Aphids, Flies, Blossom Rot on Squash & Eggplant Guide: Sustainable Precision Management for 2025
Summary: Managing Pest and Disease Challenges in Squash and Eggplant Cultivation: Focus on Aphids, Flies, and Blossom End Rot
In 2025, the sustainable and efficient cultivation of vegetables like squash and eggplant is crucial for agricultural productivity and food security worldwide. However, these crops face persistent challenges from pests such as aphids and flies, along with physiological disorders like blossom end rot, which can significantly reduce yield and quality.
Integrated, sustainable, and precision management strategies are now more essential than ever for farmers aiming to maintain healthy crops and achieve optimal harvests. This guide delivers up-to-date advice on managing aphids on squash plants, flies on squash plants, and blossom end rot on squash in the context of modern, data-driven agriculture.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Persistent Challenges: Aphids, Flies, and Blossom Rot
- Aphids on Squash & Eggplant Plants: Identification, Impact, and Management
- Managing Flies on Squash Plants: Threats, Control, and Monitoring
- Blossom End Rot on Squash: Causes, Symptoms, and Solutions
- Pest and Disease Impact and Management Strategies Comparison Table
- 2025 and Beyond: Precision Agriculture Tools and Sustainable Practices
- How Farmonaut Empowers Modern Farmers
- Frequently Asked Questions: Squash, Eggplant, and Precision Pest Management
- Conclusion: Your Path to Healthy, Productive Crops
Understanding Persistent Challenges: Aphids, Flies, and Blossom Rot in Squash & Eggplant Cultivation
Cultivation of vegetables like squash and eggplant remains at the heart of agricultural productivity, especially as sustainable practices evolve alongside global food security needs.
However, these vital crops face persistent challenges:
- Aphids on squash plants and aphids on eggplant plants — which cause severe damage and transmit disease
- Flies on squash plants — such as fruit flies and leaf miner varieties — rapidly reduce yield through feeding and oviposition
- Blossom end rot on squash — a physiological disorder that develops due to calcium deficiency and irregular moisture, affecting fruit development and overall quality
These issues significantly affect growth, health, and yield of plants. On the path to optimal harvests and resilient food systems, managing such pests and disorders remains a pressing priority for farmers everywhere in 2025 and beyond.
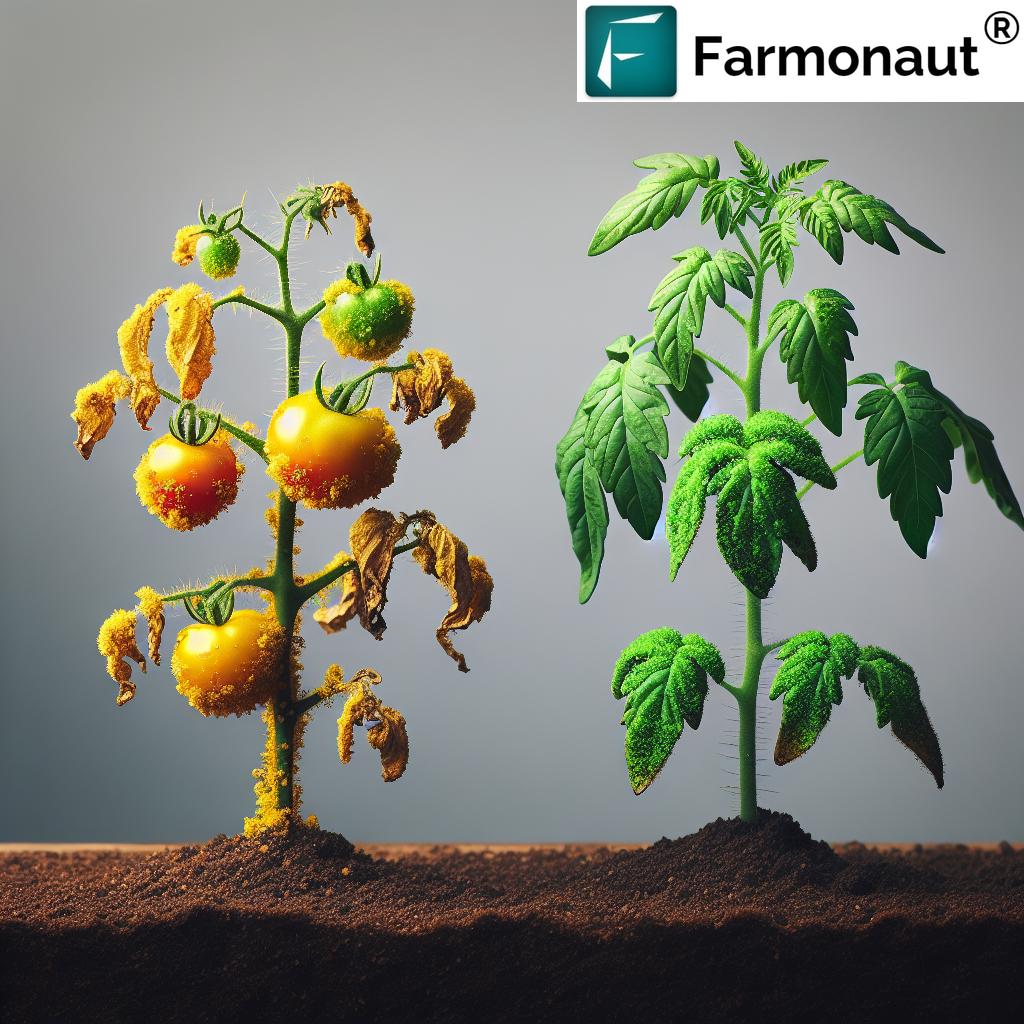
Aphids on Squash & Eggplant Plants: Identification, Impact, and Management
Aphids are notorious as pests in both squash and eggplant cultivation, often identified by their
small, pear-shaped bodies clustering on the undersides of leaves, shoots, and tender growth tips.
How Aphids on Squash Plants and Eggplant Plants Cause Damage
- Direct Feeding: Sap-sucking damages leaves and young stems, resulting in distorted foliage, stunted
growth, and decreased photosynthesis. - Honeydew Production: Aphids excrete honeydew, which fosters sooty mold on leaves,
further hindering plant health. - Vector for Viruses: Aphids can act as vectors, transmitting numerous plant viruses and
amplifying overall crop impact.
Symptoms of Aphid Infestation
- Sticky, shiny residue (honeydew) on leaves and stems
- Blackened patches from sooty mold
- Yellowing, curling, or deformation of leaves
- Poor growth and stunted plants
- Reduced or malformed fruits
Aphids on squash plants and aphids on eggplant plants remain a year-round challenge, but modern integrated pest management (IPM) practices grounded in sustainability and precision remain the cornerstone for controlling populations effectively.
Integrated Strategies for Managing Aphids (2025 & Beyond)
-
Biological Control:
- Introduce or conserve beneficial insects:
- Lady beetles (Coccinellidae) — voracious aphid predators
- Lacewings (Chrysopidae) — their larvae aggressively control aphid populations
- Parasitic wasps — lay eggs within aphid bodies, reducing numbers naturally
- Introduce or conserve beneficial insects:
-
Cultural Practices:
- Implement crop rotation to disrupt aphid life cycles
- Remove and destroy infested debris post-harvest to reduce overwintering populations
- Intercrop with repellent plants (e.g., marigolds, nasturtium) to deter colonization
-
Targeted Chemical Controls (Last Resort):
- Apply environmentally safe insecticides like neem oil or insecticidal soaps at early infestations to mitigate damage while minimizing harm to pollinators and beneficial organisms
-
Precision Monitoring and Timely Decisions:
- Deploy satellite-based monitoring and AI advisory solutions for real-time hotspot detection
Farmonaut’s platform enables advanced large-scale farm management—track aphid pressures, evaluate growth and plant health using NDVI and AI-generated advice (Try it on App). - Pest monitoring traps provide early warning and informed intervention.
- Deploy satellite-based monitoring and AI advisory solutions for real-time hotspot detection
Combined, these methods reduce dependence on harsh inputs, minimize environmental impact, and support sustainable yield improvements for squash & eggplant cultivation well into 2025.
Why Early Aphid Detection and Sustainable Management Matter in 2025
Aphid populations can multiply rapidly, especially under favorable climatic and field conditions. Delayed action risks exponential damage—from loss of leaf photosynthetic capacity to widespread viral disease outbreaks.
- Without integrated pest management, aphids on squash plants and aphids on eggplant plants can slash yield by 30% or more.
- Sustainable approaches not only protect beneficial insects but align with stricter regulatory and consumer expectations for eco-friendly produce in 2025.
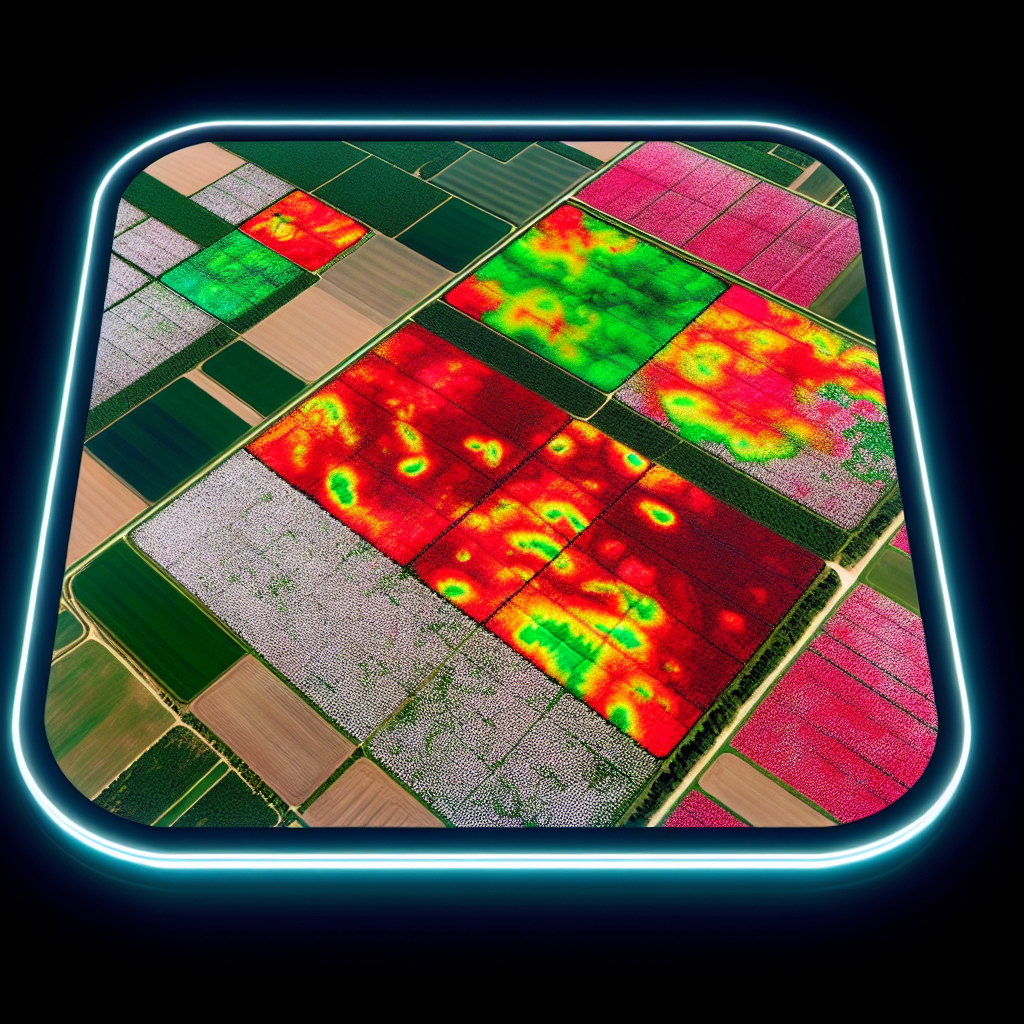
Farmonaut’s Role: Leveraging Satellite and AI for Aphid Monitoring
We at Farmonaut provide satellite-based crop health monitoring. Our platform uses advanced remote sensing and AI analytics
to deliver precise aphid risk mapping, enabling farmers to deploy interventions where they matter most.
For developers, our open API and developer documentation allow seamless integration of
these insights into farm management systems, dramatically reducing scouting time and inputs.
Managing Flies on Squash Plants: Threats, Precision Control, and Monitoring
Flies on squash plants represent diverse threats—predominantly fruit flies (Tephritidae) and leaf miner flies.
Their persistent presence in 2025 necessitates adaptive, sustainability-focused management for lasting food security.
Primary Fly Species & How They Cause Damage
-
Fruit Flies:
- Female flies insert eggs inside fruits, where larvae feed—causing internal rotting and making squash unmarketable
- Yield losses can exceed 20%
-
Leaf Miner Flies:
- Larvae tunnel between the upper and lower leaf surfaces, appearing as meandering white tracks or blotches.
- Infestation leads to reduced photosynthetic area, leaf drop, and stunted plant growth
Integrated Management of Flies on Squash: From Field Sanitation to Modern Traps
-
Sanitation:
- Remove affected fruits and leaves immediately—a crucial first step in breaking pest life cycles and reducing populations
- Dispose of plant debris away from production fields
-
Monitoring & Trapping:
- Set up bait traps and pheromone traps—these tools help in early fly identification and population suppression.
- Record data from traps and combine with visual scouting for integrated pest management
-
Biological Control:
- Encourage natural fly predators such as certain parasitic wasps, birds, and spiders into managed fields
-
Sterile Insect Technique (SIT):
- Release of sterile flies—an emerging precision agriculture approach, especially in regions with persistent fruit fly issues
-
Precision Inputs Application:
- Targeted sprays (when absolutely necessary): Always select biodegradable, safe insecticides (e.g., Spinosad) to mitigate fly populations with minimal risk to beneficial insects and the environment
How Satellite Technology and Data Analytics Enhance Fly Management in 2025
Remote sensing and digital crop monitoring tools now enable farmers to:
- Spot stress patterns caused by flies on squash plants (wilting or yellowing due to internal damage or leaf mining)
- Pinpoint hotspots for precision deployment of traps, sprays, or biological controls
- Optimize resource allocation for maximum efficiency, cost savings, and sustainability
We at Farmonaut offer large-scale field management solutions,
where satellite imagery and AI analytics help farmers make timely, data-driven control decisions for pests
like flies and aphids.
Blossom End Rot on Squash: Causes, Symptoms, and Sustainable Solutions
Blossom end rot on squash, also referred to as BER, is a physiological disorder—not an infectious disease—that affects
fruits at their critical development stage.
What Is BER, and Why Does It Happen?
- Cause: Disruption in calcium uptake and distribution within the fruit, often worsened by inconsistent irrigation and rapid plant growth
- Exacerbated by fluctuations in moisture, excess nitrogen inputs, or root injury
- Affects eggplant as well as various squash, including zucchini, acorn, and pumpkin
Symptoms: How to Spot Blossom Rot Squash and Eggplant
- Water-soaked, pale, or brown lesions at the blossom end of developing fruits
- Lesions expand, darken, and turn black and leathery
- Fruits become unmarketable and may be susceptible to secondary infections
Sustainable, Precision Approaches to BER Management in 2025
-
Maintain Consistent Moisture:
- Use drip irrigation systems for uniform watering. This prevents abrupt soil drying or waterlogging—key triggers for BER.
- Employ soil moisture monitoring tools—Farmonaut’s remote sensing app provides real-time soil status to refine irrigation scheduling.
-
Soil and Nutrition Management:
- Test and adjust soil pH (ideal: 6.2–6.8) for optimal calcium availability.
- Apply foliar calcium sprays where required—guided by periodic nutrient analysis.
- Rein in excessive nitrogen or potassium fertilizers, as these can disrupt calcium uptake.
-
Mulching and Root Health:
- Mulch around the base of plants with straw or compost—this stabilizes moisture and temperature in the root zone.
-
Select Resistant Varieties:
- Use squash and eggplant cultivars less prone to BER when available.
-
Plant Spacing and Airflow:
- Allow adequate spacing for improved air circulation, supporting healthy development.
Key Takeaway: Unlike insect pest outbreaks, managing blossom rot squash is about maintaining steady plant and soil health—changing weather patterns in 2025 make constant monitoring and adaptation essential.
For a detailed understanding of physiological nutrient disorders—including blossom end rot—see the above video on magnesium deficits and their management.
For virus-related challenges linked to aphids, watch the above on integrative virus management in cucurbits.
Pest and Disease Impact and Management Strategies Comparison Table
| Problem | Symptoms | Estimated Yield Loss (%) if unmanaged | Recommended Sustainable Control Methods | Precision Agriculture Approaches | Environmental Impact | Estimated Treatment Cost ($/acre) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aphids (Squash & Eggplant) | Stunted growth, curled/distorted leaves, sticky honeydew, black sooty mold, reduced yield, virus transmission | Up to 30% | Biological agents (lady beetles, lacewings, parasitic wasps), crop rotation, repellent plants, neem oil, insecticidal soaps, remove infested debris | Satellite-based aphid risk mapping, AI advisory, trap data integration, targeted pesticide application | Low | $12-55 |
| Flies (Fruit & Leaf Miner Flies) | Internal fruit rot, tunneling in leaf tissue, leaf yellowing, premature fruit drop, visible larvae | 10-25% | Field sanitation, bait/pheromone traps, biological controls, SIT, targeted low-impact insecticides | Stress-spotting with satellite imagery, precision trap placement, resource optimization | Moderate | $15-70 |
| Blossom End Rot (BER) | Dark, water-soaked lesions at blossom end, fruit rot, poor quality and market value | 10-50% (in severe cases, especially in calcium-deficient soils) | Drip irrigation, consistent watering, calcium inputs, mulching, cultivar selection, soil monitoring | Soil moisture & calcium status via remote sensing, AI-recommended irrigation scheduling | Low | $10-35 |
2025 and Beyond: Precision Monitoring, Inputs, and Digital Solutions
Precision agriculture technologies are redefining pest, disease, and disorder management in squash and eggplant cultivation for 2025.
- Satellite-based plant health monitoring—Pinpoints crop stress signatures correlating to aphids, flies, and blossom end rot
-
Remote sensing of soil moisture and nutrient imbalances—Facilitates targeted irrigation, calcium, and fertilizer deployment
Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting tool can assess the sustainability of your practices in real time, reducing input waste and environmental impact. - IoT-enabled traps and field sensors—Deliver instant, location-specific data on fly and aphid population spikes
- AI-driven farm advisory—Analyzes historical and current data to recommend integrated, cost-effective strategies
- Blockchain-based traceability—Consumers demand verifiable, residue-free produce; on-farm data capture builds food security and trust.
- Satellite-based crop verification—Expedites loan/insurance access for farmers based on real-time, tamper-proof records.
These next-gen solutions empower sustainable, resilient, and profitable vegetable production in the digital age.
Access the Farmonaut Platform
How Farmonaut Empowers Modern Pest & Disease Management
We at Farmonaut offer a comprehensive suite of satellite-driven solutions for farmers, businesses, governments, and institutions focused on squash, eggplant, and other vegetable cultivation challenges in 2025 and beyond.
-
Real-Time Satellite Crop Health Monitoring: Detect aphid, fly, and physiological stress hotspots using NDVI, soil moisture,
and AI-flagged alerts on our app or via API. - AI-Based Advisory and Decision Support: Our Jeevn AI system interprets satellite data and weather forecasts to provide tailored, actionable pest/disease advice, maximizing yield with minimal waste.
- Resource Optimization: Field- and zone-level insights reduce unneeded pesticide/fertilizer inputs and save on resource costs.
- Environmental Tracking: Track your carbon and water footprint for sustainability reporting using our carbon footprinting tool.
- Blockchain Traceability: Provenance and transparency for every squash or eggplant harvest (learn more).
- Financial Access Integration: Crop verification for loans & insurance, reducing paperwork and enabling rapid, secure payouts.
- Fleet and Input Management: Optimize farm machinery deployment and agrochemical delivery (more on fleet management here).
Frequently Asked Questions: Squash, Eggplant, and Precision Pest Management
Q1. What are the first signs of aphid infestation on squash and eggplant?
Aphids on squash plants and eggplant typically present as small green, yellow, or black insects clustering on new growth. Early signs include sticky honeydew, distorted or curled leaves, and visible sooty mold. Regular scouting, especially on the underside of leaves, is crucial.
Q2. Which natural enemies help control aphids?
Biological control agents such as lady beetles (Coccinellidae), lacewings (Chrysopidae), and various parasitic wasps are highly effective at reducing aphid populations naturally.
Q3. How can I monitor and manage flies on squash without heavy pesticide use?
Use a combination of sanitation (removing and destroying infested fruits/leaves), bait/pheromone traps, promoting beneficial predators, and, as a last resort, targeted applications of safe, biodegradable insecticides.
Q4. What causes blossom end rot on squash and eggplant, and how can I prevent it?
Blossom end rot is caused by calcium deficiency and irregular soil moisture. Prevent it with consistent drip irrigation, mulching, balanced fertilization, and timely calcium supplementation. Remote soil health monitoring (such as via satellite data) further helps intervene before losses mount.
Q5. What does Farmonaut offer for improving pest and disorder management in squash and eggplant cultivation?
We deliver real-time, satellite-enabled monitoring, AI-based pest risk analytics, precision irrigation insights, blockchain traceability, and resource optimization tools. These help farmers intervene earlier, reduce losses, and boost sustainability without unnecessary inputs.
Q6. Does Farmonaut support Android and iOS app access for field management?
Absolutely. Download our Android app here or our iOS app here.
Conclusion: Your Path to Healthier, Higher-Yielding Crops in 2025
The ongoing battle against aphids on squash plants, flies on squash plants, and blossom end rot on squash demands nothing less than a combination of
integrated, sustainable, and precision agriculture strategies. With robust monitoring, tailored interventions, and scalable digital tools, modern farmers are better equipped than ever
to tackle these challenges—maintaining crop health, food security, and yield resilience.
We at Farmonaut are dedicated to empowering cultivated crop protection for 2025 and beyond, ensuring that data, transparency, and
sustainability are accessible to all. Harness these advances and be proactive: Spot, act, and thrive with precision, eco-friendly management this season.
Don’t miss out—access Farmonaut’s satellite tools here, integrate our API endpoints for your digital platforms, or monitor your farm’s carbon footprint to meet tomorrow’s standards, today.