Conservation Tillage: 7 Powerful Ways to Boost Soil Health
“Conservation tillage can reduce soil erosion by up to 60% compared to conventional tillage methods.”
Table of Contents
- Introduction: Understanding Conservation Tillage
- Why Soil Health Matters in Sustainable Agriculture
- 7 Powerful Ways Conservation Tillage Boosts Soil Health
- Comparison Table: Traditional vs Conservation Tillage
- Environmental Benefits of Conservation Tillage
- Economic Advantages for Farmers
- Social and Ecological Benefits
- Considerations and Challenges in Conservation Tillage
- Technology: How Farmonaut Supports Conservation Tillage
- FAQ: Conservation Tillage Practices
- Conclusion: Towards Sustainable Farming Methods
Introduction: Understanding Conservation Tillage
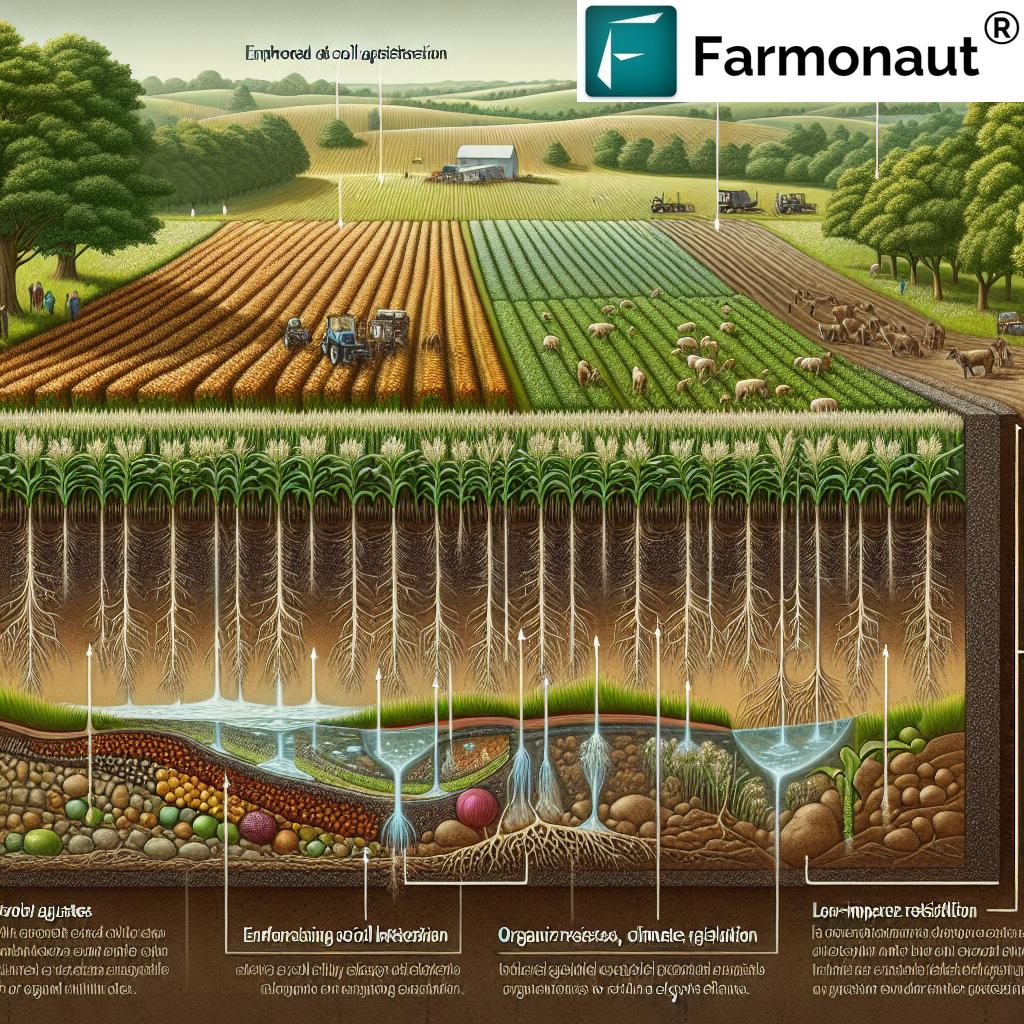
Conservation tillage represents a transformative agricultural practice that balances productivity and sustainability by minimizing soil disturbance. Unlike traditional plowing methods, which invert and break apart the soil, conservation tillage prioritizes maintaining a protective layer of crop residues on the soil surface. This method is gaining momentum globally, as farmers and agribusinesses recognize the long-term benefits for soil health, water retention, and overall farm sustainability.
At its core, conservation tillage involves reducing or eliminating conventional tilling. We achieve this by adopting techniques that keep crop residues—such as stalks, leaves, and roots—on the field after harvest. These residues act as mulch, helping retain soil moisture, suppress weed growth, and minimize soil erosion caused by wind and water. The practice not only preserves our precious topsoil but also supports beneficial soil organisms, improves soil organic matter, and boosts nutrient cycling.
We invite everyone engaged in agriculture—from smallholder farmers to large agribusinesses—to discover how conservation tillage can transform soil health, minimize losses, and promote sustainable farming for years to come.
Why Soil Health Matters in Sustainable Agriculture
Soil is more than just a medium to anchor crops; it is a living, breathing ecosystem that supports the growth of our plants, regulates water cycles, and stores essential nutrients. Soil health improvement is at the heart of all successful, sustainable farming methods. Healthy soils foster resilient crops, increase yields, and even sequester more carbon, mitigating climate change impacts. Factors such as soil structure, organic matter content, porosity, and biological activity all define the capability of soils to support robust farming systems.
Unfortunately, years of repeated plowing, over-cultivation, and poor crop residue management have left many agricultural soils degraded, compacted, and prone to erosion. This results in reduced soil fertility, diminished water retention, and weaker resistance to droughts or pests. It’s no surprise that global movements are calling for a shift from traditional tillage systems to more sustainable approaches, such as conservation tillage, to restore and maintain our crucial soil resources.
7 Powerful Ways Conservation Tillage Boosts Soil Health
Discovering the mechanisms by which conservation tillage elevates soil health is essential for anyone invested in sustainable agriculture. Let’s explore seven core benefits and practical solutions achieved by this approach—each underpinned by real, measurable improvements in the health and productivity of our farms.
-
1. Reduced Soil Disturbance for Long-Term Resilience
By reducing or eliminating plowing, conservation tillage limits soil disturbance. This method preserves the natural aggregation and structure of soils, fostering beneficial microbial and faunal populations. Less disturbance translates to fewer disruptions in the soil’s capacity to crumble, infiltrate water, and support diverse crops.
Example: In arid regions, minimizing tillage is especially helpful as it limits evaporation and reduces energy loss from exposed soils. -
2. Crop Residue Management: Building a Protective Surface Layer
Proper crop residue management is central to conservation tillage. By leaving crop residues on the soil surface, we provide a protective layer that shields the soil from raindrop impact, wind, and extreme temperature fluctuations. This mulch reduces soil erosion and conserves moisture, supporting improved root growth and healthier plant emergence.
-
3. Enhancing Soil Organic Matter through Residue Decomposition
Over time, the accumulation of residues encourages the formation of soil aggregates, increases organic matter, and supports nutrient cycling. As residues decompose, they release essential nutrients for crops and feed beneficial soil organisms. The result is a living ecosystem teeming with earthworms, nematodes, and fungi—all of which contribute to the long-term fertility, structure, and quality of our soils.
-
4. Improved Water Retention and Infiltration
Conservation tillage substantially improves water conservation in agriculture. Mulched surfaces slow evaporation, maintain higher soil moisture across seasons, and reduce compaction. This enhances infiltration rates, enabling water to penetrate deeper into the soil profile where it is available to plant roots during drought and dry spells.
-
5. Soil Erosion Prevention and Topsoil Preservation
When crop residues are left as a mulch, the soil is protected from both wind and water erosion. This reduced soil erosion practice preserves topsoil—our single most important resource for future crop growth—ensuring that fertile layers remain intact and productive over the years. Research suggests conservation tillage can decrease soil loss by up to 60% compared to conventional plowing.
-
6. Healthier Microbial Activity and Biodiversity in Farmlands
By maintaining an undisturbed habitat, conservation tillage supports diverse microbial and faunal communities. These communities are critical for breaking down organic matter, fixing nitrogen, and suppressing plant pathogens. Improved biodiversity means healthier, more productive, and resilient farms.
Tip: Fields managed with conservation tillage often become sanctuaries for beneficial insects and wildlife, further enriching the ecosystem. -
7. Increasing Farm Profitability by Reducing Inputs
Because less tillage means fewer trips across the field, farmers save on fuel, labor, and machinery expenses. Additionally, improved soil health supports higher and more stable crop yields, directly impacting profitability. Farmers practicing conservation tillage often see more consistent yields and better resource use efficiency.
“Fields using conservation tillage retain up to 30% more water, enhancing crop resilience during dry periods.”
Comparison Table: Traditional Tillage vs Conservation Tillage Impact on Soil Health
| Practice Type | Soil Erosion Reduction (%) | Water Retention Increase (%) | Organic Matter Improvement (%) | Crop Yield Impact (Est. % Change) | Long-term Sustainability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Tillage | 0-10% | 0-5% | -5 to 0% | -10 to 0% | Low |
| Conservation Tillage | Up to 60% | Up to 30% | 10-25% | 5-15% | High |
This comparison highlights why conservation tillage is a foundational sustainable farming method: it greatly reduces soil erosion, increases water retention, improves organic matter, and can lead to higher, more stable yields.
Environmental Benefits of Conservation Tillage
1. Effective Soil Erosion Reduction
Traditional tilling exposes fields to the forces of wind and water, accelerating the loss of valuable topsoil and associated nutrients. Conservation tillage, by leaving residues as a surface mulch, provides a protective barrier that significantly reduces erosion—by up to 60% in some cases (source). This practice is crucial in areas prone to severe weather events or sloped terrains.
- Prevents degradation of topsoil, preserving long-term fertility
- Minimizes runoff of fertilizers and pesticides, safeguarding downstream water quality
- Supports the formation of healthy soil aggregates, improving stability and reducing wind-blown dust
2. Improved Soil Structure and Porosity
Soil structure refers to the arrangement of solid particles (sand, silt, and clay) into aggregates. Conservation tillage minimizes compaction, preserves soil pores, and stimulates the facilitating of water infiltration, which are all vital for robust root development and nutrient uptake. The continuous presence of organic matter from residues nourishes beneficial microbes and supports the ecosystem beneath our feet.
- Enhances soil aeration and root penetration
- Boosts water holding capacity—protecting against both drought and heavy rainfall
3. Water Conservation: Reducing Evaporation and Increasing Retention
A key challenge in arid regions and during drought is maintaining soil moisture for crops. Conservation tillage helps by leaving organic residues on the soil surface, acting as a natural mulch. This not only reduces evaporation but also improves the effectiveness of irrigation and rainfall.
- Keeps soil temperature steadier, reducing stress on young plants
- Prevents crust formation, enabling better infiltration and moisture storage
4. Increasing Soil Fertility and Organic Matter
The cumulative build-up and slow decomposition of residues deliver a constant supply of essential nutrients. This results in the gradual improvement of soil fertility, greater nutrient cycling, and the creation of healthier, more resilient agricultural soils (source).
- Promotes a more stable, healthy environment for crops
- Supports higher levels of beneficial microorganisms
- Improves soil carbon content, which supports carbon footprint reduction efforts
Economic Advantages for Farmers
1. Significant Cost Savings on Fuel and Labor
By adopting conservation tillage, we reduce the number of machinery passes needed for planting and field management. This results in lower fuel consumption, less machinery wear, and reduced labor expenses (source).
- Minimizes costly equipment repair and replacement cycles
- Reduces dependency on external labor, particularly during peak seasons
2. Improving Crop Yields and Farm Profitability
Conservation tillage promotes healthier soils with improved fertility, moisture retention, and microbial activity. Healthier soils foster stronger plant growth, resulting in higher yields and more resilient crops, even in the face of climate variability. By building up soil health each season, farms see increased productivity and greater returns on investment.
- Boosts overall farm profitability through more consistent yields
- Reduces crop loss during periods of drought or excessive rainfall (see satellite-based risk management solutions)
3. Supporting Resilient Agriculture to Climate Change
One of the most important benefits of conservation tillage is increasing our resilience to extreme weather events (droughts, floods, severe windstorms). Improved soil structure, water retention, fertility, and biodiversity help farmers adapt to climate variability, securing harvests and livelihoods for the future.
- Buffers the effects of drought and high temperatures
- Reduces the risk of complete crop loss during extreme weather events
Social and Ecological Benefits
1. Enhanced Wildlife Habitat in Farmlands
By leaving crop residues undisturbed, we are also providing food and shelter for various wildlife species. Many beneficial insects, birds, and small mammals thrive in fields managed with conservation tillage, resulting in greater biodiversity (source).
- Encourages the presence of natural pest controllers (e.g., ladybugs, birds)
- Helps stabilize ecosystem functions within and beyond the farm
2. Improved Air and Water Quality
Conservation tillage reduces dust emissions and prevents runoff of soil particles and chemicals into neighboring waterways (source). This results in:
- Cleaner air for rural and neighboring urban communities
- Improved water quality due to lower sedimentation and chemical runoff
3. Building a Healthier Rural Community
Greater farm productivity and environmental sustainability translate to stronger rural economies and livelihoods. Communities benefit from improved natural resources, increased food security, and a reputation for sustainable, ecologically sound agriculture.
To maximize these ecological, social, and economic benefits, we must also address the practical challenges associated with conservation tillage.
Considerations and Challenges in Conservation Tillage
While the advantages of conservation tillage are numerous, successful implementation demands strategic management practices and awareness of certain potential barriers.
1. Managing Soil Compaction
In heavy clay soils or with repeated field traffic, soil compaction can become an issue, inhibiting root penetration and water infiltration. In such cases, farmers should periodically use techniques like subsoiling or paratilling to alleviate deep compaction (ref: SARE).
2. Residue and Weed Management Complexity
The move to conservation tillage requires deliberate attention to crop residue levels, weed pressures, and pest populations. Optimizing residue cover while maintaining efficient seeding and pest control can demand new skills, investments in specialized equipment, and adaptation in crop rotations.
- We suggest using AI-powered advisory systems for integrated farm management to monitor field conditions and make custom recommendations.
3. Pest and Disease Management
Retained residues can sometimes shelter pests and diseases over the winter. Developing an integrated pest management strategy—utilizing crop rotations, resistant varieties, and careful monitoring—helps mitigate these risks while preserving the environmental benefits of the system (SARE).
4. Machinery and Equipment Needs
Transitioning from conventional to conservation tillage may require farmers to invest in specialized seeding or planting equipment capable of handling high residue levels.
To minimize costs and maximize returns, we recommend utilizing fleet management & resource optimization tools.
5. Learning Curve & Initial Transition Period
The shift to new practices often involves an initial adjustment period, where short term yields may fluctuate or management tasks increase. However, as fields stabilize and soil health improves, the long-term benefits significantly outweigh initial challenges. Continuous learning and access to updated farm data are key to a successful transition.
Technology: How Farmonaut Supports Conservation Tillage
The role of digital agriculture is rapidly growing, adding powerful decision-making tools for anyone managing conservation tillage. Farmonaut stands at the forefront with satellite-driven, AI-powered solutions to simplify and optimize the transition to sustainable farming.
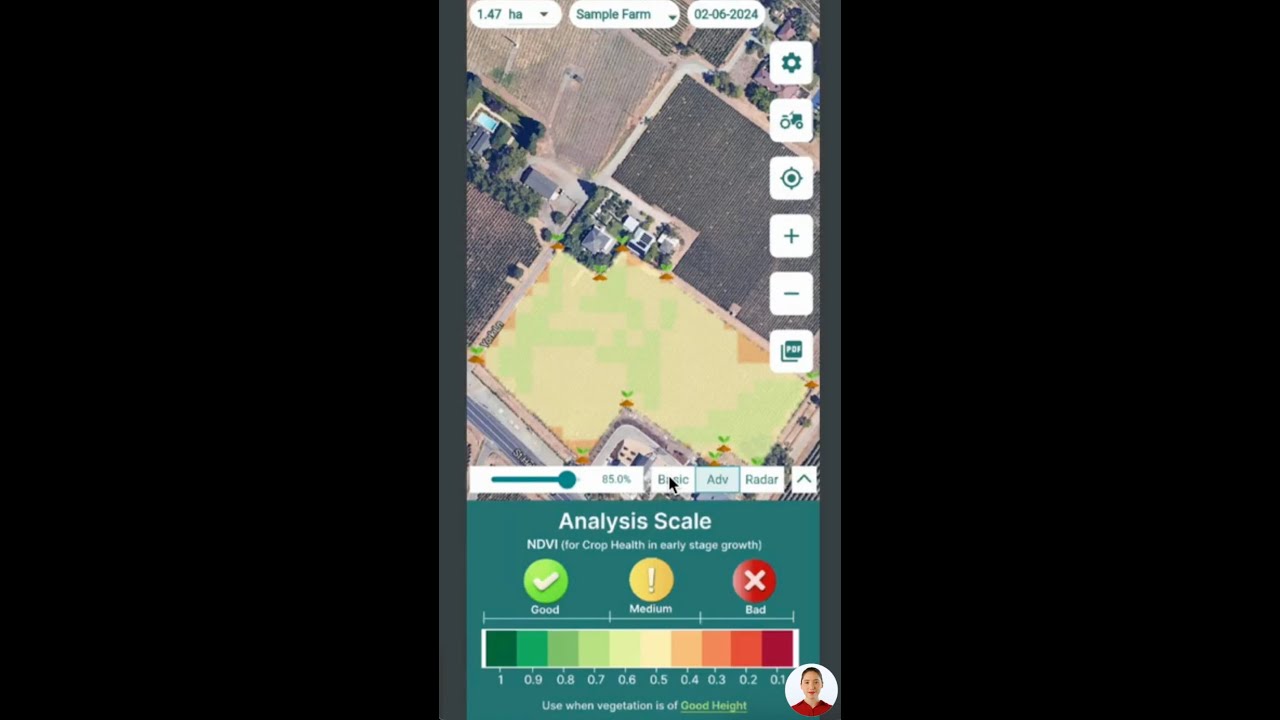
- Real-time Satellite Crop Health Monitoring: Monitor crop stress, soil moisture, and field variability for targeted input application and improved water conservation in agriculture.
- Jeevn AI Advisory System: Receive customized recommendations for crop residue management, pest control, and nutrient optimization, ensuring your practice remains as efficient as possible.
- Blockchain-Based Traceability: Provide traceable records for sustainably produced crops from field to consumer, building market credibility and trust.
- Resource and Fleet Management: Use fleet tracking to lower costs, plan maintenance, and ensure maximum machinery efficiency with minimal environmental impact.
- Carbon Footprinting: Measure, monitor, and reduce your operation’s carbon footprint for improved sustainability reporting and access to emerging environmental markets.
Farmonaut’s solutions are suitable for smallholders, cooperatives, large-scale operations, governments, and financial institutions—all accessible via web, Android, iOS, and API integrations. Developers can leverage Farmonaut’s API and developer documentation to further customize or expand solutions.
For those managing plantation forests, orchards or undertaking large-scale farm management, Farmonaut provides powerful admin tools aligning resource optimization, crop health, and sustainability documentation in one platform.
FAQ: Conservation Tillage Practices
What is the main difference between conservation tillage and traditional tillage?
Conservation tillage minimizes soil disturbance by reducing or eliminating plowing and leaving crop residues on the field. Traditional tillage often involves intensive plowing and soil inversion, which can lead to erosion, reduced organic matter, and soil degradation.
How does conservation tillage help improve soil health?
Conservation tillage boosts soil health by preserving soil structure, increasing organic matter, retaining more water, and supporting biodiversity—all critical for improved crop yields and long-term sustainability.
Can conservation tillage reduce input costs for farmers?
Yes. The approach requires fewer field operations, reducing fuel and labor costs, and leads to less machinery wear and tear. The improved soil fertility and water retention also reduce the need for irrigation and fertilizers.
What are some potential challenges of adopting conservation tillage?
Challenges may include initial learning curve, residue management, risk of increased pests/weeds, and potential soil compaction in certain conditions. However, these can be effectively managed with the right planning, monitoring, and technology support.
How do I start implementing conservation tillage on my farm?
Begin by assessing your field’s current state, selecting the right tillage system (no-till, strip-till, etc.), and investing in appropriate equipment. Monitoring with digital farm management tools will support smoother transition and ongoing success.
Can I monitor conservation tillage effectiveness using technology?
Absolutely! With solutions like Farmonaut, farmers can analyze crop health, residue cover, soil moisture, and more via satellite data—enabling data-driven management for optimizing sustainability and profitability.
Conclusion: Towards Sustainable Farming Methods
Conservation tillage is at the heart of sustainable agriculture. By reducing soil disturbance, leaving residues as mulch, and improving organic matter, water retention, and structure, we build a foundation for long-term soil health, resilience to climate change, improved biodiversity, and more profitable, ecologically sound farming.
Although the transition from traditional tillage brings certain challenges, the long-term economic, environmental, and social benefits far outweigh initial adjustments. The availability of precision technologies like Farmonaut’s real-time satellite monitoring, AI advisories, and resource optimization ensures farmers of all scales can confidently manage, measure, and maximize their success with conservation tillage.
Let’s continue to protect our soils, support our communities, and secure the future of agriculture—one conservation practice at a time. Explore smart farm management, sustainability tracking, and more on the Farmonaut platform today!