What Is InSAR & Its Role in Ground Investigations
- Overview & Introduction
- Understanding InSAR Technology
- InSAR vs. Traditional Ground Monitoring: Comparison Table
- Application of InSAR in Agriculture
- Application of InSAR in Forestry
- Why InSAR is Essential for Ground Investigations in 2025
- Farmonaut’s Role in Enabling InSAR-Based Ground Investigations
- The Future of InSAR Technology in Agriculture & Forestry
- FAQ: What Is InSAR and Why It’s Essential for Ground Investigations
- Conclusion
- Farmonaut Subscription Plans
What Is InSAR and Why It’s Essential for Ground Investigations in 2025?
What Is InSAR and Why It’s Essential for Ground Investigations, especially in agriculture and forestry, is a question that has become increasingly relevant as we move into 2025 and beyond.
Increased pressure on land resources due to growing populations, climate change, and intensive agricultural and forestry practices have heightened the global demand for accurate, timely information about soil and ground conditions. These challenges spark a new era of smart, sustainable management, where advanced technology is not a luxury – but a necessity.
Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) has emerged as a transformative, crucial remote sensing technique for continuous monitoring of soil, ground, and land movements across vast areas—regardless of weather or lighting conditions. InSAR has proven exceptionally valuable for ground investigations, offering millimeter-to-centimeter precision in mapping deformation and subtle ground changes.
In agriculture and forestry, the need for rapid, precise insights into ground movement, soil health, and surface stability has never been higher. InSAR is revolutionizing the way we detect, analyze, and mitigate risks such as subsidence, landslides, soil compaction, and waterlogging. This technology is enabling stakeholders to make faster, more informed decisions for sustainable, long-term resource management and environmental protection.
Understanding InSAR Technology for Ground Investigations
Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) combines the power of radar imaging and advanced data analysis to observe, detect, and monitor subtle surface deformations over large areas with remarkable precision.
How Does InSAR Work?
The InSAR method involves comparing two or more SAR images (synthetic aperture radar) of the same area taken at different times by satellites or airborne platforms. By analyzing the phase difference between radar signals returned from the ground’s surface, InSAR is able to map changes and deformations—often due to factors like subsidence, soil compaction, root growth, and human activities such as mining or land development.
Key Process Steps:
- Satellite SAR Image Acquisition: Satellites or aircraft repeatedly image the same ground area using radar. Popular SAR satellites include Sentinel-1, TerraSAR-X, and RADARSAT-2.
- Phase Difference Analysis: Each radar signal has a ‘phase’—the shift between two images reveals surface movement as small as 1 millimeter.
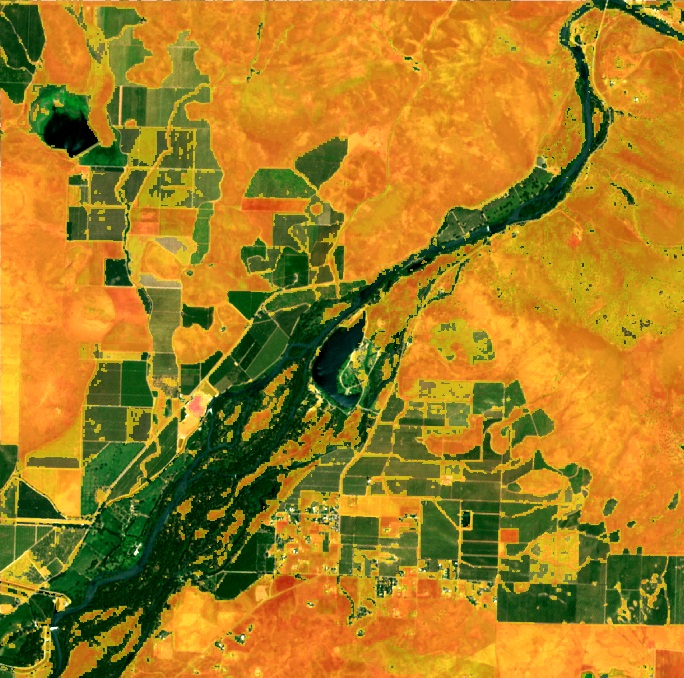
- Deformation Mapping: Processing software creates detailed color-coded maps (called interferograms), displaying variations in ground height and displacement.
Unlike optical sensors, synthetic aperture radar can penetrate clouds, function at night, and is unaffected by weather—making InSAR reliable for continuous, timely monitoring even in challenging conditions.
Benefits of InSAR for Agriculture and Forestry
- High Precision: Detects micro-level ground movement (millimeter to centimeter scale).
- Wide Area Coverage: Monitors thousands of square kilometers in a single pass.
- No Field Deployment Required: Minimal or no need for on-ground installations, reducing costs and logistical barriers.
- Continuous, Frequent Monitoring: Data can be revisited as frequently as every 6–12 days, or even daily with some satellite constellations.
- Reliable in All Weather: SAR signals penetrate clouds and operate 24/7, ideal for rounds-the-clock insights.
- Integrates with Other Data: Seamlessly fuses with crop health indices (NDVI), weather, and ground truth measurements.
What Is InSAR and Why It’s Essential for Ground Investigations: InSAR stands at the intersection of technological innovation and sustainability, giving stakeholders an unrivaled advantage in monitoring, detecting, and managing the health and stability of the Earth’s land surface.
Key Terms Explained:
- Subsidence: The gradual caving in or sinking of an area of land, often due to groundwater withdrawal or mining.
- Compaction: Soil becoming denser due to pressure (e.g., heavy machinery), impacting root growth and water infiltration.
- Landslides: Rapid movement of soil, earth, or rock down a slope, usually triggered by rainfall, earthquakes, or human activity.
InSAR vs. Traditional Ground Monitoring in Agriculture & Forestry: Comparison Table
| Parameter | InSAR Technology | Traditional Ground Monitoring | Estimated Improvement with InSAR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy of Measurements | Millimeter to centimeter precision in soil/ground movement | Centimeter to meter accuracy (dependent on instrument type) | Up to 100x improved sensitivity (1 mm vs. 10+ cm) |
| Area Coverage (sq. km) | Up to 10,000+ km² per acquisition | Limited to small plots (1–20 ha typical) | Vastly expanded ability—monitor entire regions |
| Monitoring Frequency | 6–12 days (can reach daily with some satellites) | Sporadic, manual (monthly/seasonal visits) | Near real-time tracking; earlier detection of risks |
| Cost Efficiency (Estimated % Savings) | High—remote, no field equipment needed | Costly—equipment, labor, travel intensive | Up to 75% cost savings in large-scale projects |
| Application Examples |
|
|
More applications, greater spatial and temporal detail |
The Application of InSAR in Agriculture
Agriculture is at the frontline of land use intensity, where understanding and adapting to soil and ground movement are crucial for crop productivity and sustainable resource management.
How InSAR Empowers Farmers and Agronomists
-
Monitoring Soil Moisture & Subsidence:
InSAR’s radar signals are affected by variations in soil moisture; this enables us to infer changes in content and detect subsidence—helping to prevent damage from uneven terrain and waterlogging risks. -
Detecting Land Deformation from Irrigation Practices:
Intensive groundwater extraction for irrigation can cause soil subsidence—reducing ground stability and threatening crop yields. InSAR data supports better water resource management to protect arable land from degradation. -
Assessing Root Zone & Soil Compaction:
Heavy machinery use can compact soil, reducing infiltration and harming root growth. InSAR detects areas of compaction, enabling farmers to optimize tillage and remediation interventions. -
Supporting Precision Farming:
Integrated InSAR maps inform site-specific management—optimizing inputs such as fertilizer and water, reducing waste, and boosting production.
Examples of InSAR Monitoring in Agriculture:
- Early Detection of Waterlogging: Subtle surface movement due to excessive moisture can be mapped, enabling farmers to improve field drainage and prevent crop loss.
- Tracking Soil Compaction: InSAR enables precision identification of compacted zones, so measures can be taken proactively.
- Assessing Land Degradation: Continuous monitoring identifies patterns of degradation—like salinization, subsidence, and erosion—essential for soil health in 2025.
In 2025, InSAR technology is an essential foundation for sustainable, scalable, and data-driven agricultural practices. Its ability to offer continuous monitoring, early intervention, and risk mitigation makes it invaluable for farm management.
The API Route for Developers & Corporations:
Want to integrate real-time InSAR and satellite insights into your agricultural platforms or ERP? Access Farmonaut’s Satellite API and API Developer Documentation for seamless, scalable integration of high-frequency, geospatial information across your agri-tech solutions.
Leveraging InSAR for Forestry & Forest Ground Investigations
Forests are environmental assets essential for carbon sequestration, biodiversity conservation, and ecosystem resilience. Yet, they face mounting threats from land deformation, subsidence, illegal activities, and climate-induced phenomena.
InSAR’s Multifaceted Role in Forest Health & Management
-
Tracking Ground Deformation in Forested Areas:
Landslides or subsidence under tree cover threaten not just timber resources but entire forest ecosystems. InSAR detects ground movement invisible to field surveys, enabling early measures and ecological protection. -
Monitoring Permafrost & Freeze-Thaw Cycles:
In boreal and mountain environments, dynamic soil freezing/thawing impacts tree stability—and ecosystem functions. InSAR tracks these changes, informing better forest management amid a changing climate. -
Assessing Impacts of Logging, Restoration & Reforestation:
Human activities, like reforestation, logging, or site preparation, alter ground structure. InSAR provides before-and-after maps evidencing subsidence or compaction, supporting sustainable forest management. -
Detecting Illegal Mining or Encroachments:
InSAR’s sensitive detection capabilities expose clandestine mining and land-use,
helping protect forests and natural resources in real time.
Forestry-Specific InSAR Monitoring Examples:
- Early Landslide Risks: Continuous monitoring identifies minute slope movements, helping prevent catastrophic landslides before they endanger villages, wildlife habitats, or commercial timberlands.
- Reforestation Site Stability: InSAR maps support optimal placement and management of new trees, minimizing risks due to unstable terrain.
- Illegal Activity Surveillance: Quickly alerts authorities to ground subsidence or surface movement symptomatic of unauthorized mining.
As InSAR becomes standard practice in global forestry investigations, it will continue to be an essential instrument for conservation, sustainable resource extraction, and ecosystem protection for years to come.
Why Is InSAR Essential for Ground Investigations in 2025 and Beyond?
- Growing Pressures: Climate variability, increased production demands, population surges, and erratic weather make timely, accurate information about soil and ground more critical than ever.
- High-Frequency, High-Resolution Data: Advancements in SAR satellites deliver more frequent, sharper images, translating into real-time insights for stakeholders.
- Actionable Intelligence: InSAR enables earlier detection of risks like subsidence, compaction, or landslides, supporting better management measures and resource allocation.
- Sustainability: Early warning and continuous detection support sustainable management—protecting ecosystems, crops, and communities.
- Integration with AI & Machine Learning: Predictive analytics and future-focused management—using “big data” from InSAR, weather, and field trials—are now feasible for agriculture and forestry.
By 2025, InSAR’s ability to map changes, inform informed decisions, and reduce costs will be indispensable for those looking to sustainably manage natural resources and safeguard earth’s critical ecosystems.
Optimize your sustainability strategy with Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting Tool, providing real-time emissions and resource tracking for data-driven, compliance-ready farming and forestry.
Farmonaut’s Role in Enabling InSAR-Based Ground Investigations
As a pioneering satellite technology company, we at Farmonaut provide businesses, users, and governments worldwide with cost-effective, satellite-derived ground monitoring and management solutions for agriculture, forestry, mining, infrastructure, and defence.
-
Satellite-Based Monitoring:
We utilize multispectral and radar-based imagery to deliver detailed insights into soil health, vegetation condition, structural stability, and environmental impact. -
Jeevn AI Advisory System:
Using AI to analyze satellite and InSAR data, we provide real-time advice and weather forecasts, optimizing productivity and resource management. -
Blockchain-Based Traceability:
Our traceability suite (Traceability Product) ensures transparency from field to end user—vital for modern agricultural and forestry supply chains. -
Real-Time Environmental Impact:
Environmental impact monitoring—like carbon footprint tracking—supports users in meeting compliance and sustainability targets. -
APIs & Scalable Access:
We offer API-based access (Farmonaut API) making high-frequency, trusted InSAR and SAR-derived data available for integration with your workflow across web, Android, and iOS.
Our mission is simple: to democratize satellite-powered insights so every stakeholder can make informed decisions, adapt to change, improve resilience, and achieve sustainable resource management in a changing world.
Ready to harness the power of Earth observation for better crop, forest, and soil management? Get started today via our platform and apps.
Financial institutions can streamline crop loan and insurance verification through satellite-based monitoring, reducing fraud and access bottlenecks. Learn more at Farmonaut’s Crop Loan & Insurance Solution.
For logistics and heavy equipment operators, our Fleet Management Tool optimizes resource deployment using satellite intelligence.
The Future of InSAR Technology in Agriculture & Forestry
By 2025 and beyond, expect InSAR technology to be embedded at the core of all significant land ground investigations. The increasing cadence and resolution of SAR satellites, along with AI-fueled analytics, will produce an era where prevention—rather than repair—becomes the norm.
-
Widespread Adoption:
Governments, agribusinesses, and foresters will rely on InSAR for near-automatic, large-area soil and ground monitoring. -
Predictive Risk Insights:
Integration with weather, crop, and climate models will identify risk before it materializes—enabling adaptive, resilient land management. -
Precision Decision-Making:
Whether it’s when to irrigate, where to plant, or how to respond to potential landslides, precision management will be guided by InSAR-based evidence. -
Universal Accessibility:
Advancements in cloud-based, app-driven services ensure even smallholder farmers and community foresters have access to transformative InSAR insights.
Frequently Asked Questions: What Is InSAR and Why It’s Essential for Ground Investigations
Q1: What is InSAR?
InSAR (Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar) is a remote sensing technique using satellite or airborne radar images to measure surface deformation and ground movement over large areas, with millimeter-scale accuracy.
Q2: Why is InSAR better than traditional ground-based monitoring?
InSAR provides wide-area coverage, higher precision, frequent updates, and works regardless of weather—often with up to 100x improved sensitivity over field-based equipment. It’s also more cost-effective for large-scale investigations.
Q3: How does InSAR help agriculture in 2025?
InSAR helps farmers and agronomists monitor soil moisture, prevent degradation, detect early signs of compaction, and optimize irrigation practices—enabling more precise, sustainable, and profitable farming.
Q4: How is InSAR applied in forestry?
Forestry professionals use InSAR to monitor permafrost stability, detect landslide risks, assess post-logging land changes, and identify illegal mining or encroachments under forest canopies.
Q5: Can I use InSAR insights via mobile or web platforms?
Yes, with platforms like Farmonaut, users access InSAR-powered monitoring and analysis tools on web, Android, and iOS.
Q6: Is InSAR affordable for small- and medium-scale users?
Absolutely. Modern cloud platforms and app-based services democratize satellite insights, making them accessible and affordable across operations of all sizes.
Q7: Where can I integrate InSAR and SAR data with my enterprise software?
Through developer APIs like Farmonaut’s API, businesses and software developers can plug real-time InSAR data into existing systems.
Conclusion: The Imperative of InSAR for Sustainable Land Investigations
What Is InSAR and Why It’s Essential for Ground Investigations is a challenge every stakeholder must address to thrive under today’s heightened pressure on natural resources and dynamic environmental conditions. InSAR, with its unparalleled ability to detect subtle changes and movement in soil, ground, and land, has revolutionized monitoring in both agriculture and forestry.
In 2025 and beyond, it forms the backbone of a more sustainable, efficient, and resilient approach to resource management and ecosystem protection. From wide-area coverage to ultra-fine precision, and from cost savings to real-time risk mitigation, InSAR is essential to achieving the productivity and sustainability goals set by modern agriculture and forestry.
As we move forward, platforms leveraging InSAR—like Farmonaut—will continue to empower users globally to unlock the power of satellite data, make informed decisions, and keep our planet thriving for generations.
Farmonaut Subscription Plans
Unlock affordable, advanced satellite-driven insights for your fields, forest tracts, or commercial operations via our simple, scalable subscription plans.