Ammonia in Agriculture: Boosting 2025 Crop Yields
In the dynamic landscape of modern agriculture, ammonia stands as the bedrock of crop nutrition and sustainability. As the global population continues to rise and environmental concerns intensify, the significance of ammonia in agriculture becomes increasingly apparent—especially as we approach and progress through 2025. The world’s mounting food demand now requires yields and resource efficiency at levels historically unseen. Thanks to advancements in ammonia production, green innovation, and precision farming technologies, ammonia is not just maintaining its title as the cornerstone of high-yield agriculture but is also driving the sector toward a greener, more sustainable future.
This in-depth guide explores how ammonia agriculture is revolutionizing the farming industry—from innovative production methods and green ammonia initiatives to the pivotal role of digital and satellite technologies. We’ll dive into the advantages, challenges, and future prospects of ammonia farming, and how Farmonaut’s satellite-driven platform offers actionable solutions for stakeholders worldwide.
Understanding Ammonia in Agriculture: The Cornerstone of Crop Nutrition
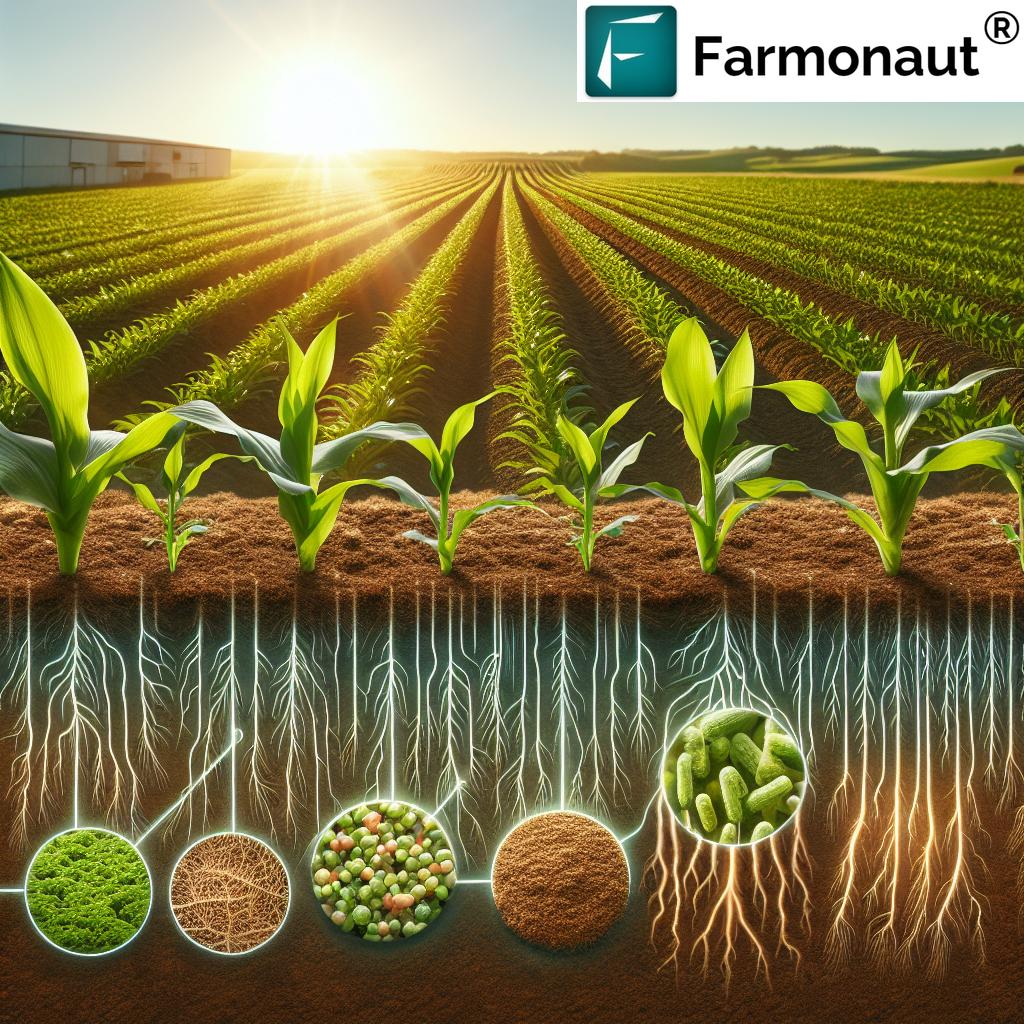
Ammonia (NH3) is a vital nitrogenous compound and a fundamental component in agricultural fertilizers. The role of ammonia in farming has grown ever more critical, particularly as the world faces unprecedented population growth and accompanying spikes in food demand. Here’s a closer look at how ammonia fuels the global food chain and why it remains indispensable in 2025.
- Key to Plant Nutrition: Nitrogen is an essential nutrient for plant growth, directly influencing core processes like photosynthesis, protein synthesis, and overall plant productivity.
- Natural Atmospheric Abundance—Yet Limited Usability: While nitrogen naturally exists as N2 gas in our atmosphere, most plants cannot utilize this form directly. Ammonia bridges this gap by serving as a bioavailable source of nitrogen for crops.
- Central Source in Fertilizers: The global fertilizer industry heavily relies on ammonia for producing synthetic fertilizers such as urea, ammonium nitrate, and ammonium sulfate. These products have made it possible to sustain the modern world’s vast food systems and high-yield agriculture.
The Science of Ammonia in Farming
Ammonia’s nitrogen content makes it irreplaceable for crop nutrition:
- Ammonium (NH4+) is readily absorbed by plant roots, ensuring a fast and effective nutrient boost.
- Bioavailable Forms: Ammonia is converted into other forms—like urea and nitrate—that plants can directly use for robust growth and optimal crop yields.
- Enhanced Protein Synthesis: Ammonia’s nitrogen acts as a core building block for plant proteins, crucial for the grain and fruit development of wheat, maize, rice, and vegetables.
Without the cornerstone role that ammonia plays in agriculture, global food security would be at significant risk. Its long-standing presence and evolving usage continues to make ammonia farming the backbone of modern farming practices worldwide in 2025.
Ammonia Production: Traditional Methods and the Push for Sustainability
The story of ammonia in agriculture would not be complete without understanding its production. Over 80% of ammonia’s global output is dedicated to fertilizers, cementing its direct link to crop yields, nutrition, and ultimately, feeding the world. Let’s examine how ammonia is produced and why 2025 is a landmark year for innovation.
Traditional Ammonia Production: The Haber-Bosch Process
- Historical Breakthrough: The Haber-Bosch process (1909) revolutionized food production by making synthetic ammonia widely available.
- The Chemistry: This method combines nitrogen gas (N2) from the air with hydrogen (primarily derived from natural gas or coal) at high temperature and pressure to form ammonia (NH3).
- High Demand, High Impact: The process supports the nitrogen demand of almost half the global population by enabling widespread fertilizer consumption.
While the importance of the Haber-Bosch process cannot be overstated, this technology is energy-intensive and heavily dependent on fossil fuels. This relies on natural resources and results in substantial greenhouse gas emissions—an increasingly urgent issue as the planet strives for carbon neutrality.
2025: Rising Pressures and New Sustainability Imperatives
- Energy Intensity: Upwards of 1% of all global energy consumption and 2% of CO2 emissions are attributed to ammonia production as of 2025.
- Environmental Concerns: Agriculture accounts for nearly half of all nitrogen fertilizer use, amplifying the urgency for more sustainable processes and products.
- Global Equity: Regions with limited access to efficient ammonia or modern technologies face a higher risk of food insecurity and environmental degradation.
Therefore, innovative production and application of ammonia in agriculture are not just desired, but essential and urgent for equitable, sustainable development.
Green Ammonia Agriculture: Innovation, Sustainability & Efficiency in 2025
2025 marks a turning point for ammonia agriculture. Emerging technologies are transforming the sector and making the impossible possible: boosting crop yields while drastically cutting environmental emissions and resource use. Here’s how:
- Green Ammonia: Instead of using fossil fuels for hydrogen, green ammonia production leverages renewable power. Hydrogen is generated via electrolysis (splitting water with electricity), which is then combined with nitrogen from the air to create NH3 with minimal carbon footprint.
- Environmental Leap: This shift drastically reduces the emissions associated with fertilizer production, supporting worldwide efforts to achieve sustainability in ammonia farming.
- Enhanced Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE): Precision application of ammonia fertilizers—enabled by digital monitoring, soil testing, and advanced analytics—ensures that every drop of ammonia goes farther, reducing wastage and pollution.
- Slow-Release and Stabilized Fertilizers: Next-generation products regulate the release of ammonia, reducing nutrient loss through volatilization, runoff, or conversion to nitrous oxide (a potent greenhouse gas).
How Is Green Innovation Integrated in Ammonia Used in Agriculture?
- Practice: Use of solar or wind-powered electrolyzers to generate hydrogen locally and produce green ammonia on-site or in regional hubs.
- Product Design: Development of coated granular fertilizers that minimize rapid ammonia loss, improving both environmental and economic outcomes.
- Data-Driven Application: Precision agriculture technologies determine exact fertilizer doses per crop/soil zone for optimal yields without harmful excesses.
These advances are making 2025 a hallmark year not only for greater resource efficiency, but also for climate-smart farming that can support future generations.
Comparative Impact Table: Ammonia-Based vs. Traditional Fertilizers in 2025
The following table provides a side-by-side comparison of ammonia-based versus traditional fertilizer practices in 2025, revealing how ammonia-driven innovation delivers measurable advantages in crop yield, resource efficiency, environmental performance, and green technology adoption.
| Fertilizer Type | Estimated Crop Yield Increase (%) | Estimated Resource Efficiency (%) | Environmental Impact Score (Low/Medium/High) |
Adoption of Green Technologies (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammonia-Based (With Green Ammonia and Precision Techniques) | 15 – 20% | 70 – 85% | Low | 60 – 75% |
| Ammonia-Based (Traditional Production) | 10 – 15% | 50 – 60% | Medium | 15 – 30% |
| Traditional Non-Ammonia Fertilizers | 5 – 10% | 30 – 40% | High | <10% |
As illustrated, integrating green ammonia and emerging technologies into fertilizer strategies offers substantial improvements in both crop productivity and sustainability.
For organizations aiming to track their carbon footprint and environmental performance, we recommend exploring Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting solution. It offers real-time environmental impact assessment, helping agricultural stakeholders comply with 2025’s regulatory standards and act on data-driven insights for emission reduction.
Precision Application in Ammonia Agriculture: Maximizing Fertilizer Efficiency in 2025
One of the most promising advances in ammonia agriculture is the precise application of fertilizers—improving both efficiency and environmental outcomes. Here’s how precision ammonia farming is changing the game:
- Site-Specific Fertilization: By leveraging data from IoT devices, drones, and satellites, farmers can deliver ammonia only where it is needed—reducing overapplication and optimizing yields.
- Variable Rate Technology (VRT): Modern spreaders use advanced mapping to adjust fertilizer application on the fly, responding to real-time soil and plant requirements.
- Digital Monitoring: Soil sensors and satellite imagery enable near-instant analysis of nitrogen status and crop health, supporting fine-tuned ammonia application.
- Farmonaut’s Satellite-Based Crop Monitoring: Our real-time NDVI and crop health solutions empower farmers to assess nutrient status and optimize fertilizer deployment. Check out our cutting-edge Large Scale Farm Management App for digital farm oversight and actionable insights!
Enhanced Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE): Limiting Losses, Pan-Global Gains
- Slow-Release Ammonia Fertilizers: Regulate the availability of nitrogen to the plant, ensuring uptake matches demand and reducing atmospheric or groundwater loss.
- Stabilized Fertilizers: Inhibit chemical processes that turn ammonium into other forms, thereby keeping bioavailable nitrogen in the soil longer.
- Satellite Technology API for NUE Monitoring: Through Farmonaut’s APIs and actionable insights, developers and agribusinesses can integrate real-time nutrient status tracking into their platforms, empowering smarter ammonia use in 2025 and beyond.
Explore our Fleet Management tools for advanced resource and input tracking!
Environmental Impact of Ammonia Farming: Reducing Harm & Meeting Global Goals
As global ammonia consumption remains high, addressing its environmental footprint is a top priority for 2025 and beyond. Main challenges include nutrient runoff, greenhouse gas emissions, and eutrophication. Here’s what’s being done:
- Greenhouse Gas Mitigation: By switching to green ammonia, emissions can be drastically reduced—sometimes by as much as 40% or more.
- Runoff Prevention: Tailored fertilizer timing and slow-release products help control ammonia loss during heavy rains or irrigation cycles.
- Nitrous Oxide Reduction: Improving nitrogen synchronization with crop needs lessens emissions of N2O, a potent greenhouse gas.
- Traceability Systems: Modern agriculture increasingly requires end-to-end visibility across supply chains. Our blockchain-based traceability solution ensures that every step of fertilizer input is verified, debt-free, and transparent, supporting product safety and regulatory compliance.
Policy and Regulation: The Role of Data-Driven Compliance
- Regional Restrictions & Bans: Policies like fertilizer bans in water-sensitive regions (see Indian River Lagoon case) are forcing rapid adoption of smarter, cleaner ammonia application methods.
- Certification & Reporting: Satellites and AI are now essential for verifying compliance with carbon, nitrogen, and environmental standards worldwide.
- See how digital tools are reshaping compliance and sustainability: Satellite-based Verification for Crop Loans and Insurance
Farmonaut: Revolutionizing Ammonia Agriculture with Satellite Intelligence
We at Farmonaut provide actionable, affordable technology to optimize ammonia used in agriculture for farmers, enterprises, and governments worldwide. By integrating cutting-edge satellite monitoring, AI, and blockchain into ammonia farming systems, we stand at the forefront of digital transformation in global farming—driving both productivity and sustainability. Here is what our solutions support:
- Satellite Monitoring & Remote Sensing: Multispectral satellite data delivers rapid insights on crop health, nitrogen uptake, and ammonia fertilizer needs for precision dosing and timing—reducing losses and boosting yields.
- AI Advisory Systems: Our Jeevn AI tool offers real-time agronomic recommendations, weather forecasts, and tailored strategies to maximize ammonia utilization and crop performance while minimizing environmental harm.
- Blockchain Traceability: End-to-end transparency in fertilizer movement enables compliance with sustainability standards and builds trust across the food value chain.
- Environmental Impact Tracking: Built-in tools allow users to monitor carbon footprints, resource use, and emissions in agriculture, supporting data-driven improvements and reporting.
- Fleet and Resource Management: Automated logistics help pinpoint where, when, and how much fertilizer to apply, ensuring optimal coverage and minimal waste.
Whether you manage a small farm, a regional agribusiness, or government-scale agriculture, explore how our satellite-driven insights can help you make smarter, greener fertilizer decisions in 2025.
Challenges, Risks, and Opportunities in Ammonia Agriculture for 2025
As ammonia in agriculture evolves, it faces a unique blend of hurdles and possibilities. Recognizing both is crucial for realizing ammonia’s full potential in sustainable, high-productivity farming.
- Environmental Risks: Overuse or mismanagement of ammonia-based fertilizers can lead to runoff, water eutrophication, and increased nitrous oxide emissions.
- Technological Barriers: Adoption of green ammonia and precision agtech can be cost-prohibitive and requires infrastructure investments, particularly in resource-limited regions.
- Scale & Equity: Many developing countries depend heavily on synthetic ammonia yet lack access to efficient, low-carbon options—presenting a significant global equity challenge.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Evolving environmental standards and market demands require quick adaptation and robust compliance systems. Digital, data-driven solutions are quickly becoming the new industry norm.
- Integration with Broader Food Systems: Ammonia innovations must align with regenerative, organic, and climate-smart practices for a resilient, inclusive agri-future. Discover how digital plantation, forest, and crop advisory using our platform empowers sustainable land management.
Opportunities on the Horizon
- AI-Powered Advisory & Decision Support: Satellite and AI-driven recommendation engines (like Farmonaut Jeevn AI) ensure optimal application of ammonia to maximize yield and minimize waste.
- Global Monitoring & Incentives: Digital tools enable verification for green finance, crop insurance, and ESG-driven investments, rewarding sustainable behavior and risk mitigation.
- Collaborative Data Sharing: Open, safe APIs connect diverse actors in the food chain to actionable information—amplifying the adoption of best ammonia farming practices globally.
The Future of Ammonia in Agriculture: What to Expect Beyond 2025
Ammonia’s role as the backbone of fertilizer-driven food security will continue to expand—but also transform. Here’s a glimpse into the future:
- Widespread Green Ammonia: As renewable energy costs fall and electrolyzer tech improves, green ammonia is projected to capture a growing share of markets—delivering sustainable nutrition to crops worldwide.
- Digitized Ammonia Agriculture Ecosystems: Platforms like Farmonaut will increasingly power full-stack farm management: real-time satellite guidance, mobile alerts, and seamless traceability integrated into the daily practice of farming.
- Regenerative Integration: Blending ammonia farming with regenerative, organic, and circular agricultural models to maximize both yields and ecosystem health.
- Hyper-Localized Solutions: Data-driven platforms will cater to hyper-local climates, soils, and regulatory contexts, ensuring every region gains from advances in ammonia agriculture.
- Policy Driving Innovation: As more countries impose emission caps, carbon pricing, and water quality regulations, scalable, compliant ammonia solutions will dominate.
Ready for climate-smart, high-efficiency farming? Check out our API developer docs and jumpstart your digital transformation for ammonia-powered agriculture!
FAQ: Ammonia in Agriculture for 2025 & Beyond
- Why does ammonia remain the cornerstone of modern agriculture?
- Ammonia is the primary source of bioavailable nitrogen for crops—essential for plant growth, photosynthesis, and protein synthesis. Without ammonia-based fertilizers, meeting global food demand would be impossible in both traditional and advanced agricultural systems.
- What is the difference between green ammonia and traditional ammonia?
- Green ammonia uses hydrogen generated via renewable-powered electrolysis, drastically reducing carbon emissions compared to traditional ammonia produced using fossil fuels.
- How does precision ammonia application improve efficiency and sustainability?
- By using satellite, IoT, and data analytics, farmers can apply just the right amount of ammonia fertilizer exactly where and when crops need it, reducing losses and limiting environmental impact.
- How is Farmonaut different from fertilizer manufacturers or marketplaces?
- Farmonaut is not a marketplace or a manufacturer. We provide crop and fertilizer monitoring, AI-guided advisory, and digital traceability tools via satellite—helping optimize fertilizer use, including ammonia, with actionable, data-driven insights.
- Can satellites help small farmers with ammonia agriculture?
- Absolutely! Satellite imagery and Farmonaut’s affordable monitoring solutions are scalable, supporting both smallholder and large-scale operators by providing clear, timely recommendations for fertilizer application.
Summary & Conclusion – Ammonia in Agriculture: The Cornerstone of Modern Farming in 2025
Ammonia’s journey from the foundational days of high-yield farming to the innovative, eco-conscious ammonia agriculture practices of 2025 underscores its status as the cornerstone of crop nutrition worldwide. The pivotal shift toward green ammonia—backed by digital precision, satellite intelligence, and smarter application practices—is redefining what’s possible in sustainable food production.
While challenges like environmental risk and technological equity remain, the steady march of progress, supported by emerging technologies and platforms like Farmonaut, is ensuring that ammonia farming will continue to grow as both a fundamental component for food security and a model for greener, smarter agriculture.
Whether you’re a grower, an agri-enterprise, or a policymaker, the time to embrace advanced ammonia in agriculture practices is now. Harness satellite-driven, data-empowered tools for yield, efficiency, and sustainability gains in 2025 and beyond.
Stay ahead—explore Farmonaut’s platform, APIs, and developer resources to unlock the potential of your fields and advance your ammonia agriculture strategy for the future of farming!