Agriculture in Algeria, Nigeria & Siberia: 2025 Trends — Sustainability, Challenges & Food Security
“Algeria aims to increase climate-smart agricultural practices by 25% by 2025 to strengthen food security.”
Table of Contents
- Summary: Agriculture in Algeria — Towards Sustainable Growth and Food Security in 2025
- Geographical and Climatic Context of Algeria’s Agriculture Sector
- Key Agricultural Products and 2025 Trends in Algeria
- Technological and Policy Developments: Driving Transformation in Algeria
- Challenges and Opportunities: 2025 and Beyond
- Environmental Sustainability and Food Security Goals
- Comparative Overview: Agriculture of Nigeria & Agriculture in Siberia
- Comparative Sustainability Practices Table: 2025
- Leveraging Satellite Technologies for Sustainable Agricultural Growth (Farmonaut)
- FAQ: Common Questions about Agriculture in Algeria, Nigeria & Siberia
- Conclusion: A Vision for Food Security and Sustainable Rural Development
Summary: Agriculture in Algeria — Towards Sustainable Growth and Food Security in 2025
The agriculture in Algeria remains a cornerstone of Algeria’s economy, playing a crucial role in rural livelihoods, national food security, and the overall development of the country. As we look towards 2025, the agricultural sector is undergoing significant transformation, propelled by government reforms, technological adoption, and an increased emphasis on sustainability to better meet food demands and reduce dependency on food imports.
Algeria’s commitment to climate-smart practices, precision technologies, and modernized crop management seeks to address challenges posed by water scarcity, land limitations, and climate variability. By 2025, new policy frameworks and innovation have started reshaping the sector for a more resilient and productive agricultural landscape aligned with national growth goals.
Geographical and Climatic Context of Algeria’s Agriculture Sector
The geographical setting of Algeria and its agricultural potential are intrinsically shaped by a diverse geography, ranging from the Mediterranean coastal zones in the north to the vast arid Saharan regions in the south. Approximately 3.5% of Algeria’s total land area is classified as arable, concentrating activity in the fertile Tell Atlas and High Plateaus that host most of the country’s crop production.
- Mediterranean Coastal Zones: Moderate climate, responsible for high-value crops including vegetables, olive trees, and citrus fruit cultivation.
- Tell Atlas & High Plateaus: More extensive, supporting the bulk production of cereals (wheat, barley) and livestock farming.
- Saharan Regions: Extremely arid, significant for date palm cultivation and burgeoning solar-powered irrigation systems.
However, water scarcity remains the primary limiting factor for agricultural growth, compounded by increasingly frequent droughts, desertification risks intensified by climate change, and soil degradation.
Discover how soil and water management are revolutionizing sustainable agriculture — essential context for the challenges Algeria faces.
Key Agricultural Products and 2025 Trends in Algeria
The agricultural landscape of Algeria is dominated by a number of key crops and livestock that are critical for national food security as well as export potential. Let’s explore the trends shaping the sector in 2025:
- Cereals:
- Wheat and Barley form the staple food base for the country, occupying over 60% of total cultivated land.
- Legumes like chickpeas and lentils are grown as rotation crops to enhance soil fertility.
- Vegetables and Horticulture:
- Vegetable production is thriving across the northern coastal regions, sustaining urban food markets and contributing to rural incomes.
- Government incentives have encouraged more farmers toward diversification into horticulture and fruit trees.
- Olive Cultivation:
- Algeria is positioned among the leading olive oil producers in the Mediterranean, with expanding markets for high-value extra-virgin oils.
- Fruit Trees:
- There’s an upsurge in almonds, dates (especially from Saharan oases), and citrus (oranges, lemons) cultivation to enhance export opportunities and value addition.
- Livestock Farming:
- Sheep and goats are especially vital to rural economies in the highlands, providing both food and income sources.
- Cattle farming has expanded, supported by improved animal breeds and veterinary services.
Recent years have seen precision farming, climate-resilient seed adoption, and the increase of drip irrigation systems — these are part of a forward-facing drive towards sustainable and efficient agriculture.
Learn how regenerative agriculture and soil health are the base of Algeria’s climate-smart growth in 2025.
“Over 80% of Algeria’s farmland relies on innovative crop management techniques to counteract extreme climate variability in 2025.”
Technological and Policy Developments: Driving Transformation in Algeria’s Agriculture Sector
By 2025, agriculture in Algeria has made considerable advances in the adoption of precision agriculture technologies and new policy frameworks aimed at sustainability, resilient growth, and sectoral modernization.
Key Technological Developments:
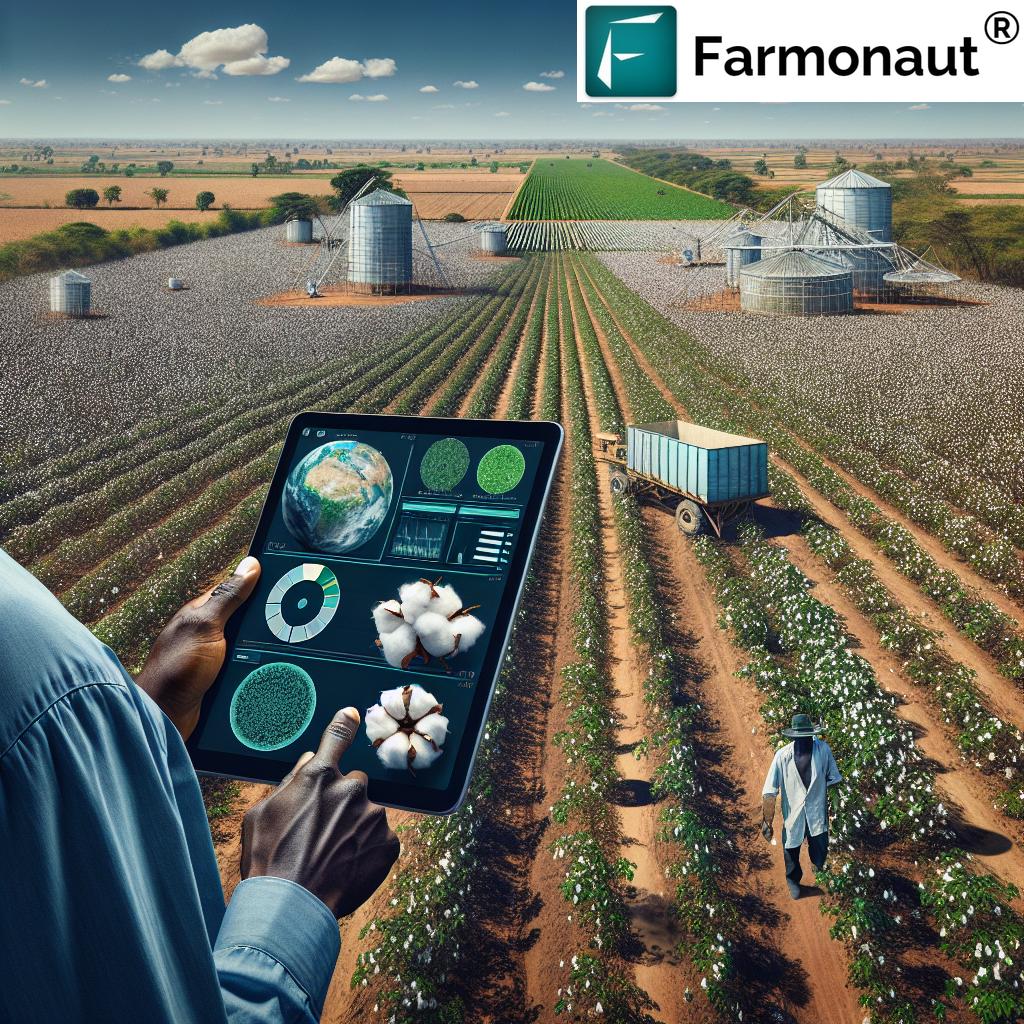
- Satellite Imagery and Sensors: Multispectral satellite images and IoT-enabled soil sensors are now routinely used to monitor crop health, detect nutrient deficiencies, and assess drought risks.
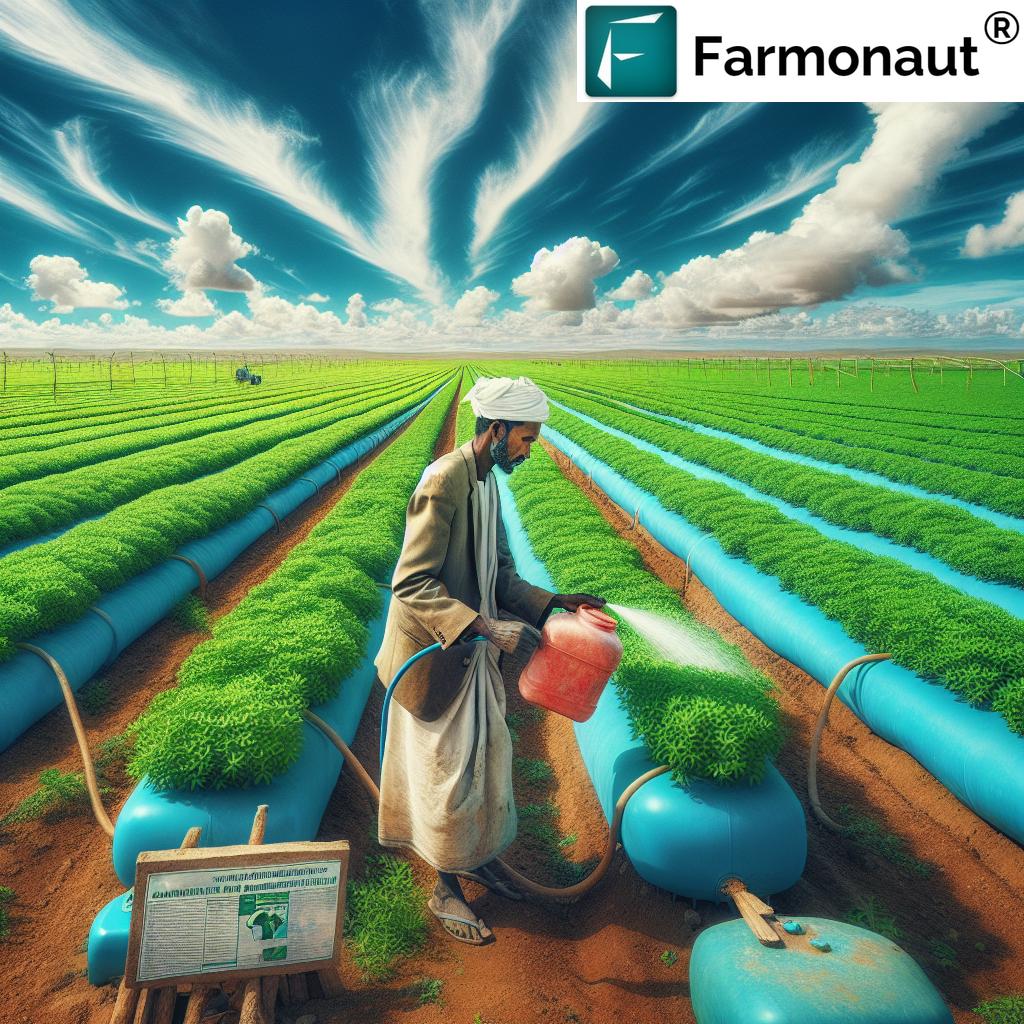
- Drip Irrigation Systems: With water scarcity becoming critical, drip irrigation is increasingly adopted to optimize water use and improve yields, conserving resources while sustaining productivity.
- Green Technologies: Integration of solar-powered irrigation pumps, greenhouse structures, and renewable energy in farm operations to reduce environmental impact and energy costs.
Farmonaut’s platform leverages real-time satellite-based monitoring to enable farmers, businesses, and governments to make data-driven decisions, optimize inputs, and enhance both sustainability and efficiency of agricultural operations.
Watch how precision technology and artificial intelligence are boosting harvests and advancing sustainability—future-proofing Algerian agriculture for 2025.
Policy Developments:
- National Agricultural Development Plan: Focused on rural infrastructure—from better roads to modern storage facilities—to reduce post-harvest losses and support market access.
- Agroecology & Land Management: A new emphasis on agroecological practices, such as conservation tillage, biodiversity preservation, and rejuvenation of degraded lands through reforestation and sustainable grazing methods.
- Extension Services: Expanded network for farmer education, with regular training on climate-resilient varieties, integrated pest management, and digital tools for improved production planning.
- Food Security Initiatives: Policies to enhance domestic production, decrease dependence on imports, and build strategic grain reserves.
Explore Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting tool for agriculture—a key resource for environmental compliance and sustainable farm management in Algeria. This product offers actionable insights into emission data, empowering agricultural producers to meet climate stewardship goals.
Access satellite-powered agricultural insights on any device to optimize your farm, orchard, or agri-business in Algeria, Nigeria, or Siberia.
Challenges and Opportunities: 2025 and Beyond for Agriculture in Algeria
Despite significant progress, agriculture in Algeria continues to grapple with notable challenges that could impede the path towards sustainable growth and national food security. Yet, 2025 also brings a host of new opportunities for the sector:
Key Challenges:
-
Water Management Issues:
- Over-extraction of groundwater threatens aquifer depletion and long-term water security.
- Drip irrigation and large-scale farm management tools are critical for optimizing resource use.
- Land Fragmentation: Small, scattered holdings inhibit mechanization, scaling, and adoption of advanced technologies.
- Limited Access to Credit: Smallholder farmers often lack collateral, making it difficult to invest in new technologies or expand production. Learn how satellite-verification can help via Farmonaut’s crop loan & insurance products.
- Price and Export Volatility: Algeria is vulnerable to fluctuations in global commodity prices and geopolitical uncertainties affecting export market stability.
- Impacts of Climate Change: Desertification, erratic rainfall, and rising temperatures pose existential risks, necessitating urgent climate adaptation strategies.
Emerging Opportunities:
- Value Chain Expansion: Investments in agro-processing industries—especially for olive oil, dates, and horticultural produce—will generate rural jobs and enhance value addition.
- Digital Agriculture Platforms: 2025 is characterized by a rapid digital transformation, fostering platforms that connect farmers to markets, inputs, and extension agents.
- Blockchain Traceability: Critical for export certification and building trust in international agri-food markets. Explore Farmonaut’s blockchain-based traceability solution for supply chain transparency and fraud prevention.
-
Satellite Monitoring and Advisory: Real-time, satellite-powered API insights boost crop health monitoring, water conservation, and sustainable management for both businesses and government agencies.
For developer integration or advanced analytics, access the API developer docs.
Explore how NDWI and satellite technology are revolutionizing water management and ensuring sustainability against Algeria’s water scarcity challenges.
Environmental Sustainability and Food Security Goals in Algeria’s Agricultural Sector
As sustainability and food security climb to the forefront of national agricultural strategy, Algeria is investing in climate-resilient systems and innovative methods to buffer against risk and promote growth.
Environmental Priorities:
- Rehabilitation of Degraded Land: National reforestation campaigns and sustainable grazing controls combat desertification and restore ecosystem services.
- Climate-Smart Agriculture: Emphasis on drought-tolerant crops, conservation tillage, and rotation systems that stabilize yields despite variable climate conditions.
- Integrated Crop-Livestock Systems: Mixed farming models recycle nutrients, enhancing both productivity and resilience within farms.
- Water-Saving Innovations: Continued rollout of efficient irrigation and rainwater harvesting infrastructure to secure agricultural water supplies in an era of scarcity.
MENA’s regional economic trends for 2025 highlight Algeria’s leading role in food security and sustainable AgTech adoption.
Achieving Food Security:
The overarching goal is to lower Algeria’s dependency on imports by bolstering local cereal, horticulture, and livestock productivity. National policies aim to diversify the food basket and strengthen emergency reserves—making the system resilient to shocks and price volatility.
Extension and education on modern, climate-adapted practices empower farmers to adopt new varieties and techniques. Farmonaut’s AI-powered advisory tools further accelerate this learning by providing custom strategies based on local soil, water, and weather data.
Explore future-forward agri-business ideas for 2025—helping reinforce food security and rural employment in Algeria.
Comparative Overview: Agriculture of Nigeria & Agriculture in Siberia (2025 Trends)
The global landscape of sustainable agriculture extends across continents, with agriculture of Nigeria and agriculture in Siberia offering contrasting contexts and comparable 2025 trends. While Algeria navigates water and land challenges, Nigeria leverages its vast arable land and diverse crop base, and Siberia adapts to harsh climates with technological innovation.
Let’s briefly examine the unique characteristics and forward-looking strategies embraced by Nigeria and Siberia:
Agriculture of Nigeria: Growth, Challenges & Future Pathways
- Diverse Crop Portfolio: Nigeria sustains a rich variety of crops, from cassava, maize, and rice to cash crops like cocoa and oil palm.
- Climate-Smart Solutions: Faced with droughts and pest pressures, Nigerian agriculture is increasingly adopting mobile advisory tools and solar-powered irrigation to empower rural smallholders.
- Export Potential: Policies incentivize non-oil commodity exports and agribusiness value chain integration, aiming to meet food demands and create rural jobs.
- Youth-Driven Transformation: Digital platforms and seed technology are enabling a new generation of agri-entrepreneurs.
Agriculture in Siberia: Adaptation in a Harsh Climate
- Climatic Constraints: The Siberian region’s cold and short growing seasons are a significant limiting factor, but climate change is opening up potential for cereal and soybean expansion.
- Technologies and Mechanization: Large-scale farms deploy advanced machinery, drones, and remote sensing to overcome labor and time constraints.
- Water and Soil Management: Melting permafrost and changing rainfall patterns demand rigorous soil and environmental management to sustain productivity.
- Food Security Contributions: Siberia’s grain, potato, and animal husbandry sectors are essential to Russia’s food reserves and national security.
Solar irrigation and tech adaptation in Africa inform strategies relevant to both Nigeria and Algeria’s climate-smart farming future.
Comparative Sustainability Practices Table: 2025
To visualize the progress and contrasts in sustainable agriculture, examine the table below—comparing climate-smart practices, projected yield improvements, and food security impacts across Algeria, Nigeria, and Siberia for 2025.
| Region / Country | Estimated Climate-Smart Practice Adoption Rate (%) | Projected Yield Improvement (%) | Estimated Reduction in Water Usage (%) | Expected Impact on Food Security |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algeria | 25 | 18 | 20 | Substantial improvement in self-sufficiency; reduced import dependency |
| Nigeria | 30 | 16 | 15 | Greater resilience, especially in drought-prone North; improved rural incomes |
| Siberia | 20 | 21 | 10 | Stabilized grain supplies for Russia; supports national food security |
*Data are estimates based on current 2025 trends and policy targets.
Leveraging Satellite Technologies for Sustainable Agricultural Growth: The Farmonaut Advantage
For anyone seeking to future-proof agriculture in Algeria, Nigeria, or Siberia, satellite technology and AI-driven analytics are essential. At Farmonaut, we commit to making advanced, satellite-based solutions affordable and accessible, driving sustainability and operational excellence in every region.
How Farmonaut Empowers Agricultural Progress:
- Satellite-Based Monitoring: We use multispectral imagery to provide on-demand crop health, soil status, and irrigation insights—even across challenging geographies from the Mediterranean to Siberia.
- AI-Powered Advisory Systems: Our Jeevn AI delivers customized, real-time weather and crop strategies—vital for adapting to changing climates and reducing crop failure risks.
- Blockchain-Based Traceability: By integrating blockchain, we help users ensure product authenticity and supply chain transparency, supporting both export ambitions and domestic food integrity.
- Fleet & Resource Management: With our fleet management system, agricultural businesses, large-scale cooperatives, and infrastructure managers can optimize vehicle and machinery operations, minimizing costs and boosting efficiency.
- Environmental Impact Tracking: Our platform enables users to track carbon footprints and monitor regulatory compliance—positioning farms of all sizes for climate stewardship.
- Scalability: From smallholders to national agencies, our modular apps scale to meet unique operational and reporting needs.
- Access to Financing: Satellite verification of crops and lands (see crop loan and insurance options) streamlines the agricultural credit process, helping more farmers access vital capital.
Our technologies are accessible in Algeria, Nigeria, Siberia, and worldwide through
web, Android, and iOS platforms, as well as via API. Experience hands-on advanced agricultural monitoring with our large scale farm management app—engineered for growth that is both efficient and sustainable.
Learn how AI and satellite data improve resilience and efficiency in global agriculture, including the unique needs of Algeria, Nigeria, and Siberia.
Choose a Farmonaut Subscription to Unlock These Benefits:
All Farmonaut subscription plans come with secure payment and instant access to satellite-powered tools for agriculture, mining, and infrastructure.
FAQ: Common Questions about Agriculture in Algeria, Nigeria & Siberia
-
What are the main challenges for agriculture in Algeria in 2025?
Major challenges include water scarcity, climatic variability, over-extraction of groundwater, land fragmentation, and limited access to credit for smallholders. The sector must also address desertification risks and growing market volatility.
-
How is the government driving agricultural reform in Algeria?
By introducing climate-smart policies, subsidizing efficient irrigation systems, expanding rural infrastructure, and incentivizing diversification into high-value crops and livestock.
-
What role do digital technologies and satellite imagery play in 2025 agriculture?
These allow for real-time monitoring of crop health, precise irrigation, early detection of problems, and optimal resource allocation. Farmonaut’s platform offers these tools for enhanced productivity and environmental stewardship.
-
How can satellite-based tools help with financing and insurance for farmers?
Satellite-based verification makes loan and insurance processes faster, more reliable, and less prone to fraud. Agricultural banks and insurers use these tools to lower risk and improve access to credit.
-
What opportunities exist for growth in Algeria’s agricultural value chain?
Agro-processing, export development, blockchain-based traceability, and agro-industry integration are key opportunities for job creation and rural economic expansion.
-
How does agriculture in Nigeria compare to Algeria in terms of sustainability in 2025?
Nigeria has a slightly higher adoption of climate-smart techniques, focusing on drought resilience, digital extension, and expanding non-oil exports. Both countries prioritize rural livelihoods and self-sufficiency.
-
What unique factors shape agriculture in Siberia?
Harsh winters, a short growing season, and recent climatic shifts define agriculture in Siberia. Advances in mechanization, cold-resilient crop varieties, and environmental management help maintain regional food stability.
-
How can I access Farmonaut’s satellite technologies for my agricultural project?
Download the app for web, Android, or iOS. Developers can also integrate Farmonaut with their solutions using our API.
Conclusion: A Vision for Food Security and Sustainable Rural Development in 2025
Agriculture in Algeria stands at the threshold of a transformative era—where digital innovation, climate-resilient strategies, and environmentally minded management converge to meet the complex demands of food security and sustainable development. Despite persistent challenges regarding water scarcity, climatic variability, and land limitations, government policy, technological adoption, and active engagement with farmers herald an optimistic future in 2025 and beyond.
With climate-smart practices, crop diversification, and real-time monitoring, Algeria, alongside agriculture of Nigeria and agriculture in Siberia, is redefining rural growth, environmental responsibility, and national resilience. Stakeholders, from policymakers to agri-entrepreneurs, must continue support for collaborative innovation and knowledge exchange to ensure agriculture remains a robust cornerstone of prosperity, health, and security across these regions.
Unlock the potential of tomorrow’s farms with satellite technology—empowering sustainable, data-driven agriculture in Algeria, Nigeria, and Siberia for years to come.