Rhizoctonia Blight Treatment: 7 Shocking Cure Secrets!
Meta Description: Rhizoctonia blight management is essential for healthy, high-yield crops. Discover the 7 shocking cure secrets for Rhizoctonia solani control and integrated pest management!
“Over 40% of global crop losses are linked to soil-borne diseases like Rhizoctonia blight each year.”
Table of Contents
- Overview: Understanding Rhizoctonia Blight
- Signs and Symptoms of Rhizoctonia Blight in Key Crops
- The Impact: Yield Loss Due to Rhizoctonia Blight
- Rhizoctonia Blight Treatment: 7 Shocking Cure Secrets
- Comparison Table of Rhizoctonia Blight Management Strategies
- How Farmonaut Empowers Disease Management
- FAQ: Rhizoctonia Blight Control and Management
- Conclusion
Overview: Understanding Rhizoctonia Blight
Rhizoctonia blight, caused by the aggressive soil-borne fungus Rhizoctonia solani, is a major threat to agricultural productivity globally—impacting core crops such as rice, sugarbeet, soybean, and groundnut. Its adaptive habits, infecting various plant tissues (roots, stems, leaves), result in widespread disease, complicated control, and significant yield losses and grain quality degradation.
As we dive deep into Rhizoctonia blight management, our goal is to empower you with integrated, actionable strategies: from precise disease control and early prevention, to the latest biological and chemical methods. Together, we’ll explore how diagnostic insights, like those from satellite-based platforms such as Farmonaut, can transform integrated pest management for crops, sharply reducing the risk of yield loss due to Rhizoctonia blight.
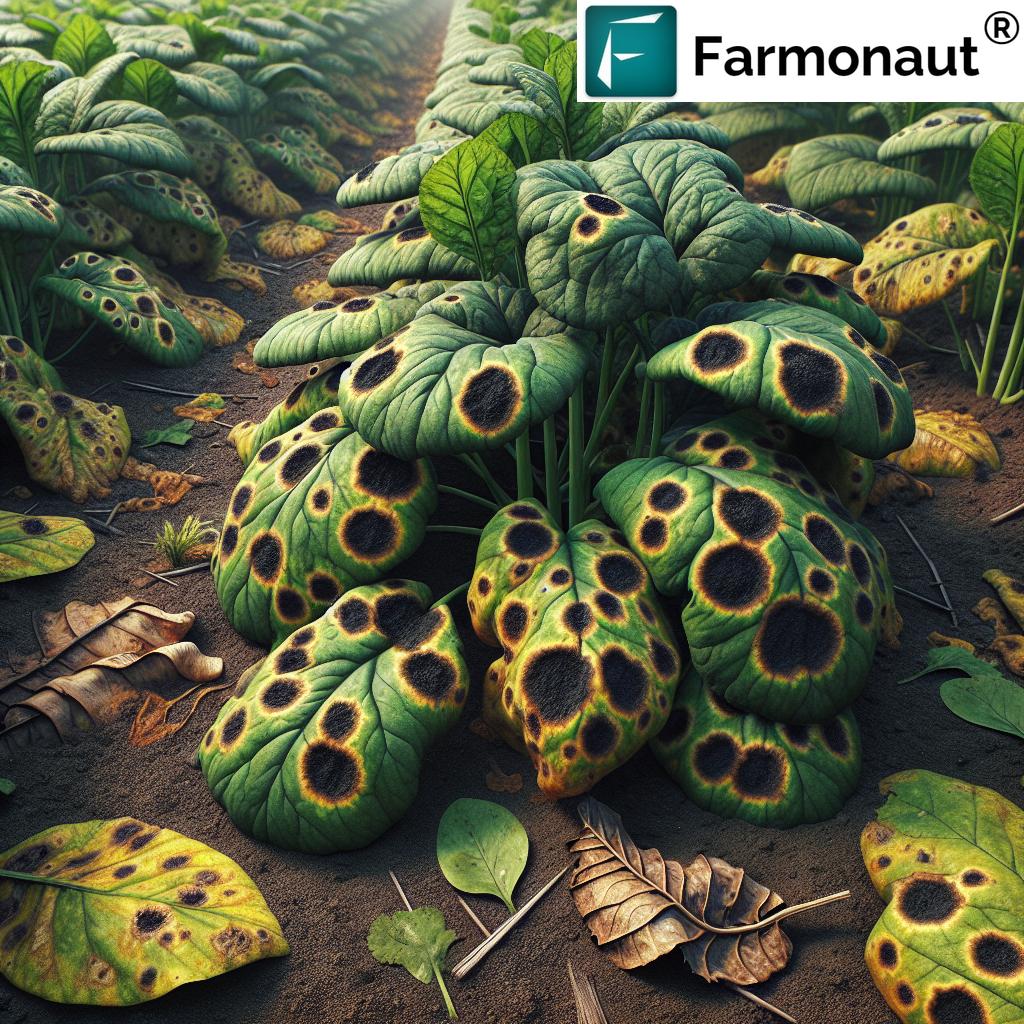
Signs and Symptoms of Rhizoctonia Blight in Key Crops
To achieve effective management, recognizing and understanding signs of Rhizoctonia blight is essential for timely intervention:
- Rice: Look for sheath blight—characterized by water-soaked lesions on leaf sheaths that expand, causing lodging and grain quality decline. Affects yield and makes ripening grain prone to secondary infections.
- Soybean: Aerial blight results in rapid leaf defoliation, reduced pod development, and weakened seed quality, especially in humid climates.
- Sugarbeet: Crown and root rot provokes wilting, root decay, and a measurable drop in sugar content, directly impacting farm profitability.
- Groundnut: Root rot leads to stunting, poor pod formation, and diminished oil yields; often accompanied by visible rot at the base of stems.
The Impact: Yield Loss Due to Rhizoctonia Blight
Let’s address why Rhizoctonia solani is such a formidable foe in crop disease management strategies. The losses go much deeper than what meets the eye:
- Direct yield loss: A single outbreak can decimate up to 40% of field production, as confirmed in diverse geographies and numerous scientific assessments.
- Quality degradation: Infected grain, root, and oil crops experience diminished market value due to poor seed and oil content.
- Productivity setback: Fields affected by decay and wilting often require costly restoration, delaying the crop cycle and increasing labor costs.
- Soil pathogen buildup: Once established, R. solani sclerotia persist for years—complicating control and threatening subsequent crops in rotation.
With integrated pest management for crops and digital platforms like Farmonaut supporting real-time monitoring, we can intercept threats early, safeguard yields, and improve farm system resilience.
Want to optimize your plantation management year-round?
Try Farmonaut’s Plantation & Forest Advisory Tools for holistic, data-driven crop health assessments and timely pest/disease notifications.
“Integrated pest management can reduce Rhizoctonia blight incidence by up to 60% in susceptible crops.”
Rhizoctonia Blight Treatment: 7 Shocking Cure Secrets
After deep research and best-practice integration, here’s our comprehensive take on the 7 shocking secrets to Rhizoctonia blight treatment, each supported by science and actionable on your farm.
1. Cultural Practices for Disease Control: Crop Rotation & Field Sanitation
Cultural management remains the backbone for Rhizoctonia solani control:
- Crop Rotation: Implement at least a three-year rotation using non-host species (e.g., cereals like wheat after sugarbeet) to disrupt the soil pathogen lifecycle and prevent build-up in the soil. This simple switch alone can cut disease risk by over 30%.
- Field Sanitation: Thoroughly remove or decompose infected crop residues and weeds. Chopping and plowing under residues, then promoting decomposition, eliminates inoculum sources and prevents further infection.
- Optimal Soil Management: Maintain good drainage, avoid compaction, and irrigate plants in the early morning to foster rapid leaf drying—thus reducing disease risk.
See more cultural practices for disease control in Farmonaut’s resource-efficient guides for large-scale farm management, which empower farmers to manage every field operation with precision.
2. Biological Control of Soil Pathogens: Trichoderma, Bacillus & PGPRs
Harnessing beneficial soil organisms is a sustainable, eco-friendly approach for controlling the pathogen in the soil:
- Trichoderma for Plant Disease Management: Trichoderma asperellum and related species antagonize R. solani, directly suppressing its spread while promoting plant health and yield. Apply as a soil amendment or seed treatment for maximum protective effect.
- Bacillus subtilis: Acts both as an effective pathogen suppressant and a plant growth promoter. Granular or liquid formulations, applied to the soil or seeds, can deliver up to 40% reduction in disease incidence.
- Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPRs): Seed priming with selected PGPRs hinders sclerotia (fungal bodies) development, keeping crops like rice protected before the onset of blight.
Such biological control of soil pathogens forms a core component of integrated pest management for crops,
especially in organic, sustainable, or high-value crop production. Farmonaut supports such practices with field health analytics, so you know exactly where and when to act.
3. Chemical Treatments: Fungicides for Rhizoctonia Blight
Sometimes, targeted chemical control is essential for outbreak containment:
- Seed Treatments: Application of systemic fungicides like carbendazim or tebuconazole on seeds protects against early-stage infection and bolsters seedling survival in susceptible crops such as rice and soybean.
- Soil Applications: Modern products such as azoxystrobin and flutolanil targets soil reservoirs of the fungus. Uniform application, especially on sugarbeet or groundnut fields, is both potent and fast.
- Foliar Sprays: When above-ground symptoms emerge, azoxystrobin-based sprays break the infection cycle on stems, leaves, and sheaths.
Learn about different fungicides for Rhizoctonia and how to integrate them effectively by leveraging Farmonaut’s farm API for real-time, field-level risk profiling, or explore the developer documentation here.
4. Integrated Pest Management for Crops (IPM): The Holistic Approach
We cannot overstate the power of combining all control measures! Integrated pest management for crops (IPM) leverages the strengths of each tactic, ensuring lasting disease suppression at lower risk and cost:
- Resistant Varieties: Utilizing plant varieties with inbuilt resistance to R. solani directly reduces incidence and yield loss.
- Timely Fungicide Applications: Applying chemical controls at the optimal growth stage (pre/post-emergence) or in response to digital alerts amplifies efficacy.
- Field Management: Improve drainage, control volunteer grains and weeds, and avoid susceptible crop sequences to keep the field environment unfriendly for the fungus.
Farmonaut’s platform streamlines field management operations for both individual farmers and large agribusinesses, delivering IPM recommendations personalized to local soil, climate, and crop data.
5. Soil Solarization: Harness the Sun Against Soil Pathogens
When tackling root and crown rot in crops associated with R. solani, soil solarization can be remarkably effective:
- Cover moist, finely tilled soil with clear plastic during the hottest part of the year for 4-6 weeks.
- The increased soil temperature (to 45–60°C) destroys sclerotia and other pathogenic forms.
- Can decrease soil inoculum by up to 90%, making it perfect as part of a rotation or for newly reclaimed fields.
Combine with other cultural tools as part of Rhizoctonia blight management for optimal long-term results.
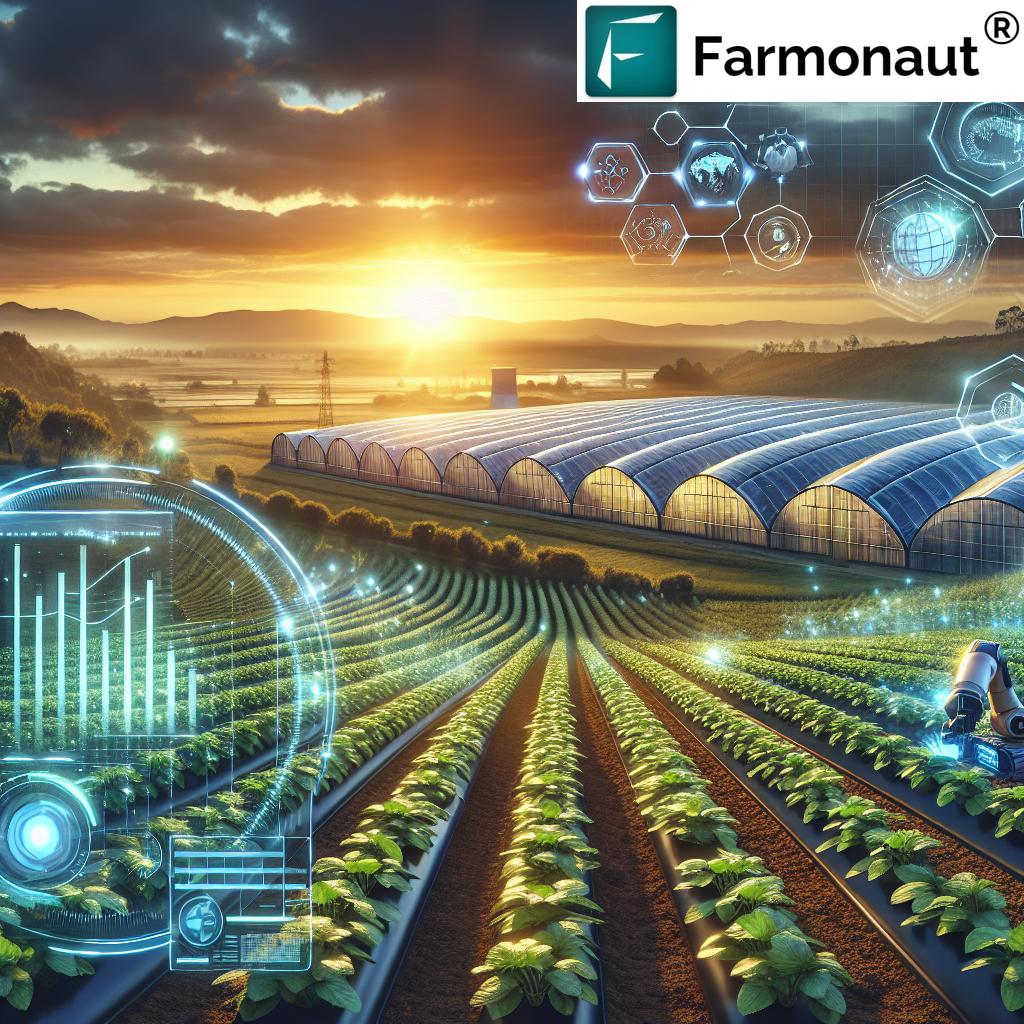
6. Advanced Data-Driven Monitoring & Decision Support
The modern farm’s edge comes from real-time data. Using platforms like Farmonaut, you can:
- Monitor crop health from satellite: Identify early disease outbreaks, monitor growth, and assess plant stress before visual symptoms emerge.
- Receive AI-based IPM advisories: Get personalized recommendations for fungicide applications, rotation timing, and biological treatments based on localized risk.
- Optimize resources: Avoid over-spraying, ensure timely interventions, and achieve optimal soil moisture for preventing Rhizoctonia blight.
This technology is now accessible through web, Android, iOS, and API integrations. Try Farmonaut’s web app for seamless, site-specific disease alerts and interventions.
Secure your yields!
With Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop loan and insurance verification tools, minimize risk and support farm recovery after disease events—ensuring bank and insurer confidence.
7. Blockchain Traceability for Disease-Free Supply Chains
For corporate clients and export-oriented growers, integrating blockchain-based traceability with crop disease management strategies is a game changer:
- End-to-end documentation: Every step (including disease management interventions) is recorded, verified, and accessible, ensuring transparent, trustworthy supply chains for buyers and end users.
- Enhanced reputation: Verified disease-free product journeys fetch higher market premiums and consumer trust.
Explore Farmonaut’s traceability solutions to modernize your compliance and market positioning.
Comparison Table of Rhizoctonia Blight Management Strategies
| Treatment Method | Estimated Disease Reduction (%) | Estimated Cost per Acre (USD) | Time to Results (Days/Weeks) | Crop Safety Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fungicide Application | 60–80% | 25–50 | 7–14 days | Medium |
| Crop Rotation | 30–45% | <10 | Seasonal | High |
| Biological Control | 35–50% | 15–35 | 2–4 weeks | High |
| Integrated Pest Management (IPM) | 55–70% | 20–60 | 2–6 weeks | High |
| Resistant Varieties | 25–65% | Varies | Seasonal | High |
| Soil Solarization | 60–90% | 30–80 | 4–6 weeks | High |
| Improved Drainage | 20–35% | Varies | Immediate-Seasonal | High |
How Farmonaut Empowers Rhizoctonia Blight Management
Farmonaut is a pioneering agricultural technology platform committed to making precision agriculture affordable and accessible for all. Our offerings directly transform how farmers, agribusinesses, and corporates manage Rhizoctonia blight and similar crop diseases:
- Satellite-based crop health monitoring: With real-time NDVI, soil moisture, and vegetation stress data, we enable pre-symptom disease detection and efficient resource management.
- Jeevn AI Advisory: Our AI-driven platform delivers localized weather updates, integrated pest management recommendations, and precise intervention schedules—maximizing disease control while reducing unnecessary applications.
- Blockchain-based traceability: Ensure every batch, from field to shelf, is transparently tracked via immutable ledgers—protecting your product’s market value.
- Fleet and Resource Management: Optimize logistics, reduce costs, and respond rapidly to field-level pathogen outbreaks (see Fleet Solutions).
- Carbon Footprinting: Monitor and minimize environmental impacts while implementing sustainable disease control strategies (details here).
Our platform’s modular model means individual farmers on small plots get the same decision-quality information as international estates. By combining satellite data and advisory, you’ll enjoy superior results in Rhizoctonia blight management while saving costs and supporting sustainability.
Farmonaut Subscriptions: Choose Your Path to Precision
FAQ: Rhizoctonia Blight Control and Management
What is the focus keyword for Rhizoctonia blight management?
Focus keyword: “Rhizoctonia blight management” encapsulates all major crop disease management strategies—from cultural controls to advanced AI-supported decision systems. This ensures effective pathogen suppression and healthy yields.
Which crops are most severely affected by Rhizoctonia solani?
Rhizoctonia solani primarily targets rice, soybean, sugarbeet, and groundnut, but can impact over 180 plant species globally. Severity depends on climate, soil conditions, and crop rotation practices.
Are biological solutions effective for controlling Rhizoctonia blight?
Yes. Trichoderma asperellum, Bacillus subtilis, and specific PGPRs show robust results when applied correctly, reducing disease incidence and supporting plant growth.
Can we rely solely on fungicides to eliminate Rhizoctonia blight?
No. While fungicides such as azoxystrobin offer quick relief, reliance on single methods leads to resistance. Integrated approaches (mixing biological, cultural, and chemical controls) yield the most lasting results.
How can digital agriculture help in managing soil-borne diseases?
Digital platforms like Farmonaut analyze satellite imagery for early stress signs, map risk, and help farmers intervene before large-scale crop loss occurs. This makes management timely, data-driven, and more cost effective.
What is the best time to apply fungicides for Rhizoctonia blight?
Pre-planting seed treatments and early post-emergence foliar sprays are most effective. For ongoing outbreaks, targeted applications on visible lesions or during high-risk weather events is recommended.
Are there secondary benefits to managing Rhizoctonia blight?
Absolutely! Effective blight control also reduces secondary plant diseases, keeps soil pathogens in check, and supports overall soil health—contributing to long-term farm profitability.
Conclusion
Rhizoctonia blight, driven by the formidable R. solani fungus, remains a leading cause of yield losses and productivity setbacks in high-value crops worldwide. Through a blend of cultural, biological, chemical, and integrated pest management approaches, we can curb both incidence and severity—preserving yield, soil health, and long-term farm viability.
Adopting next-generation digital solutions like Farmonaut accelerates these advances by fusing real-time satellite imagery, AI advisories, and traceability tools into everyday farm management. By integrating these science-backed strategies, every farmer and agribusiness can outpace pathogens, maintain high-quality produce, and safeguard the food chain for generations to come.
Let’s fight Rhizoctonia blight—using science, technology, and holistic approaches to achieve healthy, vibrant, and profitable crops!