Biotechnology Innovations in Agriculture: 2025 Advances
“Over 60% of new crop varieties in 2025 are developed using advanced gene-editing biotechnology.”
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- The 2025 Landscape of Biotechnology Innovations in Agriculture
- Genetic Engineering and Gene Editing Transforming Crops
- Beyond Modification: Advanced Biotechnological Tools
- Livestock and Animal Biotechnology Innovations
- Precision and Digital Farming Technology Innovations
- Biofertilizers, Biopesticides, and Green Solutions
- Sustainability, Environmental Impact, and Circular Economy in Agriculture
- Farmonaut: Satellite Technologies Empowering Digital and Biotech Agriculture
- Comparison Table of Key Biotechnology Innovations in Agriculture (2025)
- Future Outlook: Challenges and Opportunities
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion
Introduction
In 2025, the convergence of biotechnology innovations in agriculture with next-generation farming technology innovations is shaping a future of sustainable, efficient, and resilient agricultural practices. With rising challenges including climate change, food security, and diminishing arable land, biotechnology in agriculture is proving indispensable. Advanced genetic engineering, digital tools, and new eco-friendly inputs are empowering farmers worldwide to produce higher yields using fewer resources while minimizing environmental pollution and safeguarding the very ecosystems that agriculture depends on.
This detailed overview explores the key innovations and practices revolutionizing the agriculture sector in 2025. We will delve into gene editing technologies, advanced breeding programs, precision agriculture, satellite-driven insights, and the role of sustainable biotechnological solutions in building an agriculture future fit for our planet.
The 2025 Landscape of Biotechnology Innovations in Agriculture
The agriculture sector has been fundamentally revolutionized over recent years through biotechnology and farming technology innovations. By 2025, these advancements are not just supplementary—they are core to modern farming practices. The sector’s transformation is defined by:
- Dramatic increases in crop yields and farm productivity through gene editing and advanced breeding.
- Minimized environmental impact via reduced chemical inputs and smarter resource management.
- Resilient responses to climate challenges with drought-tolerant, pest-resistant, and disease-resistant crop varieties.
- Digital transformation—integrating satellite imagery, AI, and sensor-based data for precision decision-making.
- A paradigm shift from traditional inputs (synthetic fertilizers and chemical pesticides) to sustainable, bio-based alternatives.
These innovations align with the dual goals of ensuring global food security and maintaining sustainability in the face of population growth and environmental constraints. The future of agriculture lies in adopting these leading-edge technologies and integrating them into farm management at every scale.
Genetic Engineering and Gene Editing: The Foundation of Biotechnology Innovations in Agriculture
At the core of biotechnology agriculture in 2025 is genetic engineering and gene editing. These technologies empower scientists to directly enhance crop traits, ushering in an era of rapid and precise crop improvement that was unimaginable just a decade ago.
The Rise of Gene Editing Technologies: CRISPR and Beyond
- CRISPR-Cas9 and other advanced gene editing tools allow targeted modification of plant DNA without introducing foreign genes.
- These methods are more precise, faster, and less controversial compared to traditional genetic modification, making crops developed via gene editing more acceptable to both regulators and consumers concerned about GMOs.
- In 2025, over 60% of new crop varieties are developed using advanced gene-editing biotechnology (see trivia above).
Benefits of Gene-Edited Crops
- Drought Tolerance: Enables crops to withstand prolonged dry periods, securing stable yields in arid regions facing erratic rainfall patterns due to climate change.
- Pest and Disease Resistance: Minimizes crop losses, lowers dependence on chemical pesticides, and protects beneficial insect populations.
- Improved Nutrient Use Efficiency: Crops can thrive on fewer fertilizers, reducing input costs and nutrient runoff that contributes to water pollution.
- Enhanced Quality: Features like fortified nutrition, improved shelf life, and better taste/texture can now be precisely engineered.
Example: Wheat engineered for fungal resistance and potatoes resistant to late blight via CRISPR editing are reducing the need for fungicides and enhancing food security in regions like North America and Europe, as well as crucially benefiting countries with high food insecurity.
How Precision Gene Editing Differs from Traditional Genetic Modification
- Gene editing enables the alteration of endogenous genes—making tiny changes like switching “off” a susceptibility gene—rather than introducing completely foreign DNA.
- This distinction is vital for regulatory acceptance and consumer trust.
- Gene-edited crops are now mainstream in 2025, with rapid development cycles, high adoption, and clear labeling requirements.
“Biotech innovations in 2025 reduce pesticide use in agriculture by approximately 40% compared to 2020 levels.”
Accelerated Crop Development for a Changing Climate
Biotechnology agriculture offers agility. The speed of gene editing enables the fast development of new varieties that can respond to emerging climate challenges, such as heat, drought, and new pest/disease pressures. This is critical as global warming shifts growing zones and stresses crops in unexpected ways.
These innovations ensure our food systems remain resilient and adaptive, empowering farmers everywhere to sustain production and yields even as environmental conditions become less predictable.
Beyond Modification: Advanced Biotechnological Tools for Efficient and Sustainable Farming
Biotechnology innovations in agriculture extend beyond crop modification. They now encompass a suite of tools for smarter input management, disease detection, and resource optimization. These advances further support efficient, resilient, and environmentally sound farming practices.
Rapid Disease Diagnostics and Monitoring
- Portable genetic diagnostic devices leverage CRISPR-based assays for fast, on-site detection of pathogens in fields.
- Early identification minimizes crop losses and helps target interventions, reducing waste and unnecessary treatment.
Biological Sensors for Smart Inputs
- Microbial biosensors and plant-based indicators enable continuous monitoring of soil health, nutrient availability, and pollution levels.
- Data-driven, targeted action is now possible on an unprecedented scale.
Decision Support Systems Powered by AI and Big Data
- Artificial Intelligence analyzes satellite imagery, sensor data, and genomic information to tailor farm recommendations—improving yield, reducing loss, and optimizing input use.
- Integration with blockchain ensures traceability and authenticity in food and input supply chains.
Livestock and Animal Biotechnology Innovations for 2025
Technology and innovation in agriculture are not limited to plants; biotechnology in livestock and animal management has also undergone tremendous change in recent years.
Genomics-Driven Breeding Programs
- Advanced genomic tools now facilitate highly selective breeding programs in cattle, poultry, and aquaculture species.
- Animals with better disease resistance, higher productivity, and improved feed efficiency are developed through identification of favorable genetic markers.
Animal Health Management and Disease Control
- Biotechnological vaccines and therapeutics tailored to emerging diseases reduce mortality.
- On-farm genetic testing for parentage, disease susceptibility, and market traits accelerates decision-making and enhances yield.
- Efficient feeding systems powered by AI minimize feed wastage while maximizing growth rates.
These advances are central to ensuring food security and efficient, ethical animal agriculture practices in 2025 and beyond.
Precision and Digital Farming Technology Innovations
The synergy between biotechnology and digital tools is perhaps the most transformative aspect of agricultural advancement. Precision agriculture harnesses geospatial technologies, data analytics, and AI to put actionable insights in the hands of farmers, leading to:
- Optimal resource allocation—applying water, fertilizers, and pesticides only where and when needed.
- Sustainability—by minimizing environmental impact and preserving natural resources.
- Cost reduction—lowering inputs while maximizing output and farm profitability.
- Enhanced decision-making via real-time monitoring and analysis.
Examples of such digital farming technology innovations in 2025 include:
- Satellite-based monitoring (for NDVI, soil moisture, crop health, etc.)
- Drones (for precision spraying, field mapping, crop scouting)
- Sensors (soil, moisture, nutrient, weather)
- AI-based advisory systems (data-driven, automated crop management advice)
- Blockchain-integrated traceability (ensuring food origin and supply chain transparency)
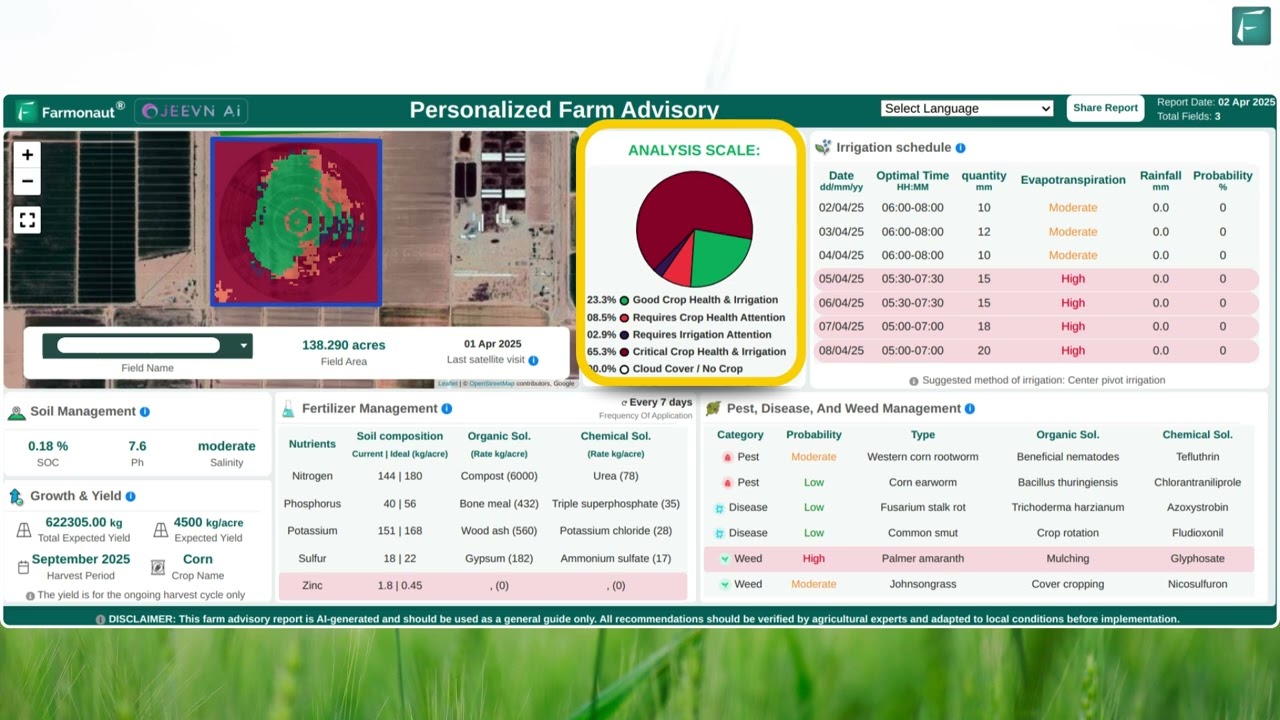
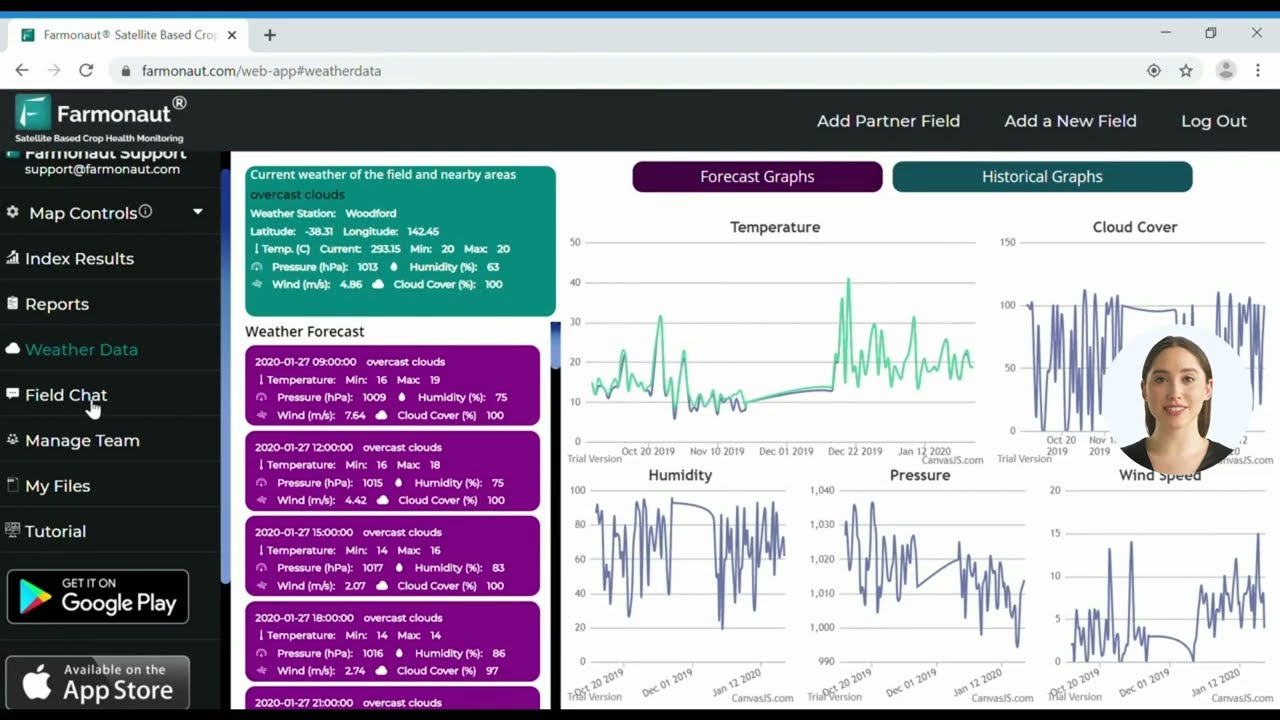
Farmonaut’s satellite-driven insights empower users with farm monitoring, NDVI mapping, soil health assessment, and more, aligning digital and biotechnological innovation for smarter and more resilient farm management. Through easy access to our Farmonaut Satellite Monitoring API and comprehensive API developer documentation, businesses and innovators can seamlessly integrate advanced agricultural intelligence into their digital platforms.
Biofertilizers, Biopesticides, and Green Biotechnological Solutions
Biotechnology innovations in agriculture have paved the way for the replacement of synthetic inputs with powerful biological solutions that work with nature rather than against it. This is essential for sustainable agriculture and reducing the environmental and health impacts of conventional farming.
Biofertilizers and Soil Health
- Biofertilizers are living microbial products that enhance soil nutrient availability, restore soil biodiversity, and improve crop productivity.
- Introduction of mycorrhizal fungi, nitrogen-fixing bacteria, or phosphate-solubilizing microbes is now routine in sustainable agriculture.
- These biological inputs are crucial for regenerating soil on lands degraded by intensive monoculture or chemical fertilizer overuse.
Biopesticides and Natural Pest Control
- New generations of biopesticides, including peptide-based and RNAi products, have shown strong efficacy against major crop pests, while being safe for pollinators and beneficial insects.
- Spinach-derived peptides, for instance, are successfully combating major diseases like citrus greening and zebra chip, resulting in dramatic yield increases.
- By 2025, pesticide use is reduced by 40% (see trivia above), driving sustainability and safeguarding environmental and human health.
Reduced Chemical Dependency
- Smart farming practices use biotechnology innovations to target inputs, meaning fewer synthetic chemicals are needed.
- Residue on food is greatly reduced, and local water and air quality is improved.
Explore Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting feature to measure, monitor, and reduce your farm’s or agribusiness’s environmental impact—helping transition to a carbon-neutral, climate-smart operation in the age of sustainable biotechnology.
Sustainability, Environmental Impact, and the Circular Economy
Biotechnology in agriculture is transforming the paradigm of sustainable farming, targeting not only productivity but also the long-term vitality of ecosystems, communities, and the global food system.
- Biodegradable mulches and bioengineered plant-based packaging reduce plastic use and pollution, and can decompose safely after a single season.
- Soil conditioners made from bio-sourced materials help improve soil quality and structure in a regenerative, rather than extractive, manner.
- Blockchain-based traceability systems like those available through Farmonaut (Product Traceability) ensure transparent supply chains and build consumer trust—boosting the market for sustainably produced food.
To further support ethical and sustainable agriculture, Farmonaut also provides satellite-based crop loan and insurance verification, streamlining access to finance for forward-thinking farmers adopting biotechnological and digital innovations.
Farmonaut: Satellite Technologies Empowering Digital and Biotech Agriculture
As the agricultural landscape becomes more complex and technologically advanced, real-time, reliable data becomes a crucial driver of productivity and sustainability. At Farmonaut, we harness satellite technology, AI, and blockchain to offer accessible, cost-effective, and scalable solutions that integrate seamlessly with biotechnological innovations in agriculture.
Satellite-Driven Insights and AI Advisory
- Real-time satellite-based crop monitoring: Provides farmers and agribusinesses with visual and quantitative assessments of crop health, soil moisture, disease/pest outbreaks, and invasive weed encroachment.
- AI-powered Jeevn advisory system: Converts satellite and ground data into actionable, field-specific recommendations for irrigation, fertilization, pest control, and harvesting—maximizing yields and resource efficiency.
- Environmental impact monitoring: Continuously tracks parameters such as carbon footprint (see: Farmonaut Carbon Footprinting) to help users adopt greener, more regenerative practices and comply with evolving environmental regulations.
- Blockchain-based traceability: Ensures authenticity and transparency from seed to table, strengthening market access and consumer trust for sustainably produced crops.
- Fleet and resource management tools: Optimize the deployment of machinery and vehicles, enhancing labor efficiency and reducing operational costs (Fleet Management).
- Large-scale farm management: Our Agro Admin App supports streamlined operations for agribusinesses overseeing multiple plots or regions (Large Scale Farm Management).
Explore our apps and APIs today—empowering your farm with next-generation satellite, AI, and biotechnology intelligence.
Comparison Table of Key Biotechnology Innovations in Agriculture (2025)
| Innovation Name | Estimated Year of Mainstream Adoption | Key Benefits | Application Area | Estimated Impact on Yield/Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRISPR Gene-Edited Crops | 2024-2025 | Drought/pest/disease resistance, targeted trait improvement, rapid crop development | Staple and specialty crops (wheat, potatoes, rice, corn, etc.) | +25–40% |
| Biofertilizers | 2023-2025 | Enhanced soil fertility, reduced synthetic fertilizer inputs, improved soil health | Global croplands and horticulture | +12–25% |
| Next-Gen Biopesticides (e.g., Spinach Peptide Phytoprotection) | 2024-2026 | Reduced chemical pesticide use, protects beneficial insects, improves yield | Fruit, vegetable, and row crops | +10–20% |
| Gene Diagnostic Sensors | 2024–2027 | Real-time disease/pest detection, targeted intervention, loss prevention | All crops and protected agriculture | +8–15% |
| Precision Agriculture Platforms (e.g., satellite+AI) | 2023–2025 | Resource optimization, input reduction, data-driven farm management | Row crops, orchards, large and small farms | +15–30% |
| Livestock Genomic Selection | 2024-2026 | Improved feed efficiency, disease resistance, enhanced productivity | Cattle, poultry, aquaculture | +18–27% |
| Blockchain Traceability | 2023 – ongoing | Supply chain transparency, fraud reduction, consumer trust | Commodity and specialty agriculture, retail | +3–9% |
| Satellite-based Environmental Impact Tracking | 2023–2025 | Real-time carbon/water/energy tracking, regulatory compliance, sustainability | All farming systems, agribusiness | Indirect, supports 10–20% improvement in sustainable practices |
Future Outlook: Challenges and Opportunities in Biotechnology Agriculture
The future of biotechnology in agriculture is bright, but not without challenges. As biotechnological and farming technology innovations continue to evolve and scale across geographies, stakeholders must address several critical themes to ensure a sustainable, equitable, and productive global food system.
- Regulatory Adaptation & Public Trust
- Equitable Global Access
- Interoperability & Integration
- Ongoing Research and Innovation
- Environmental Stewardship
Robust, science-based regulatory frameworks are essential for ensuring the safety and acceptance of new genetic technologies. This includes clear labeling, rigorous risk assessment, and transparent communication to consumers about GMO and gene-edited crops.
All farmers, including smallholders and those in developing countries, must have access to the benefits of biotechnology innovations, digital tools, and advanced inputs. Policy, training, and low-cost technology deployment are central to avoiding an agricultural divide.
The convergence of digital and biotechnological tools presents opportunities and challenges for data management and system interoperability. Seamless integration will be key for maximizing benefits at each step of the production and supply chain.
Whether responding to new diseases, evolving pests, or changing environmental conditions, constant research is imperative. Support for public and private R&D will drive next-generation biotechnology, ensuring agriculture remains adaptive and resilient.
As biotechnology enables higher productivity, a continued focus on soil health, water availability, carbon sequestration, and biodiversity preservation is vital. Sustainable practices must remain central to all technological advancement in agriculture.
Innovative companies like Farmonaut help bridge the gap by making advanced insights and monitoring solutions accessible to all, regardless of farm size or budget.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the top biotechnology innovations in agriculture for 2025?
Leading innovations include gene-edited crops using CRISPR, biofertilizers, next-gen biopesticides, genomic selection in livestock, precision farming platforms (satellite, AI), blockchain-based traceability, and real-time environmental monitoring.
How do gene-edited crops differ from traditional GMOs?
Gene-edited crops are developed by making small, targeted changes to the plant’s own DNA (often removing or deactivating specific genes), without introducing foreign genetic material. This makes them more acceptable to consumers and regulators compared to traditional GMOs.
Can biotechnology help smallholder farmers?
Yes. When made affordable and accessible, biotechnology innovations such as digital agronomy advice, biofertilizers, and disease-resistant varieties can provide major yield, cost, and sustainability benefits for smallholders worldwide.
How is biotechnology helping agriculture adapt to climate change?
Through development of drought- and heat-tolerant crops, disease and pest-resistant varieties, resource-efficient livestock, and real-time climate-smart management tools, biotechnology is crucial for resilient food systems.
How does Farmonaut support biotechnology-driven agriculture?
Farmonaut’s satellite technology, AI-based advisory systems, blockchain traceability, fleet/resource management, and environmental monitoring provide comprehensive support for farmers adopting biotechnological, precision, and sustainable farming innovations.
Where can I access Farmonaut’s platform and satellite insights?
Users can access the Farmonaut platform via the web app, Android app, and iOS app. Businesses and developers can integrate satellite insights using the API and refer to detailed API documentation.
What sustainability-focused services does Farmonaut offer?
Farmonaut provides carbon footprinting, blockchain-based product traceability, and environmental impact monitoring—all critical for progressive, climate-smart, and sustainable agricultural operations.
Conclusion
Biotechnology innovations in agriculture have truly arrived at the heart of modern farming by 2025. With genetic engineering and gene editing, crop varieties are more drought-tolerant, pest-resistant, and nutrient-efficient than ever. The reduction of chemical inputs—by as much as 40%—underscores the environmental promise of these advances. Digital and satellite-driven technologies, such as those available on the Farmonaut platform, complement biotechnological strides—empowering users to enhance productivity, practice sustainability, and ensure transparency.
As agriculture continues to face the challenges of climate change, food security, and diminishing arable land, the integration of biotechnology, precision tools, and eco-friendly solutions is not just beneficial—it is essential. The future of agriculture lies in continued investment, research, and equitable deployment of these innovations to empower all farmers, protect the environment, and feed a growing global population.
At Farmonaut, we are dedicated to supporting this transition by delivering real-time satellite, AI, and blockchain-powered solutions—bringing the power of biotechnology and smart agriculture to every field, everywhere.
Together, let’s cultivate a resilient, efficient, and sustainable agricultural future—powered by the very best of science, technology, and innovation.