security, industrialization, income generation, and sustainable development. -
How much cassava does Nigeria produce annually?
As of 2023, Nigeria produced over 63 million tonnes of cassava, and projections for 2025 put the figure at 70 million tonnes. -
How does technology benefit cassava farmers and industries?
Technology—including satellite monitoring, AI-based advisory, digital market platforms, and blockchain traceability—helps increase yield, reduce losses, ensure transparency, and improve the entire supply chain for cassava Nigeria. -
What are the primary challenges facing the industry?
Key challenges include limited access to modern farming inputs, poor infrastructure, financing barriers, market volatility, and knowledge gaps in modern agricultural techniques. -
How can Nigerian cassava processors access Farmonaut’s solutions?
Farmonaut’s suite of satellite-based monitoring, AI advisory, traceability, and fleet management tools can be accessed via our web and mobile platforms and integrated API solutions.
Conclusion: The Growth and Potential of Agro Based Industries in Nigeria, Cassava Nigeria Trends 2025
In summary, the cassava sector is vital for Nigeria’s vision of a diversified, sustainable, and resilient economy. Its unmatched adaptability, high yield, and versatility fuel food security, create jobs, and anchor industrial development across Africa’s most populous nation. As agro based industries in Nigeria continue their ascent in 2025 and beyond, the synergy between policy innovation, private sector investment, digital transformation, and grassroots empowerment will unlock new opportunities—making cassava not just a staple crop, but a catalyst for sustainable prosperity.
To achieve these transformative goals, timely investments in infrastructure, technology, and human capacity are essential—empowering millions of smallholder farmers, processors, and entrepreneurs across the value chain. Nigeria’s leadership in cassava production and processing, supported by technologies such as Farmonaut, is paving the way for a new era of agricultural excellence, inclusive rural development, and global competitiveness.
Agricultural trends, industry news, and policy shifts in agro based industries in Nigeria, cassava Nigeria will continue to shape Africa’s food and economic landscape for years to come—making now the ideal time to learn, innovate, and invest for the future.