Accurate Pest Control: 7 Shocking Eco Hacks for Crops

“Over 70% of global crops benefit from integrated pest management, reducing chemical pesticide use significantly.”
Table of Contents
- What is Accurate Pest Control?
- 1. Integrated Pest Management (IPM): A Holistic Approach
- 2. Biological Pest Control: Harnessing Nature’s Predators
- 3. Cultural Pest Control: Sustainable Farming Practices
- 4. Physical & Mechanical Pest Control: Direct Eco Methods
- 5. Targeted Chemical Pest Control: Smarter, Safer, Less
- 6. Precision Agriculture Pest Management: Tech Meets Eco
- 7. Push Pull Pest Management: Innovative Crop Companions
- Eco Hacks Comparison Table
- Farmonaut: Technology for Accurate Pest Control
- Sustainable Practices & Environmental Considerations
- FAQ: Accurate Pest Control Strategies
- Conclusion: Eco-Friendly Crop Protection for Our Future
What is Accurate Pest Control?
As we usher in a new era of agriculture, accurate pest control is emerging as a fundamental pillar of sustainable farming, forestry, and land stewardship. It’s no longer about blanket spraying of chemicals—today’s effective approach focuses on the precise identification, continuous monitoring, and strategic management of pest populations to minimize crop damage, reduce chemical and pesticide use, and protect our shared environment.
Instead of “spray-and-pray,” we now have an arsenal of eco-friendly methods, integrated strategies, and high-tech tools. This comprehensive guide will present seven shocking eco hacks designed to transform your perspective and upgrades your pest management game.
1. Integrated Pest Management (IPM): A Holistic Approach
When we talk about integrated pest management (IPM), we’re referring to a coordinated, multi-pronged approach that blends biological, cultural, physical, and chemical control methods into one unified system. The goal? To minimize the use of chemical pesticides, reduce their potential environmental impact, and achieve long-term sustainability for our crops and forests.
- Monitoring and Identification: We use regular field scouting, satellite mapping, and technologically advanced sensors to accurately identify pest species and assess their populations. Precise identification ensures that only the most necessary measures are deployed—no wasted resources or accidental harm to beneficial species.
- Threshold Levels: Our approach is not reactive but proactive—we only intervene when pest populations exceed action thresholds. This prevents unnecessary applications and fosters resilience.
- Multiple Control Methods: IPM encourages the combination of biological methods (like using natural predators), cultural practices (crop rotation), physical barriers, and—if necessary—chemical measures as a last resort.
The result? A coordinated methodology that protects both yields and biodiversity, placing ecological health, sustainability, and accurate pest management at the core of agricultural success.
2. Biological Pest Control: Harnessing Natural Predators
Biological pest control methods are rapidly gaining ground among producers looking for environmentally friendly pest control that treats both crops and ecosystems with care. This practice involves using natural enemies—predators, parasitoids, and pathogens—to keep pest populations in check. Examples include:
- Introducing ladybugs to feasts of aphids, or deploying predatory mites to vanquish spider mite outbreaks.
- Utilizing microbial agents like Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt), which produces proteins fatal to certain pest insects but harmless to most other life forms.
We must be careful to avoid invasive species introductions—always select local, compatible biological agents. When managed properly, these tools offer:
- Long-term pest suppression that minimizes pest resurgence
- Reduced reliance on chemicals and the promotion of natural biodiversity
- Cost-effectiveness over time, since natural predators often persist beyond a single season
Harnessing nature’s own defenders as part of an integrated pest management system is one of the top sustainable pest control hacks today.

3. Cultural Pest Control: Sustainable Farming Practices
Cultural pest control means altering our agricultural practices to create conditions less favorable for pests—in other words, outsmarting them through crop management. Here are the central techniques:
- Crop Rotation: By alternating plant families each season, we disrupt the life cycles of crop-specific pests and soil-borne pathogens, drastically reducing the buildup of pest populations.
- Use of Pest-Resistant Varieties: Selecting and planting crop varieties bred for resistance to certain insects, diseases, or nematodes offers built-in protection.
- Optimizing Planting/Harvesting Times: Sowing and harvesting at the right times helps avoid peak pest periods, minimizing the window of pest attack.
- Proper Spacing and Sanitation: Ensuring enough space between plants increases airflow, reduces moisture (discouraging diseases), and makes it harder for pests to spread. Removing infected plant debris prevents pest harborage.
When woven into an integrated approach, these methods dramatically reduce the pressure on crops and forests, lowering both damages and input costs.
“Precision agriculture can cut pesticide application by up to 50%, promoting healthier ecosystems and sustainable farming.”
4. Physical & Mechanical Pest Control: Direct Eco Methods
Physical and mechanical methods are all about direct intervention—physically keeping pests away or removing them from the environment. These eco hacks are a key part of organic agriculture and sustainable pest management worldwide. Common techniques include:
- Physical Barriers: Insect nets, row covers, and fine mesh screens keep out flying pests and larger invaders like birds or rabbits.
- Mechanical Traps: Devices such as pheromone traps, sticky boards, or pitfall traps catch pests without chemicals, helping with both population monitoring and control.
- Soil Solarization: Covering soil with plastic sheets during hot periods raises soil temperature, killing off many soil-borne pathogens, nematodes, and weed seeds (a highly effective non-pesticidal management option).
- Handpicking & Deep Plowing: For smaller-scale operations, physically removing pests or plowing to expose hidden pest life stages are tried-and-true eco techniques.
These practices are effective for localized infestations, greenhouses, and organic systems, minimizing environmental impact and chemical input.
5. Targeted Chemical Pest Control: Smarter, Safer, Less
Chemical control remains part of many pest management strategies, but our mission is to reduce pesticide use in farming through data-driven, targeted application. Here’s how we approach this responsibly:
- Only use when pest populations exceed economic threshold levels—avoiding unnecessary sprays.
- Choose pesticides with high selectivity and low persistence to protect beneficial species and reduce environmental contamination.
- Implement precision application—modern equipment allows targeted spraying only where needed, supported by data from remote sensing and scouting.
- Emphasize rotation of chemical classes to minimize resistance development in pest populations.
Whenever possible, we integrate this step with biological, cultural, and technological approaches to minimize negative environmental impacts and promote sustainable pest control.
Training and accurate dosing are critical. Modern digital guidance tools and easy-to-understand resources, like those available on the Farmonaut platform, play a key role in responsible pesticide management.
For those investing in crop traceability for safer market access and transparency, Farmonaut’s blockchain-based product traceability solution ensures every step, including pest management actions and chemical use, is securely recorded and verifiable through farm-to-market supply chains.
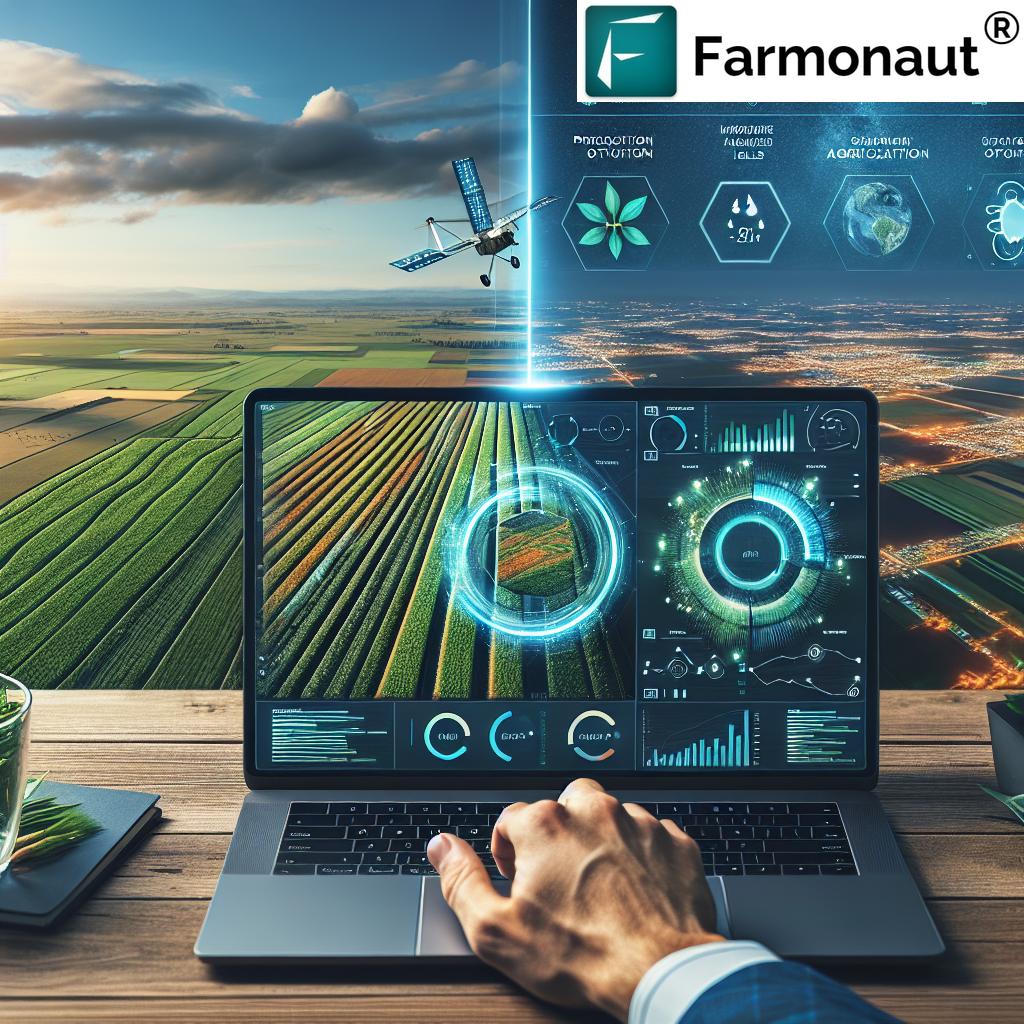
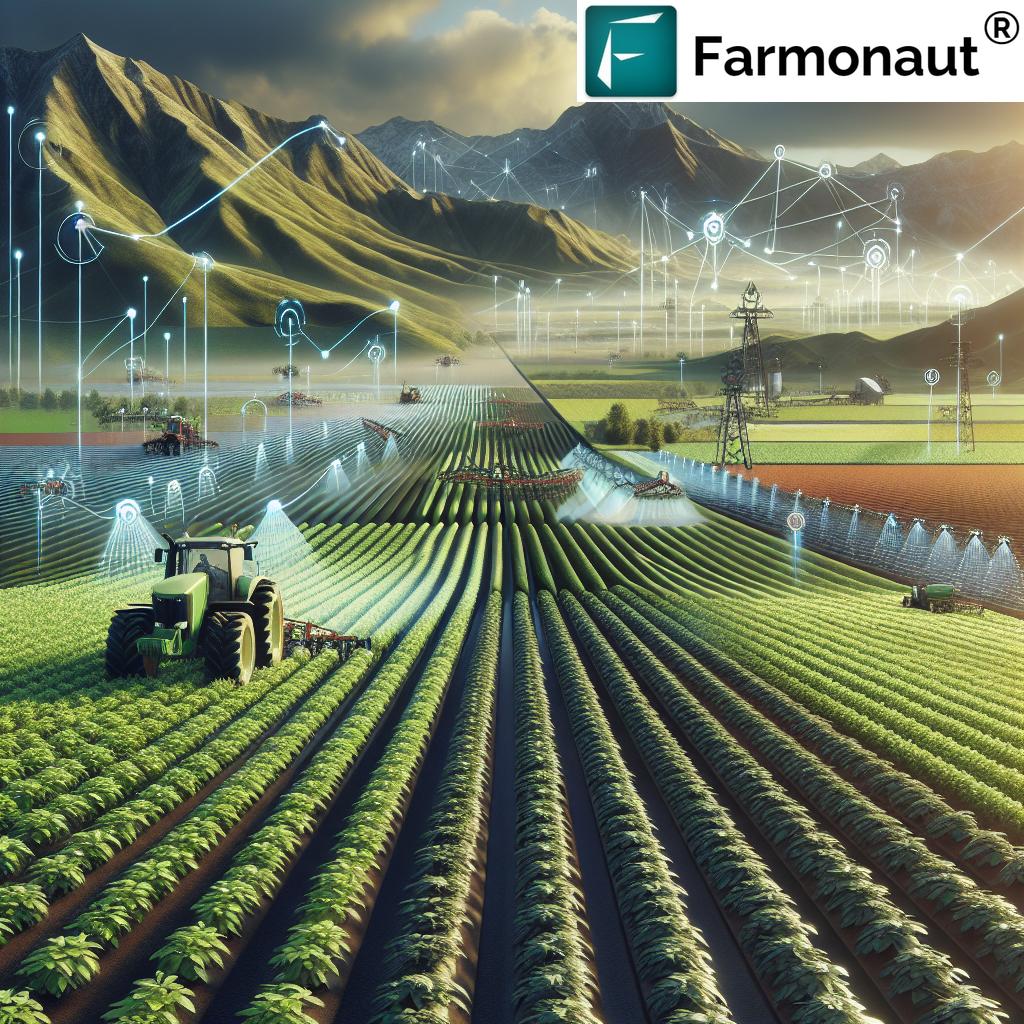
6. Precision Agriculture Pest Management: Tech Meets Eco
Precision agriculture pest management has ushered in a new era of farming, where technology and ecology work hand in hand to refine pest control. We now use an arsenal of high-tech tools to monitor pest populations, diagnose field health, and apply interventions only where truly needed. Major breakthroughs include:
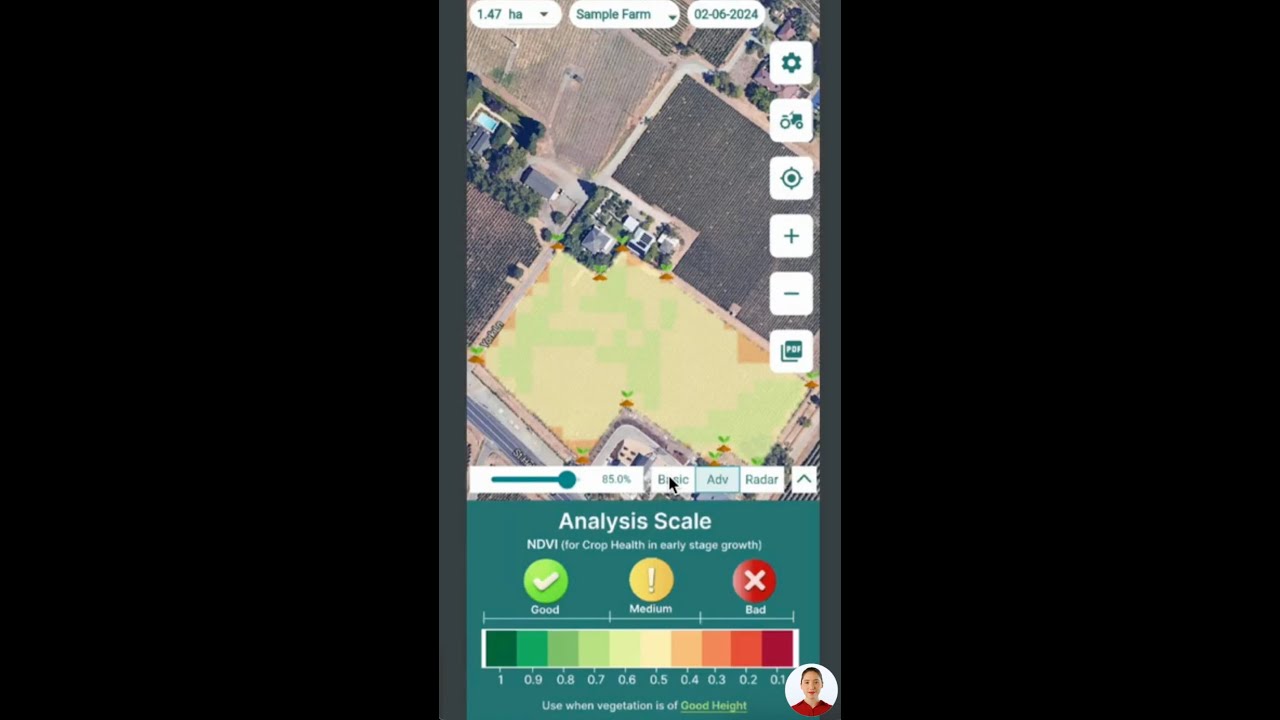
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Platforms like Farmonaut deliver high-resolution, multispectral satellite imagery. This enables us to detect stressed crop areas that may indicate pest or disease infestations quickly and accurately—providing vital, early-warning insights.
- Remote Sensing & Drones: Drones equipped with cameras and sensors can scan large farms in minutes, identifying patches of pests or disease hotspots invisible to the naked eye. This leads to more precise scouting and targeted action.
- IoT Sensors & AI-driven Monitoring: Internet-of-Things sensors are embedded in the field to monitor real-time soil moisture, temperature, and microclimate—all factors for pest development. Advanced platforms like Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI Advisory System turn this data into actionable pest management advice.
- Machine Learning for Outbreak Prediction: By analyzing trends from past satellite and on-ground data, AI-powered analytics predict outbreaks so farmers can intervene before populations explode.
Embracing precision agriculture pest management means fewer pesticides, lower costs, and better crop protection—while actively promoting the health of ecosystems and biodiversity.
Ready to make the leap to high-tech, eco-friendly farming? Try the Farmonaut App or leverage Farmonaut’s API and Developer Docs to integrate satellite & weather data into your own agri systems.
7. Push Pull Pest Management: Innovative Crop Companions
The push-pull strategy is one of the most remarkable examples of eco hack ingenuity in sustainable pest control. This method uses a multi-layered system of companion plants to both repel (“push”) and attract (“pull”) pests away from main crops like maize:
- “Push” Plants: Species like Desmodium are interplanted among maize rows. Desmodium releases volatile compounds that repel key maize pests (notably stem borers) and disrupt pest host-finding behavior.
- “Pull” or “Trap” Plants: The field’s edge is planted with Napier grass or other enticing species. These draw pests away from the crop, where they are trapped and cannot reproduce.
- Bonus Benefits: Some push plants also fix nitrogen in the soil, suppress weeds, and increase biodiversity, all while minimizing pesticide use and increasing yield in maize and other cereals.
This is an outstanding environmentally friendly pest control system—simple, elegant, and scalable worldwide.
Eco Hacks Comparison Table: Accurate Pest Control Methods
| Eco Hack/Technique | How It Works | Est. Effectiveness (% Reduction in Pests) | Environmental Impact | Est. Cost ($/acre) | Additional Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biological Pest Release | Introduce natural predators (e.g., ladybugs, parasitoids, Bt bacteria) to target pests | 60-80% | Low | 40–100 | Long-term regulation, boosts biodiversity |
| Companion Planting (Push-Pull) | Use repellent and trap crops (e.g., Desmodium & Napier grass with maize) | 75–90% | Low | 25–80 | Improved soil, weed suppression, higher yields |
| Cultural Practices | Crop rotation, resistant varieties, timing, spacing | 35–65% | Low | 5–30 | Enhances soil health, reduces disease risk |
| Physical & Mechanical | Nets, traps, hand removal, solarization | 50–70% | Low | 10–50 | No chemical residues, compatible with organic |
| Precision Agriculture (Remote Sensing/Drones) | Use satellite data, drones, AI, and IoT sensors for targeted detection/intervention | Up to 85% | Low–Medium | 20–120 (tech access dependent) | Resource efficiency, preemptive action, data for advisories |
| Targeted Chemical Application | Responsible, data-driven pesticide use only above thresholds | 60–95% | Medium–High | 30–130 (depends on input) | Prevents resistance, protects beneficials |
| Non-Pesticidal Management | Neem oil, trap crops, field sanitation, local solutions | 25–55% | Low | 5–40 | Restores ecosystem balance |
Farmonaut: Technology for Accurate Pest Control
At Farmonaut, we are dedicated to making precision agriculture affordable and accessible to farmers globally. Our suite of advanced solutions supports all pillars of accurate pest control by aligning high-tech data with traditional practices. Here’s how our system empowers your sustainable pest management framework:
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Access detailed NDVI imagery, soil moisture insights, and crop health trends in real time to identify early warning signs, pinpoint pest outbreaks, and target interventions before large-scale damage occurs.
- Jeevn AI Advisory System: Our AI-powered advisor provides personalized, real-time recommendations on when and how to act against pest threats, based on a fusion of satellite imagery, climate data, and agricultural best practices.
- Blockchain-Based Product Traceability: Transparency and compliance are vital in today’s food systems. Our blockchain traceability suite can record pest management activities, giving you and your buyers greater peace of mind.
- Fleet and Resource Management: Our fleet management tools help track equipment and schedule maintenance, reducing downtime during critical pest control windows.
- Carbon Footprinting: Track and minimize your environmental impact as you optimize resource use—including chemicals—throughout your operations.
- Access to Financing: Satellite-verified field data from Farmonaut supports easier, faster approvals for crop loans and insurance coverage, crucial for risk mitigation in modern pest management.
Try Farmonaut today—on Android, iOS, or Web—and join the agricultural revolution.
Sustainable Practices & Environmental Considerations
The cornerstone of every strong pest management program is a genuine commitment to environmental responsibility. Here’s what we recommend:
- Regularly conduct environmental impact assessments before deploying any control measures. Ensure benefits outweigh potential ecosystem risks, and always prioritize long-term soil and water health.
- Provide continuous training in responsible pesticide handling and application to reduce risks to applicators, communities, and wildlife.
- Promote field sanitation, buffer strips, and conservation biocontrol—simple design tweaks that can make your farm or forestry project more resilient to pest outbreaks while fostering beneficial species.
- Integrate carbon footprint tracking into your management routines using tools like Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting platform to monitor and continually reduce environmental impact.
Responsible pest management is not an isolated practice, but an ongoing journey of education, monitoring, collaboration, and adaptation.
Subscribe to Farmonaut’s Precision Agriculture Platform
Choose a subscription package—fitting for all scales: from individual farmers and cooperatives to large agribusinesses. Enjoy real-time crop monitoring, AI advisories, traceability, and more—no expensive hardware, just advanced satellite technology.
FAQ: Accurate Pest Control Strategies
What are the main benefits of integrated pest management (IPM)?
- Combines multiple eco-friendly pest control practices for sustainable pest management
- Reduces chemical and pesticide use, lowers environmental impact, and promotes biodiversity
- Emphasizes monitoring and accurate identification, only intervening when truly needed
How do precision agriculture technologies reduce pesticide use?
- Pinpoint areas of pest infestation and crop stress, minimizing unnecessary blanket spraying
- Allow for preemptive, localized interventions—cutting overall pesticide application, saving resources
- Provide data-driven, AI-based advisories for smarter pest control decision-making
What is push-pull pest management and where is it useful?
- A strategy using “push” (repellent) and “pull” (trap) crops around fields—especially maize
- Reduces the need for chemicals and supports natural pest regulation, boosting yields
- Widely adopted in Africa, Asia, and increasingly around the world for staple crops
How can farmers access Farmonaut’s pest management technologies?
- Through the web, Android, or iOS apps
- Integrate Farmonaut data with existing systems via API and developer documentation
- Choose a flexible subscription plan—see above for options!
Why is minimizing chemical pesticide use important?
- Prevents environmental pollution of soil, water, and air
- Protects beneficial insects (like pollinators and natural pest predators)
- Avoids pesticide residues in food, supporting safer supply chains
- Minimizes risk of pests developing resistance to chemicals
How do satellite data and AI help with pest identification and monitoring?
- Provide wide-area, real-time monitoring of crop health, quickly flagging stress signals
- Support earlier, more accurate pest and disease diagnosis—even in inaccessible terrain
- Foster data-driven interventions and continuous improvement in farm management
Conclusion: Eco-Friendly Crop Protection for Our Future
Accurate pest control is the backbone of modern sustainable agriculture. By integrating biological, cultural, mechanical, and targeted chemical approaches—with the added power of precision agriculture and digital technology—we can effectively manage pest populations while protecting our crops, forests, and environment for generations to come.
Now is the time to embrace holistic, sustainable pest control. From deploying ladybugs to leveraging satellite monitoring via Farmonaut’s platforms, every farm—small or large—can access cutting-edge tools for accurate identification, monitoring, and eco-friendly interventions. This ensures healthier ecosystems, more productive fields, and a thriving agricultural future.
Ready to make your farm more resilient, profitable, and sustainable?
Visit Farmonaut’s Crop Plantation and Forest Advisory page to get personalized recommendations for your fields or forests.
Let’s unite for a world where accurate pest control powers sustainable abundance and environmental harmony!