Tree Storm Support System Services for Crop & Livestock: Enhance Sustainability, Protect Crops & Livestock, and Boost Farm Resilience
Introduction: Why Tree Storm Support Systems Matter
Tree storm support systems represent a proactive approach to sustaining crop and livestock production within an ever-changing climate. These agroforestry practices, including windbreaks, shelterbelts, and riparian buffers, are strategically planted tree and shrub systems that buffer farmland from harsh weather, reduce erosion, protect crops and livestock, and enhance biodiversity. As climate change brings increasingly unpredictable storms, drought, and weather conditions, adopting such systems is not just an option—it’s crucial for farm sustainability, productivity, and environmental stewardship.
This comprehensive guide explores the integral role of these tree storm support systems for crop & livestock management, diving deep into windbreaks for farms, shelterbelts for livestock protection, and the use of riparian buffers in agriculture. Learn how implementing these systems can reduce soil erosion, improve farm resilience to weather, and deliver significant environmental benefits.
What are Tree Storm Support Systems?
A tree storm support system refers to the intentional design and implementation of rows of trees, shrubs, and vegetation within agricultural landscapes to support crops and livestock against weather extremes. The primary types are:
- Windbreaks: Linear plantings to reduce wind speed and protect fields.
- Shelterbelts: Multiple flowered rows for livestock and broad farm protection.
- Riparian buffers: Vegetation stripes along waterways for water protection and wildlife habitat.
Each system is strategically designed to address specific environmental and agricultural needs, providing a wide array of benefits from minimizing storm impacts to enhancing farm biodiversity and boosting yields.
Windbreaks for Farms:
Reduce Wind Erosion & Protecting Crops
Windbreaks are rows of trees and shrubs strategically planted to reduce wind speed and protect crops, livestock, and soil from wind damage. They act as a living shield, making them a cornerstone of tree storm support systems. Their application has transformed agricultural sustainability in several regions, notably in the Great Plains and similar landscapes facing frequent storms and drought.
How Windbreaks Work
- Disrupt wind flow: Slowing gusts and dispersing storm energy.
- Reduce soil erosion: Decreasing wind-blown topsoil loss by keeping soils stable and nutrient-rich.
- Protecting crops from storms: Minimizes lodging and breakage, boosting crop yields.
- Enhance water efficiency: Less evaporation means more moisture for crops.
- Conserve energy: Reducing wind chill boosts energy efficiency on farms.
According to USDA research, windbreaks can decrease wind speed by up to 50% within their protection zone. This drastically reduces lost soil and physical damage to crops, contributing to higher and more stable yields, especially in wind-prone regions like the Plains.

Benefits of Windbreaks for Farms
- Reduce Soil Erosion: A single tree row can cut wind erosion by 30-50%, preserving critical topsoil and supporting long-term soil health.
- Increase Crop Yields: By protecting against wind damage, yield improvements of 5-20% are commonly observed near the shelter zone.
- Enhance Farm Resilience to Weather: Providing a buffer during drought and storm impacts, especially relevant as climate events become more unpredictable.
- Improved Microclimates: Creating milder growing conditions, supporting crop growth, and extending growing seasons.
- Support Biodiversity: Rows of native trees and shrubs offer habitats for various wildlife species, promoting ecological balance.
Shelterbelts for Livestock Protection & Biodiversity Enhancement
Shelterbelts share functional similarities with windbreaks but are designed specifically to protect livestock in addition to crops and land. Shelterbelts consist of multiple rows of trees and shrubs, often combining evergreen and deciduous species for year-round shade and shelter. Their role in livestock protection and improved welfare is particularly valuable on mixed-use farms and broadacre operations.
Shelterbelts: Key Functions
- Shade and Shelter: Protect animals from harsh weather conditions (heat, cold, wind, rain), reducing heat stress and winter chill.
- Enhances Animal Welfare and Productivity: Numerous studies reveal reduced heat stress translates to improved weight gain, milk yields, and overall animal health.
- Biodiversity Hotspots: The dense plantation serves as habitats for birds, pollinators, and beneficial organisms, supporting diverse farm ecosystems.
- Increase Crop Yields: Shelterbelts provide wind protection for neighboring fields, boosting crop productivity.
- Buffering Storm Impacts: The width and density of shelterbelts slow wind, minimize drifting snow accumulation and create safer, more stable landscapes.

Research from Teagasc highlights that well-managed shelterbelts not only reduce livestock energy losses but also increase overall productivity. Livestock mortality during cold spells is significantly reduced, while shade in warmer climates dramatically boosts comfort and animal welfare.
Shelterbelts and Biodiversity
- Wildlife Corridors: Serving as vital linkages for over 80 species of wildlife in many agricultural landscapes.
- Native Plantings: Support pollinator populations and beneficial insects, contributing to improving farm biodiversity.
- Soil Improvement: Leaf drop and root turnover from shelterbelt trees boost soil organic matter and nutrient cycling.
Riparian Buffers in Agriculture:
Water Quality and Wildlife Habitat
Riparian buffers are strips of trees, shrubs, and grasses planted along waterways—such as streams, lakes, and rivers—serving multiple environmental and agricultural benefits. These buffers are essential for reducing water pollution, stabilizing banks, and enhancing aquatic habitat, making them a core element in sustainable agroforestry practices.
Key Functions of Riparian Buffers
- Reduce nutrient runoff: Intercept fertilizers and pesticides from entering water bodies.
- Stabilize stream banks: Tree and shrub roots prevent erosion and buffer stormwater flows.
- Improve water quality: Filtration of sediment and pollutants supports healthy aquatic environments and maintains water quality.
- Enhance biodiversity: Providing food, shelter, and migration corridors for both terrestrial and aquatic species.
- Support ecosystem services: Including flood mitigation, carbon storage, and creating microclimates that benefit adjacent crops.
The USDA Forest Service recognizes that well-maintained riparian buffers are instrumental in reducing agricultural runoff, controlling erosion, and providing crucial wildlife habitat in diverse agricultural and forestry settings.
Importance of Riparian Buffers in Farming
- Reduce Soil Erosion: Grass and woody strips filter incoming runoff and anchor soils during storms.
- Protect Waterways: Reduced pollutant loads mean healthier streams, ponds, and reservoirs for both wildlife and farm use.
- Support Aquatic and Terrestrial Biodiversity: Riparian buffers enhance connectivity for animals and create climate-resilient farm corridors.
Comparative Benefits Table: Windbreaks, Shelterbelts, and Riparian Buffers
For a quick comparison, the table below summarizes how the three primary tree storm support systems differ in their environmental and agricultural impacts:
| System Type | Key Function | Estimated Soil Erosion Reduction (%) | Crop Yield Improvement (%) | Livestock Protection | Biodiversity Enhancement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windbreaks | Reduce wind speed; protect crops and soil | 30–50% | 5–20% | Medium | Medium–High |
| Shelterbelts | Shade and shelter for livestock & crops | 40–60% | 10–20% | High | High |
| Riparian Buffers | Protect waterways; filter runoff | 50–85% | 3–15% | Low–Medium | Very High |
Agroforestry Practices Benefits: Integrating Resilience
Integrating agroforestry practices—such as tree storm support systems, alley cropping, silvopasture, and forest farming—into your agricultural management offers multifaceted advantages. These agricultural systems harness the synergy between trees, crops, livestock, and the natural landscape, ensuring that farms are not only productive but also sustainable and resilient.
- Diversified Production: Timber, fruits, nuts, and forage from tree systems supplement farm income.
- Improve Farm Biodiversity: Mixed-species plantings create habitat mosaics, fostering diverse ecosystems and beneficial organisms.
- Enhance Soil Health: Deep-rooted trees improve soil structure, organic matter, and nutrient cycling, reducing erosion and minimizing input needs.
- Resilience to Weather Extremes: Alley cropping, silvopasture, and combinations of tree and livestock integration provide insurance against crop losses from storms, drought, and market volatility.
- Environmental Benefits: Agroforestry reduces the farm’s carbon footprint, enhances water quality, and protects wildlife corridors.
Silvopasture—integrating trees with livestock and pasture—is particularly beneficial. Trees offer shade and shelter for animals, reducing livestock stress and heat-related loss, while also producing timber and non-timber forest products. This combination enhances productivity and sustainability, especially on larger operations.
Effective Implementation and Management Strategies
Unlocking the full potential of tree storm support systems requires careful planning, implementation, and ongoing management. Here’s a step-by-step guide to ensuring your windbreaks, shelterbelts, and riparian buffers are effective and durable:
- Assessment & Design: Evaluate your farm’s weather patterns, soil type, topography, and existing vegetation before selecting system types and placement.
- Selecting Appropriate Species: Choose a combination of evergreen and deciduous trees and shrubs adapted to local conditions. Native species are ideal for ecosystem health and resilience.
- Strategic Planting Layout: Plan for row orientation, length, spacing, and density for optimal wind and storm protection.
- Proper Spacing: Maintain sufficient room for tree and shrub growth and airflow, enhancing system longevity and effectiveness.
- Ongoing Maintenance: Regularly prune, monitor for disease/pests, and irrigate newly established rows to ensure healthy vegetation.
- Longevity Planning: Replace failed or old trees, rotate species if necessary, and adapt the system as farm needs evolve.
How Farmonaut Empowers Storm Resilience & Sustainability
At Farmonaut, we are committed to making precision agriculture affordable and accessible worldwide. Our satellite-based app and API platform enables all farm types to easily monitor crop and tree health, optimize resource use, and adapt to climate and weather extremes. Here are ways our technologies complement tree storm support systems:
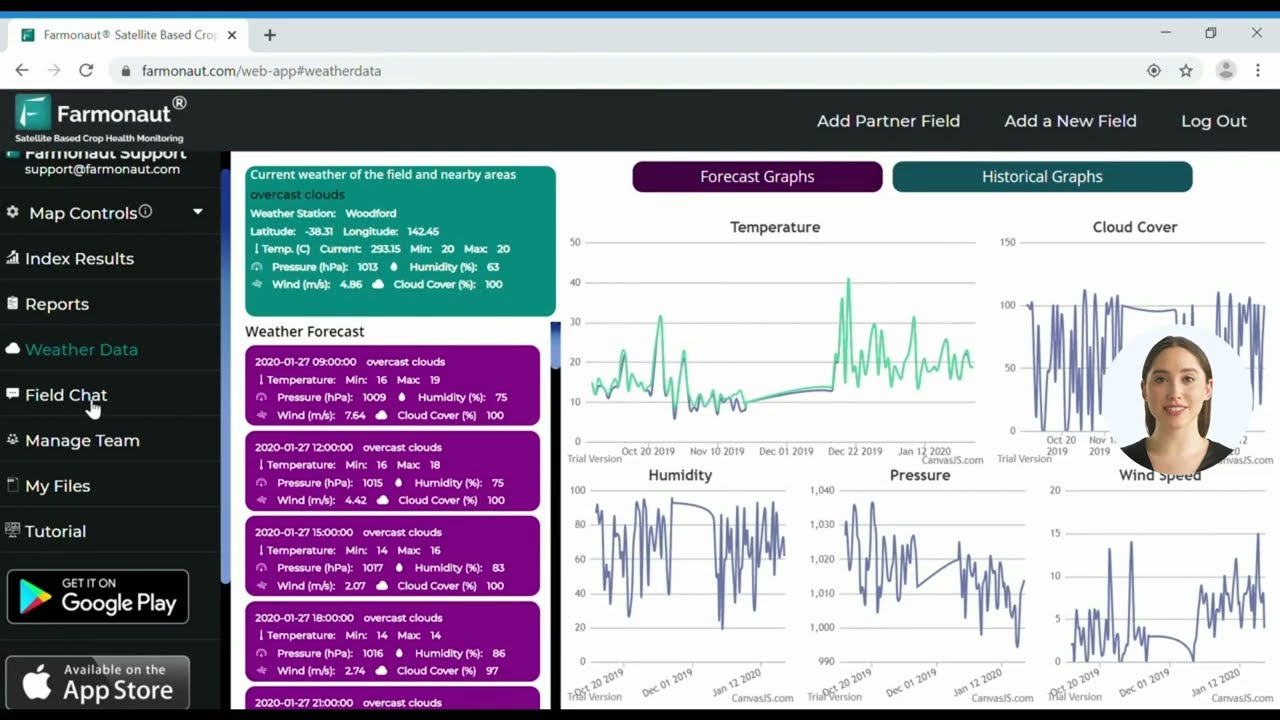
- Satellite-Based Crop & Tree Monitoring: Our NDVI maps and high-resolution imagery reveal vegetation health, soil moisture, and storm damage across windbreaks, shelterbelts, and riparian buffers.
- AI-powered Farm Advisory: The Jeevn AI system delivers weather forecasts, disease alerts, and custom strategies to improve yield and resilience for your tree storm support systems.
- Blockchain-based Traceability for Agroforestry Products: Increase trust and transparency for products derived from tree-based systems with Farmonaut Product Traceability.
- Fleet and Resource Management: Use our advanced tools to manage tractors, harvesters, irrigation equipment, and field logistics efficiently.
- Monitor and Reduce Environmental Impact: Our carbon footprinting solution helps farms align with sustainability and environmental targets.
- Insurance and Financing: Satellite-based field verification simplifies crop loan and insurance access, reducing risks and improving farm financial security.
- API Access for Developers and Agritechs: Seamlessly integrate our satellite & weather data API into custom systems, or explore developer documentation here.
By integrating innovative satellite and AI technologies with tree storm support systems, farmers can proactively plan, monitor, and optimize their agroforestry investments—with the added benefit of real-time, data-driven insights from anywhere.
Try Farmonaut’s tree and crop monitoring platform today for a resilient, sustainable farm future!
Tree Storm Support Systems in Action (Gallery & Videos)
Flexible, Affordable Precision Agriculture Subscriptions
Choose a Farmonaut plan that fits your crop, livestock, and agroforestry management needs. Improve your yields, sustainability, and profitability—powered by advanced satellite and AI technology!
Conclusion: Building Farm Resilience Amidst Increasingly Unpredictable Weather
Tree storm support systems—windbreaks, shelterbelts, and riparian buffers—form the backbone of climate-resilient, sustainable, and environmentally sound farming. These agroforestry practices deliver wide-ranging benefits: they reduce soil erosion, protect crops and livestock, filter water runoff, enhance biodiversity, and increase crop yields. Effective implementation and management of these systems not only safeguards farm profitability but also contributes to global conservation goals.
By integrating both traditional tree planting strategies and modern tools like Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring, AI advisory, and traceability services, today’s farmers are well-equipped to meet the dual challenges of production and environmental responsibility. Whether your goal is improving farm biodiversity, protecting crops from storms, or enhancing farm resilience to weather, strategic use of tree rows for wind protection, livestock shelter, and water buffers will remain instrumental in achieving lasting sustainability in agriculture and forestry.
FAQ – Tree Storm Support System Services
Windbreaks are linear plantings of trees/shrubs to reduce wind speed and erosion, shelterbelts are often wider with more rows to protect livestock and enhance habitat, and riparian buffers run along waterways to filter runoff and protect water quality.
Select native or locally adapted species (a mix of evergreens and deciduous). Assess your soil, climate, and exposure to determine the best combination for wind and weather protection.
Conduct annual inspections for disease, deadwood, and proper growth. Prune as needed, manage weeds, and replant where gaps occur to maintain full protection.
Yes. These systems reduce crop and livestock losses from storms, improve yields, offer marketable timber and non-timber products, and qualify for biodiversity and conservation incentives.
We provide satellite and AI-powered monitoring, crop health assessment, weather advisory, and resource management tools. Our platform helps with system planning, ongoing vegetation health tracking, and digital record-keeping for sustainability, traceability, and financial planning.
Yes. Many governments and organizations offer cost-share, grants, or payment for ecosystem services. Enhanced carbon sequestration and ecosystem conservation can qualify your farm for additional incentives. Farmonaut’s carbon monitoring supports these efforts.