Cannabis Aphids Treatment: Stop Aphid Damage Fast [Ultimate 2025 Guide]
“In 2025, advanced gene-editing targets over 80% of cannabis aphid population, enhancing crop resilience and yield.”
Cannabis Aphids and Crop Protection: 2025 Overview
The cannabis industry continues to expand worldwide, driven by increasing legalization, medicinal, and industrial demand. However, the challenge posed by the persistent cannabis aphid (Phorodon cannabis) is intensifying. Aphids are more than just another pest – their ability to reproduce rapidly and cause significant damage to plants and yields makes advanced management a top concern as we enter 2025.
This comprehensive post explores the biology and damage pattern of cannabis aphids, focusing on sustainable treatment and control methods, integrating new IPM trends, digital tools, and biotechnological solutions.
You’ll also discover how Farmonaut is transforming real-time pest monitoring and advisory with cutting-edge satellite-based, AI-driven, and blockchain-enabled technologies—empowering growers across commercial and small-scale operations.
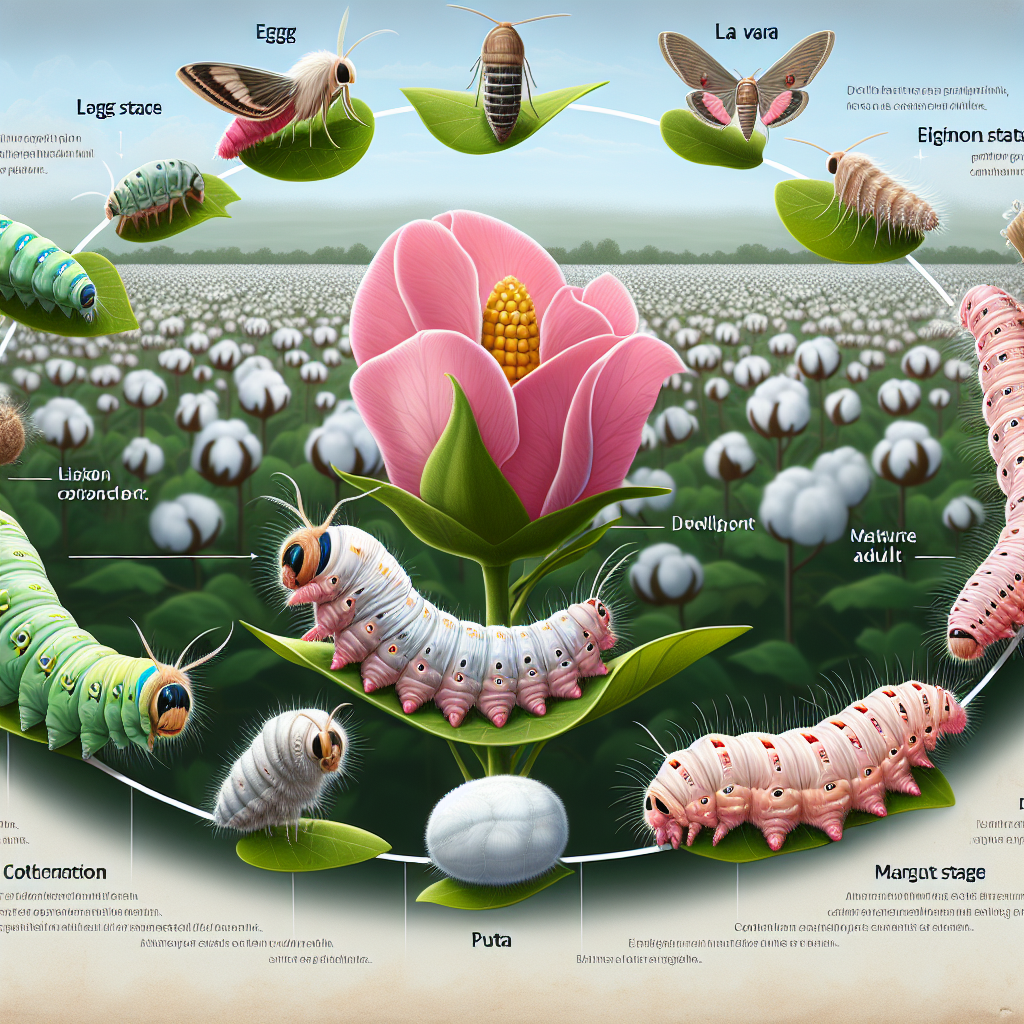
Understanding Cannabis Aphids and Their Damage
Cannabis aphids are soft-bodied, green or yellowish insects of the Phorodon genus, uniquely adapted to feed on cannabis. Their piercing-sucking mouthparts extract vital phloem sap from leaves, stems, and even buds. Here’s why their damage is particularly challenging:
- Rapid Reproduction: Under favorable conditions (humidity, warmth, abundant hosts), aphid populations can explode within weeks.
- Direct Plant Impact: Aphid feeding removes essential nutrients, leading to reduced vigor, stunted growth, curled and yellowing leaves, and lowered cannabinoid content—every grower’s nightmare in medicinal or high-value markets.
- Sticky Honeydew and Mold: Aphids secrete sticky honeydew which coats leaves and buds, fostering sooty mold fungi. This mold cover further blocks photosynthesis, reducing quality and marketability of your crop.
- Virus Transmission: Cannabis aphids may act as vectors for plant viruses, compounding risk and potential losses. Research is ongoing, but a preventative approach is always prudent.
Unmanaged, aphid infestations can result in severe losses, impacting both industrial and medicinal cannabis cultivators globally.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM): The 2025 Gold Standard for Cannabis Aphids Treatment
By 2025, integrated pest management (IPM) remains the cornerstone for effective and sustainable cannabis aphids treatment. IPM focuses on minimizing environmental impacts, maximizing crop safety, and ensuring regulatory compliance. The modern IPM process is a multi-pronged approach built upon:
- Monitoring and Early Detection (using digital and manual methods)
- Biological Control (introduction or support for aphid predators and parasitoids)
- Cultural Practices (hygiene, plant vigor, timely removal of infested material)
- Chemical Control Innovations (safe, selective, and minimal-residue insecticides)
- Gene-Editing and Technology (novel breeding and target-specific solutions)
Let’s explore how each method aligns with current research, growers’ experiences, and 2025 standards.
Monitoring, Early Detection & Digital Innovations for Cannabis Aphid Management
Early detection of cannabis aphids is essential for successful treatment and reducing damage. Regular scouting enables growers to respond before aphids reach damaging thresholds.
Key Methods in 2025
- Visual Inspections: Manual inspection of stems, leaves (especially undersides), and bud bases. Look for clusters of small, pale-green insects or sooty mold on honeydew.
- Yellow Sticky Traps: Beneficial for trapping flying aphid stages and estimating population trends.
- Emerging Digital Tools: In 2025, AI-powered image recognition apps and drone technology now seamlessly detect aphid infestations, even across large commercial farms.
- Threshold Setting: Regular monitoring allows for development of customized intervention thresholds, optimizing timing for aphid treatment.
Tip: Combining traditional visual inspections and digital tools creates a more responsive, robust early warning system.
Biological Controls: Sustainable Cannabis Aphids Treatment in 2025
One of the most effective sustainable methods for cannabis aphids treatment in 2025 is biological control: harnessing natural enemies of aphids. This approach offers several advantages:
- Reduces reliance on chemical insecticides, supporting safe crop profiles for medicinal or food-grade markets.
- Preserves beneficial insects and wider ecological health.
- Proven effectiveness: Current studies reveal biological controls can reduce aphid damage by up to 65% in integrated systems.
Key Biological Agents
- Lady Beetles (Coccinellidae): Both larvae and adults devour aphids in abundance.
- Lacewings (Chrysopidae): Larvae are voracious predators of small soft-bodied insects, especially aphids.
- Parasitic Wasps (Aphidius spp.): These wasps lay eggs inside aphids, with emerging larvae decimating the aphid from within.
- Predatory Midges and Hoverflies: Also effective in many grow environments.
Growers in 2025 now integrate companion planting (e.g., marigold, dill, fennel, or other nectar sources) to support beneficials or use commercial biocontrol releases in greenhouses.
“Biological controls cut aphid damage in cannabis by up to 65%, integrating tech-driven monitoring for rapid intervention.”
Cultural Practices, Mechanical Removal & Crop Hygiene for Aphid Management
Robust cultural practices are indispensable to any aphid management strategy. These measures directly impact aphid populations and plant health:
- Crop Sanitation: Regular removal of heavily infested material (including lower leaves and stems) breaks pest cycles.
- Water Sprays: Gentle spraying of foliage with water dislodges aphids, especially useful for small-scale or minor infestations.
- Weed Management: Eliminate alternative hosts to prevent aphids from staging reinfestation.
- Stress Reduction: Maintain optimal irrigation and nutrition, since healthy plants recover from pest pressure more effectively.
- Crop Rotation & Intercropping: Disrupt life cycles and reduce local aphid pressure.
Maintaining meticulous crop hygiene not only prevents population build-up but also reduces the risk of virus transmission.
Chemical Control & Biopesticide Advancements in Cannabis Aphid Treatment
Although chemical control has a place in IPM, 2025 sees a shift toward selective, minimal-residue insecticides and biopesticides:
- New-Generation Insecticides: Regulators increasingly approve systemic or contact agents with minimal residual effects, short re-entry intervals, and targeted modes of action (e.g., flupyradifurone phase-in, insect growth regulators for hemp aphid management).
- Biopesticides: Neem oil, pyrethrins, essential oils (thyme, peppermint), and soaps provide eco-friendly solutions to control aphid populations on cannabis plants. These are often integrated as rotational treatments in IPM programs.
- Spray Timing: Targeted applications outside of pollinator or beneficial insect activity periods maximize efficacy while maintaining ecological balance.
Choose products with proven efficacy on cannabis, always adhere to residue regulations for medicinal or industrial crops, and rotate modes of action to delay insecticide resistance.
Gene-Editing and Biotechnology: The Next Generation of Cannabis Aphid Resistance
2025 is a breakout year for biotechnology in cannabis aphid control. The latest directions in research introduce game-changing options for persistent pest resistance:
- CRISPR Gene-Editing: Allows breeders to engineer aphid-resistant plant varieties—without diminishing cannabinoid profiles. Plants may express deterrent compounds or structural defenses against aphid feeding.
- Microbiome Manipulation: Altering endophytic and soil microbe communities fosters plants that are less attractive or less susceptible to aphid damage.
- RNAi and Precision Biocontrols: Cutting-edge approaches deploy RNA interference, silencing aphid feeding genes or virus transmission pathways.
These innovations supplement but do not replace integrated management: gene-edited cultivars work best alongside robust detection, biological control, and good cultural practices.
Comparison Table of Cannabis Aphid Treatment Strategies (2025)
| Treatment Method | Mechanism of Action | Estimated Effectiveness Rate (%) | Time to Noticeable Results (Days) | Environmental Impact | Cost Estimate (USD/acre) | Adoption Rate in 2025 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biological Control | Predation/Parasitism by beneficial insects | 55–65% | 7–21 | Low | 100–200 | 60 |
| Chemical Control | Direct toxicity to aphids (systemic/contact agents) | 75–95% | 1–5 | Medium–High | 150–350 | 40 |
| Gene-Editing Solutions | Genetic resistance (CRISPR-mediated traits) | 75–85% | N/A (embodied in plants) | Low | 300–500 (seed premium) | 20 |
| Tech-Based Monitoring | Early detection/prevention via digital tools | 45–60% (damage avoidance) | Immediate | Low | 30–120 | 75 |
| Cultural Practices | Sanitation, plant vigor, mechanical removal | 35–55% | 3–14 | Low | 10–50 | 85 |
2025 Challenges, Regulatory Landscape & Future Directions in Cannabis Aphids Management
Aphid management is complicated by:
- Pesticide Regulations: Regulations differ globally, limiting what insecticides are available for cannabis treatment in medicinal, recreational, or industrial applications. Always confirm local laws before application.
- Resistance Development: Aphids develop resistance to chemical treatments, requiring ongoing rotation of active ingredients and alternative controls.
- Cross-Crop Threats: Aphids readily jump between cannabis, hemp, and surrounding flora, making containment a persistent challenge, especially in outdoor or mixed cultivation regions.
- Research Gaps in Virus Transmission: Virus transmission in cannabis by aphids is still poorly understood. Until more evidence emerges, prudent management assumes preventative protocols.
Ongoing research continues to expand options, especially with the latest genetic, microbiome, and digital detection methods.
Farmonaut Satellite Technology & Smart IPM for Cannabis Aphid Treatment
As the global cannabis cultivation landscape becomes increasingly tech-driven, the need for precise, efficient IPM tools has never been higher. This is where Farmonaut offers a game-changing advantage for farmers, agribusinesses, and governments:
- Satellite-Based Crop Monitoring: With NDVI, multispectral imagery, and AI interpretation, you can detect early stress—often signaling aphid infestation before visible damage appears.
Use Case: Monitor crop health in real time, enabling earlier, targeted aphid interventions [Learn about Large-Scale Farm Management Tools] - Jeevn AI Advisory System: Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI delivers customized notifications on stress hot-spots, potential pest/disease outbreaks, and tailored treatment guidance, elevating decision-making from detection through remediation.
Benefit: Faster, more accurate aphid management decisions. - Blockchain Traceability: Trace every input, crop event, and harvesting detail for transparency—crucial for medicinal and export cannabis compliance. [Explore Cannabis Product Traceability]
- API & Developer Integration: Build custom dashboards or integrate real-time monitoring with your ERP/farm management software via Farmonaut’s robust API and Developer Docs.
- Environmental Impact Monitoring: Track changes in your farm’s carbon footprint by implementing sustainable IPM or organic methods. [Analyze & Improve Your Cannabis Farm’s Carbon Footprint]
- Crop Loan & Insurance: Growers benefit from satellite-based verification for crop loans and insurance, simplifying paperwork and reducing fraud.
Farmonaut is dedicated to making advanced monitoring and resource management tools accessible and affordable, enabling everyone from small growers to government agencies to thrive in the era of smart, sustainable cannabis agriculture.
FAQ: Cannabis Aphids Treatment & Modern IPM (2025)
Q1: What is the most effective cannabis aphids treatment in 2025?
There’s no single “silver bullet.” Integrated Pest Management (IPM), combining early detection, biological controls, robust cultural practices, and judicious use of selective insecticides is the most effective strategy. Emerging gene-editing solutions and digital scouting further optimize outcomes for both commercial and small growers.
Q2: How quickly can I stop aphid damage on cannabis?
Chemical controls act within days, while biological controls and cultural removal may take one to three weeks for significant reduction. Early detection using digital or satellite-based monitoring ensures intervention before severe yield losses occur.
Q3: Are there approved insecticides for medicinal cannabis in 2025?
Yes—but approved options vary by jurisdiction and are typically limited to products with minimal residues and short pre-harvest intervals. Always check local regulatory guidelines for compliance before application.
Q4: Can Farmonaut help identify cannabis aphid infestations?
We provide advanced satellite-based crop monitoring and AI advisory tools that flag crop stress (which could indicate aphid infestations), allowing for timely inspection and action. Our technology is available to both individual growers and enterprises.
Q5: Are gene-edited, aphid-resistant cannabis plants commercially available?
Gene-edited cultivars are emerging in select markets. Adoption is growing, especially in regions with supportive regulations and high-value medicinal/industrial crops. However, these plants are best integrated as part of a broader IPM program.
Q6: How do I ensure aphid control strategies are sustainable?
Use a combination of digital monitoring, biological controls, cultural practices, and minimal-use, targeted chemicals. Avoid sole dependence on insecticides—integrate multiple tactics for sustainable, long-term crop health.
Q7: How can I access Farmonaut services for my cannabis farm?
Simply download our app on Android or iOS, or visit the web portal to begin. Our platform scales for individual or enterprise needs.
Conclusion: Safeguarding Cannabis Crops from Aphid Damage in 2025 and Beyond
Cannabis is a transformative crop whose growth—in both regulatory acceptance and therapeutic application—is matched by the challenge of managing persistent pests like Phorodon cannabis. Understanding aphid biology, damage mechanisms, and recognizing early signs are vital to minimize risk and secure quality yields.
By 2025, integrated pest management, driven by cutting-edge technology, biological methods, and sustainable innovations—including gene-editing—sets the standard for effective, long-term control of cannabis aphids.
We, at Farmonaut, are committed to empowering growers, businesses, and institutions with affordable, scalable, and innovative tools for real-time monitoring, AI advisory, blockchain traceability, and resource management.
Take action this season: Integrate these modern strategies and digital solutions to proactively stop aphid damage fast—safeguarding crop health, maximizing yield, and driving sustainable cannabis cultivation worldwide.