Almond Tree Growing Zones & Pruning: 7 Proven 2025 Practices
Introduction to Almond Cultivation: Importance & Evolution
Almond cultivation stands as a significant component of the global agricultural landscape, especially across regions with mediterranean climates. As we approach 2025, the need for improved sustainable farming practices, adaptation to climate uncertainty, and the strategic use of technology have never been more crucial. Understanding the optimal almond tree growing zones, leveraging scientifically backed pruning techniques, and embracing informed crop diversification will empower farmers to maximize yield, promote soil health, and future-proof their operations.
The almond’s journey—from its origin in the arid regions bridging Asia and the Mediterranean to dominance in places like California and Spain—reflects centuries of adaptation and innovation. Modern farming now integrates sustainability into every step, from crop selection and pruning to precision irrigation and remote monitoring. Let’s explore how the latest trends in agricultural management and technology are shaping almond tree cultivation going into 2025 and beyond.
Almond Tree Growing Zones: Global Regions & Climate Insights
One of the most crucial decisions in almond cultivation is selecting the right zones for planting. Almond trees thrive best in mediterranean-like climates that are characterized by mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers. In the United States, notably California, the USDA Hardiness Zones 7-9 provide the perfect balance of chilling hours, temperature, and rainfall, creating a powerhouse for global almond production.
Let’s detail the key climate features and soil requirements in these productive almond tree growing zones:
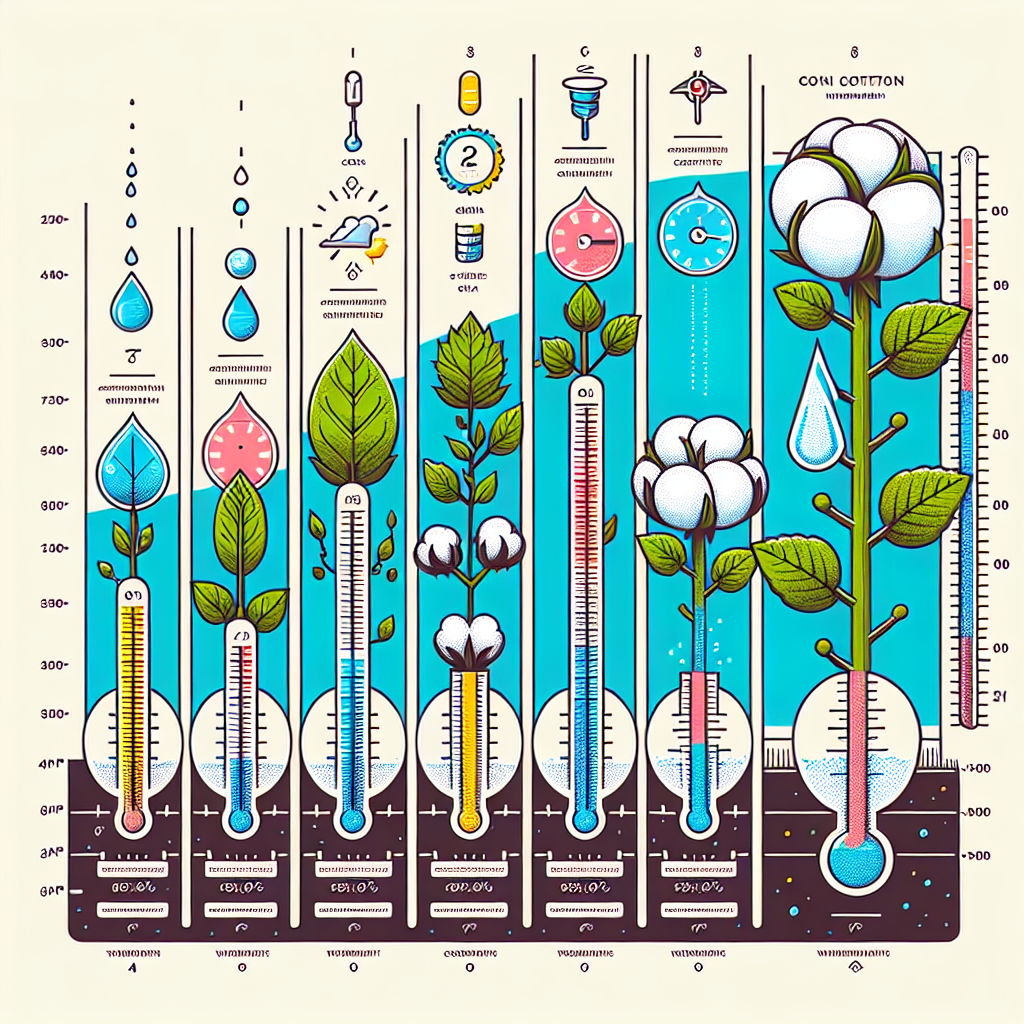
- Temperature: Almond trees require enough “chill hours”—generally 250 to 500 hours below 45°F (7°C)—during winter dormancy to stimulate healthy flowering and fruit set.
- Seasonality: Distinct wet winters paired with long, hot, dry summers are ideal.
- Soil: Well-draining, loamy soils are optimal. Waterlogged soils or salinity issues can reduce yield and vigour.
- Sunlight: Full sun exposure is essential for maximum growth and productivity.
- Air Circulation: Open, breezy sites discourage disease by enabling canopy dryness after rains or irrigation.
Leading almond-producing regions include:
- California Central Valley, United States: Dominates global almond production due to ideal climate and advanced management practices.
- Spain (Andalusia, Catalonia): Mediterranean climate, but often faces challenges with water availability and periodic drought.
- Australia (Riverina, Sunraysia): Warm, dry, and sunny; adaptive to pest management and water conservation techniques.
- Middle East (Iran, Turkey): Traditional almond-growing zones facing modern pressure from climate change and water scarcity.
- Northern India (Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh): Emerging as a niche player with sustainable farming practices adapted for local climates.
Why it matters: Watch how advances in regenerative agriculture will transform carbon management, soil health, and climate resilience by 2025 and beyond!
The Science Behind Almond Tree Growing Zone Success
- USDA Hardiness Zones 7-9: Temperatures rarely fall below -17°C (0°F); minimal risk of frost during bloom.
- Chill Hour Requirements: 250-500 hours below 45°F (7°C) are necessary to break dormancy and trigger a uniform bloom.
- Rainfall: 400-600mm/year is optimal—excess may increase disease risk, while deficit leads to competition for water.
- Soil Structure: Loamy-sand to clay-loam, good drainage, pH between 6.0 and 7.5.
Almond Tree Growing Zone Trivia
Climate Change, Shifting Patterns & 2025 Projections
Climate change remains a central concern for almond farmers as growing zones and climate patterns continue to shift. Rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, erratic rainfall, and reduced chill hours threaten traditional growing zones and potentially diminish yields.
As scientists, agronomists, and growers work on studying adaptive practices across various regions, several solutions are emerging as critical in sustaining almond cultivation into 2025:
- Rootstock Selection: Opting for species and hybrids that tolerate water stress and soil salinity.
- Varietal Breeding: Developing almond varieties requiring fewer chill hours or better suited for warmer climates.
- Precision Irrigation: Implementing large-scale farm management systems with drip or micro-spray irrigation, soil moisture sensors, and satellite monitoring.
- Automated Disease Detection: Using blockchain-traceability and AI to spot outbreaks and reduce chemical use.
- Integrated Pest Management: Biological controls and smart analytics help balance beneficial insects and minimize pesticides.
Discover cutting-edge water and sustainability methods transforming wine and almond regions in California’s Central Valley.
Zones at Risk: Adapting to Reduced Chill Hours
- California and Australia: Both face increased heat stress and uncertain winter chilling. Scientists recommend adaptive practices, such as selecting rootstocks better suited to altered climate patterns.
- Mediterranean and Middle East: Facing drought and water scarcity, which threaten long-term sustainability. Innovations in soil management (cover crops, mulching) and water recycling are in rapid development.
Farmonaut Technology Insight
- Our satellite-based multispectral crop monitoring tools allow precise, zone-specific tracking of almond tree health, NDVI readings, and soil moisture status. These insights help farmers adjust irrigation, fertilization, and pruning schedules, supporting sustainability and maximized yield across changing climate patterns.
See how intelligent water phase detection using Farmonaut satellite imagery helps orchards optimize their water management routines, crucial for sustainable almond production.
Pruning Almond Trees: 7 Proven Practices for 2025
Pruning is an indispensable aspect of almond tree management, directly influencing tree health, productivity, and harvest efficiency. The right timing and techniques—especially in the context of climate changes anticipated in 2025—are vital for successful almond operations.
What Is Almond Tree Pruning & Why Is It So Crucial?
Pruning involves the removing of dead, diseased, or weak wood while maintaining an open canopy that allows better sunlight penetration and air circulation. These actions help reduce disease incidence, improve nut quality, and boost overall yield.
- Pruned trees have up to 20% higher yields and better resistance to fungal/bacterial threats.
- Open canopies facilitate technical management, including mechanical harvesting and pest treatments.
Modern orchards utilize AI-driven analytics and satellite data to perfect their pruning practices, ensuring healthy growth and resilient yields.
7 Proven Almond Tree Pruning Practices for 2025
-
Winter Pruning for Dormancy Management
Most pruning is conducted during late winter to early spring (dormant season). This period reduces disease risk, encourages vigorous new growth, and supports even flowering. -
Balancing Old & New Wood
Remove old, unproductive limbs while preserving younger, fruitful shoots to maximize future yield. -
Canopy Thinning for Sunlight and Air Circulation
Open up the canopy: improves light penetration and airflow—key for disease prevention and nut quality. -
Reverse Pyramid or “Vase” Training
Shape young trees into an open vase form, encouraging strong frameworks and accommodating mechanical harvesting. -
Mechanical Pruning in Large-Scale Orchards
Mechanical hedgers now see widespread use, but require careful planning to avoid excessive injury or stress to trees. Manual touch-up pruning is often needed. -
Targeted Pruning by AI-Monitored Tree Health
Advanced systems, such as our large-scale farm management platform, let farmers use AI and satellite data to identify trees needing urgent pruning—optimizing labour and reducing waste. -
Sanitation Pruning to Reduce Pest and Disease Pressure
Quickly remove diseased wood and dispose of prunings away from the orchard to avoid reinfection.
Modern Pruning: Combining Tradition With Tech
- Use of Remote Sensing: Farmonaut’s satellite imagery provides detailed maps of canopy density, supporting precise, zone-targeted pruning plans.
- Data-Driven Planning: Monitor tree growth year-round, fine-tune fertilization and irrigation to complement pruning outcomes.
- AI Advisory: Jeevn AI provides tailored, orchard-level recommendations for both young and mature almond trees.
Harness the predictive power of satellite crop monitoring to fine-tune orchard yield forecasts and match pruning intensity—a 2025 must-have.
Crop Diversification: Asparagus Growing, Amish Hemp & Niche Integration
Sustainable almond production increasingly relies on crop diversification to:
- Improve soil health
- Buffer against market volatility
- Enhance ecosystem resilience
- Reduce pest and disease pressure
Farmers are pioneering the integration of asparagus growing, amish growing hemp, and other niche crops in almond orchards or adjacent fields. This approach supports more stable long-term operations, creates new revenue streams, and fosters sustainability.
Asparagus Growing: The Ideal Partner in Almond Zones
- Climate Requirements: Thrives in well-drained soils, mild climates, and requires little water after establishment.
- Longevity: Asparagus crowns are planted once and can produce for up to 15 years.
- Ecosystem Benefits: Acts as a perennial crop, stabilizing soil and reducing weed competition.
- Complement to Almonds: Similar soil, nutrient, and climate preferences make asparagus compatible in many almond-growing regions.
Amish Growing Hemp: Traditions Meet Innovation
- Sustainable Practices: Amish communities blend traditional, chemical-free methods with rotational farming to enhance soil health.
- Rotational Benefits: Hemp improves soil structure, achieves effective pest suppression, fixes carbon, and complements almond orchards when used as a break crop.
- Market Demand: There is a rising trend toward specialty hemp products (fibres, food, CBD) grown in a sustainable system.
Through integrating asparagus and hemp, farmers are moving toward a resilient, diversified landscape that withstands market and environmental fluctuations.
Explore how AI and drone technologies are remaking pest management and survival for niche and mainstream crops like almonds, asparagus and hemp in 2025.
Sustainability, Water & Resource Management for Future-Ready Orchards
No single factor is more crucial for almond orchards in 2025 than water management. As drought and scarcity become the new norm, innovative solutions are vital to maintain yield without ecological harm.
- Drip Irrigation: Delivers water to almond root zones precisely where needed, reducing evaporation and waste.
- Soil Moisture Monitoring: Real-time data (from carbon footprinting tools and smart sensors) guide irrigation timing, conserving water amid shifting rainfall.
- Drought-Resistant Rootstocks: Breeding for deeper roots and heat tolerance continues to increase zone sustainability.
- Biodiversity and Pollinator Health: 2025 best practices include wildflower strips, hedgerows, and managed bee populations for robust pollination and ecosystem benefits.
See how traceability and pollinator tech advances are helping almond farmers and beekeepers collaborate toward sustainable production in sensitive growing zones.
Other sustainable management practices include:
- Organic Fertilization: Emphasizing composts, manures, and cover crops to replace synthetic inputs.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Leveraging natural pest enemies, crop monitoring, and minimal chemical use.
- Smart Traceability: Product origins confirmed with satellite and blockchain tools, as showcased in Farmonaut’s Traceability Platform.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: Regular use of carbon monitoring technology to meet climate and market demands.
Almond Tree Growing Zones: Climate & Pruning Practices (2025 Outlook)
| Growing Zone (USDA/Region) | Annual Temp Range (°C) | Rainfall (mm/year) | Recommended Pruning Practice | Sustainable Adaptation Tip | Yield/ha (kg) | Crop Diversification Option |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| California Central Valley (USDA 8-9) | 12–28 | 350–600 | Dormant mechanical + manual thinning | Drip irrigation, remote canopy monitoring | 2,600–3,200 | Asparagus, rotational hemp |
| Spain (Andalusia, Catalonia, USDA 8) | 10–27 | 300–500 | Winter manual pruning, open vase | Mulching, water recycling | 950–1,600 | Lavender, chickpea, hemp |
| Australia (Riverina, Sunraysia, USDA 9) | 13–29 | 250–450 | Mechanical, followed by corrective hand pruning | Drought-tolerant rootstocks, IPM | 2,000–2,500 | Lupins, vetch, rotational hemp |
| India (Kashmir, Himachal, USDA 7–8) | 7–22 | 600–900 | Manual, focused on air flow and structure | Rainwater harvesting, intercropping | 700–1100 | Peas, saffron, wheat, hemp |
| Middle East (Turkey, Iran, USDA 7–8) | 5–25 | 200–500 | Manual, open center for airflow | Greywater irrigation, mulch cover | 800–1,200 | Barley, legumes, hemp |
Note: Yields listed are broad estimates for well-managed orchards in 2025. Local results depend on pruning, water management, climate adaptation, and crop diversification.
Farmonaut: Satellite-Fueled Sustainability in Almond Farming
At Farmonaut, we champion the next era of sustainable almond cultivation through cutting-edge satellite technology, AI, and robust data-driven platforms. Our solutions are designed to empower farmers, businesses, and governments with actionable insights—optimizing resource use, supporting resilience, and fostering sustainability.
- Satellite Crop Health Monitoring: Real-time NDVI, vegetation status, and soil condition tracking for precision irrigation and pruning decisions.
- AI-Based Advisory (Jeevn AI): Tailored, weather-responsive recommendations for pruning, fertilization, integrated pest management, and yield estimation.
- Blockchain Traceability: Unmatched supply chain transparency for almonds and diversified crops. See our product traceability platform for details.
- Fleet & Resource Management: Smart logistics and field team tracking reduce costs across large orchards—explore fleet management solutions.
- Carbon Footprint & Environmental Impact: Reduce emissions, verify sustainability claims, and access green certification with carbon footprinting technology.
- API & Developer Access: Seamless integration with existing management systems. Integrate our data with the Farmonaut API or consult API developer docs for agricultural automation.
Dive into how Farmonaut’s monitoring suite delivers actionable orchard health insights, maximizes both yield and sustainability for almond growers worldwide.
FAQs on Almond Tree Growing Zones & Pruning (2025)
1. What are the optimal almond tree growing zones in 2025?
Almond trees thrive best in USDA Hardiness Zones 7-9, featuring mild wet winters and hot, dry summers. Leading regions include California Central Valley (USA), Andalusia (Spain), Riverina (Australia), and parts of the Middle East and northern India.
2. How many chill hours do almonds need to break dormancy?
Almonds require 250–500 chill hours (below 45°F/7°C) during winter dormancy to ensure even bud break and flowering.
3. What are the most effective almond tree pruning practices for yield and health?
Key practices include winter pruning during dormancy, removing old/non-productive wood, thinning canopies for sunlight/airflow, open-vase training of young trees, mechanical pruning in large orchards (with manual correction), AI-targeted health interventions, and removing diseased wood promptly.
4. Which niche crops can be integrated with almonds for sustainable diversification?
Asparagus growing and rotational hemp (such as amish growing hemp) are increasingly popular. These crops share similar climate/soil requirements and build long-term soil and economic resilience.
5. How do new technologies support almond farming sustainability?
Remote satellite monitoring, AI-based advisory, blockchain traceability, and carbon accounting from providers like Farmonaut help optimize water use, schedule precise pruning, manage environmental impact, and verify product sustainability throughout the supply chain.
6. How can Farmonaut’s platform specifically assist in almond orchard management?
Our satellite-based services deliver real-time crop health monitoring, custom pruning schedules (via AI), water/soil data tracking, and transparent traceability, streamlining operations and boosting both yield and resilience.
Conclusion: Adapting Almond Operations for 2025 and Beyond
Almond cultivation is at a crossroads in 2025, where the intersection of climate adaptation, advanced pruning, and strategic crop diversification defines success. Mastering the nuances of almond tree growing zones, championing sustainability through smart water management and soil stewardship, and integrating crops like asparagus and hemp will ensure leading yields amid uncertainty.
By leveraging Farmonaut’s satellite-driven insights, orchard managers worldwide can respond swiftly to changing weather patterns, optimize every acre, and build a legacy of resilient, efficient, and eco-conscious almond farming.
The future of almond orchards is rooted in information, precision, and partnership between sustainable practices, advanced technology, and adaptive strategies—ushering a thriving agricultural landscape for decades to come.
For those seeking seamless automation and granular data, integrate our APIs directly into your orchard or farm management systems.
API documentation & onboarding: API Developer Docs
Ready to optimize your almond orchard for the future? Embrace precision, sustainability, and diversification for resilient growth in 2025 and beyond with Farmonaut.