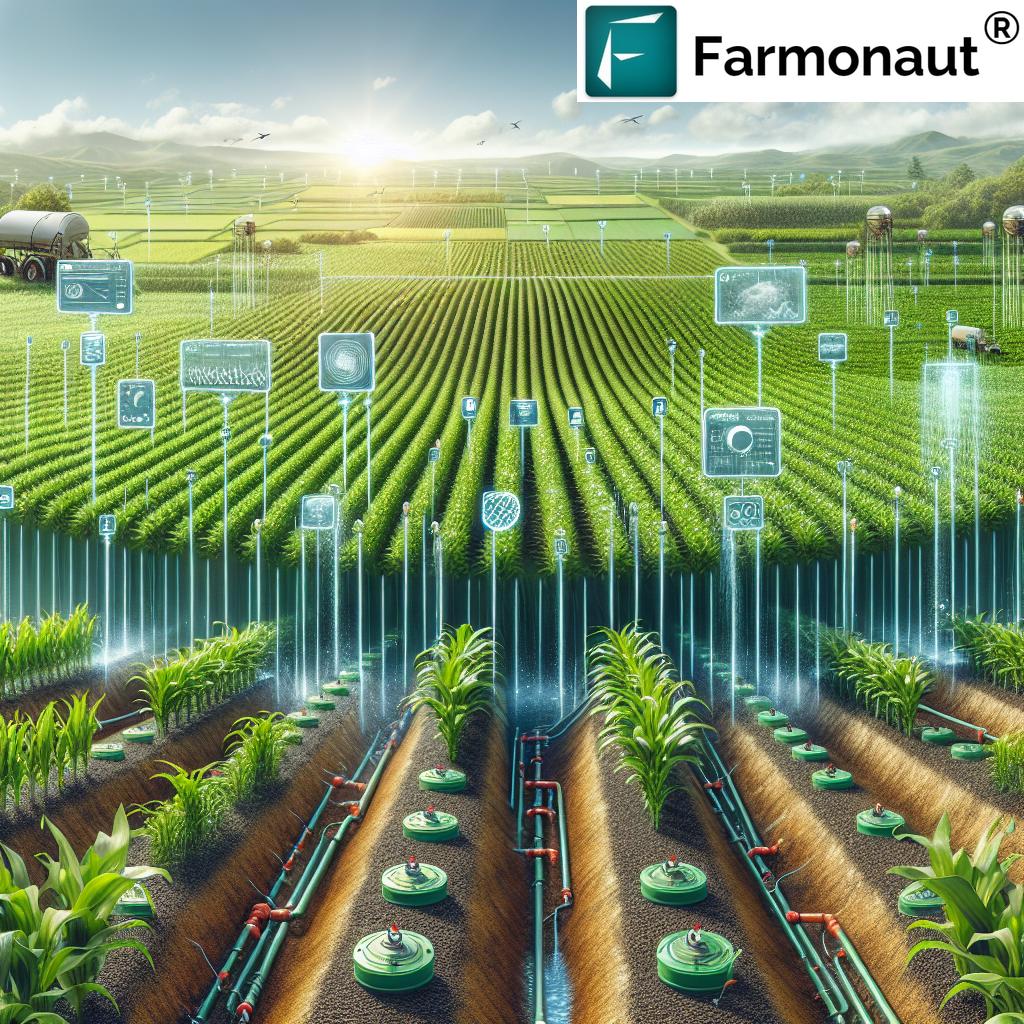
IoT Sensors in Agriculture: 7 Ways IoT Farming Sensors Boost Yields in 2025
“By 2025, over 75% of large farms worldwide are expected to use IoT sensors for real-time soil monitoring.”
Introduction: The IoT Revolution in 2025 Agriculture
The world stands at a defining crossroads in agricultural innovation as we reach 2025. The explosive rise of IoT sensors in agriculture is revolutionizing every aspect of farming—boosting crop yields, increasing efficiency, enabling real-time data-driven decisions, and making precision, sustainable farming a global reality. As climate challenges intensify and the need for higher productivity grows, leveraging technology to optimize resources and address food security challenges is rapidly becoming not just beneficial, but necessary.
IoT (Internet of Things) sensors agriculture technologies now allow farmers to monitor everything—from soil moisture and nutrient levels, to humidity, animal health, equipment use, and more—across fields, equipment, and livestock. The combination of real-time data, AI analysis, and automated systems is ushering in an era of efficiency, intelligence, and sustainability in farming.
In this comprehensive guide, we uncover the 7 most impactful ways IoT farming sensors are boosting yields and reshaping the future for farmers, food production, and our planet in 2025 and beyond.
What are IoT Sensors in Agriculture?
IoT (Internet of Things) sensors in agriculture refer to interconnected, embedded devices deployed across farms, fields, equipment, and livestock. They are designed to collect and transmit real-time data on critical parameters—like moisture content, temperature, humidity, nutrient levels, and animal health. These agriculture sensors IoT enable farmers to monitor conditions continuously, optimize management practices, and make informed decisions that directly enhance crop yields, resource efficiency, and sustainability.
- They can be installed directly in fields or soil, attached to machinery, or worn by livestock.
- Common types include soil moisture sensors, weather stations, nutrient and pH sensors, animal wearables, and smart greenhouse controllers.
- Collected data is then analyzed by AI, machine learning, or other computing systems for predictive insights and automation.
The integration of IoT sensors agriculture is pivotal for addressing global food security challenges, especially as climate variability and resource limitations increase.
“IoT sensors can reduce water usage in precision irrigation by up to 30%, according to recent agricultural studies.”
7 Transformative Ways IoT Farming Sensors Boost Crop Yields
From foundational soil monitoring to advanced fleet and resource management, let’s explore the seven most impactful applications of IoT sensors in agriculture that will define crop productivity in 2025.
1. Soil Moisture Sensors for Precision Irrigation
Soil moisture sensors are one of the most prevalent applications of IoT sensors in farming today. These devices are embedded directly into the soil, measuring moisture content at various depths and transmitting this real-time data to automated irrigation systems or mobile dashboards. This precision monitoring ensures that water is delivered only when and where crops need it, significantly improving irrigation efficiency and promoting sustainability.
- Reduces waste by lowering unnecessary water use and preventing over-irrigation, critical in regions facing water scarcity.
- Lowers costs by minimizing water bills and energy consumption from pumping.
- Enhances crop yields by maintaining optimal hydration levels for root development and plant growth.
- Minimizes environmental impact through efficient resource use.
When linked to automated irrigation systems, soil moisture sensors empower farmers to set precise, data-driven schedules for watering crops—even remotely or based on predictive analytics, harnessing the power of AI.
2. Weather Stations & Microclimate Monitoring
Weather and environmental sensors are another critical use case for IoT sensors agriculture. IoT weather stations monitor temperature, humidity, rainfall, wind, and solar radiation in real-time, providing farmers with hyperlocal, granular insights into microclimate variations across different zones within their fields or large farms.
- Enables early prediction of pest infestations, diseases, and frost risks by monitoring weather conditions favorable for their emergence.
- Guides variable-rate application of inputs (fertilizers, pesticides, etc.), ensuring uniform crop growth.
- Supports climate adaptation strategies in regions frequently facing unpredictable weather shifts.
For example, integrating weather station data with Farmonaut’s Sat-Weather API enables agronomists and app developers to deliver real-time, site-specific weather forecasts and alerts directly to farmers, facilitating timely, informed interventions.
3. Nutrient Sensors for Targeted Fertilization
Maintaining optimal soil nutrient levels is vital for high crop productivity. IoT nutrient sensors are deployed in fields to measure key elements such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and even pH. This data is invaluable for creating smart fertilization schedules that deliver inputs precisely when and where needed.
- Reduces fertilizer waste by preventing over-application or runoff, protecting surrounding ecosystems.
- Lowers input costs for farmers.
- Ensures plants receive essential nutrients during critical growth stages, enhancing quality and yield.
- Minimizes environmental impact by reducing nutrient leaching into waterways.
Incorporating nutrient sensor data with platforms like Farmonaut’s AI-based advisory system enables tailored recommendations on fertilizer type, amount, and timing, further boosting farm efficiency and sustainability.
4. Crop Health Sensors & Early Disease/Pest Detection
Combining IoT crop health sensors (such as leaf wetness, chlorophyll, and multispectral imaging sensors) with aerial (drone/satellite) technologies, gives farmers the ability to detect problems before they become losses.
- Identifies early signs of plant stress, nutrient deficiency, diseases, or pest infestations—often before they’re visible to the human eye.
- Enables proactive measures (targeted pesticide or fungicide application), significantly reducing reliance on chemical sprays and minimizing environmental impact.
- Supports uniform growth by guiding timely interventions across large or multi-zone farms.
With Farmonaut’s real-time crop health monitoring and NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) analytics, even remote or large-scale farm operators can track every critical metric, improving yield and protecting crops.
5. Livestock Sensors for Health & Welfare Monitoring
Livestock and animal wearable IoT sensors are transforming animal husbandry by enabling continuous monitoring of health, behavior, and location.
- Wearable sensors collect and transmit vital signs (heart rate, temperature, movement patterns) and quickly detect illness or distress in animals, enabling early intervention and reducing livestock losses.
- GPS-enabled trackers help in managing grazing patterns, preventing theft or loss, and optimizing field use.
- Improves overall welfare and aids compliance with animal health and security standards.
Automated data collection from livestock sensors minimizes manual labor and enhances decision-making for both large-scale dairy, meat, and mixed farming operations, further enhancing productivity and profitability.
6. Smart Greenhouse Sensors & Automated Environment Control
Indoor and protected environment agriculture is evolving rapidly with the deployment of smart greenhouse sensors. These multi-sensor systems monitor and automatically regulate:
- Light intensity
- CO2 levels
- Soil nutrients
- Temperature and humidity
Automated adjustment of climate variables within greenhouses—including shading, ventilation, irrigation, and lighting—maximizes plant growth, reduces manual intervention, and supports year-round high-quality crop production.
- Yields increase significantly, as each crop receives custom microclimate conditions for optimal health.
- Production costs and energy consumption are lowered as systems only operate in direct response to plant needs.
- Supports cultivation of high-value or off-season crops, giving farmers new market opportunities.
7. Sensors for Fleet, Resource & Environmental Management
The modern, connected farm leverages IoT sensors not only within fields or greenhouses, but also across fleets and facilities to increase operational efficiency and sustainability.
- Fleet & Equipment Monitoring Sensors: Embedded in tractors, planters, sprayers and harvesters to track usage, location, fuel consumption, and maintenance needs.
- Environmental Sensors: Measure air, water, and soil parameters for carbon footprinting, pollution control, and compliance with ecological standards.
- Resource Usage Sensors: Monitor electrical, water, and fertilizer input use for optimal allocation and waste reduction.
Explore Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting tools to track and minimize your farm’s environmental impact, or Fleet Management features to optimize machinery and logistics for cost reduction.
Comparison Table: 7 Key IoT Agricultural Sensors & Their Benefits
| IoT Sensor Type | Primary Function | Typical Data Measured | Estimated Yield Improvement (2025) | Application Area |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Moisture Sensor | Monitors soil water content for optimal irrigation | Soil moisture %/VWC | 10–25% | Irrigation management, drought mitigation |
| Weather Station | Tracks local climate and forecasts weather risks | Temperature, humidity, rainfall, wind, solar | 5–15% | Pest control, disease management, scheduling |
| Nutrient Sensor | Measures soil nutrients and pH for fertilization | Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium, pH | 10–20% | Fertilization, precision input application |
| Leaf Wetness & Chlorophyll Sensor | Detects plant health, stress & early disease symptoms | Leaf wetness, chlorophyll fluorescence | 8–18% | Disease alerting, crop health monitoring |
| Livestock Wearable Sensor | Tracks animal health, behavior & location | Heart rate, temperature, GPS position | 5–12% | Livestock health, managing grazing, early intervention |
| Greenhouse Sensor Array | Controls climate & nutrient variables automatically | CO2, light, temp, humidity, soil EC | 12–22% | Greenhouse climate, hydroponics, controlled production |
| Fleet Tracker & Environmental Sensor | Monitors machinery, emissions, and resource usage | Location, run time, energy, emissions data | 6–15% | Fleet, resource, & environmental management |
IoT Integration & Tech Advancements Shaping Agriculture in 2025
The value of IoT sensors in agriculture is magnified by advances in connectivity, analytics, and integration with complementary technologies. As we move deeper into 2025:
- Widespread use of 5G and Low Power Wide Area Networks (LPWAN) makes IoT deployment in rural and remote regions feasible and cost-efficient, even on smallholder and developing-world farms.
- Sensor hardware is becoming more durable, with longer battery lives and robust designs to withstand harsh agricultural conditions.
- AI and machine learning platforms integrate incoming sensor data, providing predictive analytics for harvest timing, yield forecasting, risk assessment, and precision planning.
- Automated systems make real-time adjustments to irrigation, fertilization, and environmental controls—minimizing labor and maximizing yield.
- Blockchain-based traceability solutions, such as Farmonaut’s traceability platform, ensure trusted, tamper-proof records of all farm inputs and outputs from seed to shelf.
How Farmonaut is Empowering Precision Agriculture with Data & Insights
As a leader in agtech, we at Farmonaut champion the principle that every farmer—whether managing a small plot or a vast estate—should have affordable access to real-time, actionable data. That’s why our platform leverages satellite imagery, AI, and the latest in agricultural science.
-
Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring:
- We employ multispectral satellite images to deliver NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index), soil moisture analytics, and pest/disease alerts to any connected device.
- This allows farmers to optimize irrigation, fertilization, and crop protection strategies.
-
Jeevn AI Advisory:
- Our AI engine provides personalized crop management, weather forecasts, and expert advisories that incorporate both IoT sensor and satellite data for maximum precision.
-
Blockchain Traceability:
- Assures product authenticity for food and textile supply chains. Learn more on blockchain-based traceability here.
-
Fleet and Resource Management:
- Helps manage equipment logistics and optimize operational costs; see our Fleet Management dashboard.
-
Carbon Footprinting & Sustainability:
- Offers real-time tracking of emissions and compliance tools; more details at our Carbon Footprinting solution.
-
Crop Loan & Insurance Support:
- We facilitate satellite-based verification for crop loan approvals and insurance risk assessment. Visit Crop Loan & Insurance services for details.
Our platform is accessible via Android, iOS, Web App, or API, making precision agriculture accessible and scalable everywhere.
Challenges and the Future of IoT Sensors in Farming
Despite IoT sensors in agriculture revolutionizing farming practices, several challenges need continued attention:
- Data Security & Privacy: With increased connectivity, safeguarding farm and personal data against breaches and misuse becomes critical. Strong cybersecurity protocols and trusted platforms are essential.
- Interoperability: As sensor brands and platforms proliferate, ensuring devices from different makers can communicate and integrate smoothly is vital for a seamless farm management ecosystem.
- Farmer Training & Adoption: Maximizing the benefits of IoT requires digital skills. Ongoing training and intuitive interfaces lower the barriers for adoption by all groups of farmers.
- Cost & Accessibility: While sensor prices are falling, upfront costs can challenge smallholder or developing-region farmers. Affordable, scalable solutions—like those provided by Farmonaut—are closing this gap.
- Connectivity: Rural broadband and mobile coverage remain uneven in some areas, though advances in 5G/LTE/Mesh networks are rapidly improving accessibility.
Looking to 2025 and beyond, we anticipate IoT in agriculture will further integrate with robotics, AI, satellite tech, and even blockchain-based supply chain transparency—giving rise to the truly intelligent, fully sustainable smart farm.
- Automated drones for seeding, spraying, and monitoring will become common.
- Real-time, blockchain-verified crop history and input use will be a standard for food markets.
- Climate-resilient farming strategies will rely on multi-source IoT data for adaptive planning.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are IoT sensors in agriculture?
IoT sensors in agriculture are connected, data-collecting devices installed in fields, equipment, or on livestock to monitor environmental and operational variables. They provide farmers with real-time insights that enable precision management for higher crop yields and resource efficiency.
How do soil moisture sensors benefit farming in 2025?
Soil moisture sensors measure the water content in soil, allowing automated irrigation systems to deliver water only where and when crops need it. In 2025, these sensors help farmers optimize water usage, increase yields, minimize waste, and combat drought conditions efficiently.
Are IoT sensors only for large farms?
No, while large farms are rapidly adopting IoT sensors, modern sensor technology (including satellite-based solutions) has become increasingly affordable and scalable for smallholder and medium-sized farms.
How can IoT sensors help with climate change and sustainability?
IoT sensors optimize resource use, minimize wastage, reduce reliance on chemical inputs, and enable data-driven sustainability practices. They also provide carbon footprint monitoring—empowering farmers to adapt to and mitigate the effects of climate change.
What role does Farmonaut play in IoT-enabled agriculture?
We empower farmers worldwide with affordable, satellite-driven crop health and soil moisture analytics, Jeevn AI advisory, blockchain-based traceability, and resource management tools—all integrated with IoT concepts. Our mission is to make precision and sustainable agriculture accessible to all, powering a smarter food future.
Conclusion: Embracing the Digital Future of Agriculture
As we step into 2025, the integration of IoT sensors in agriculture is revolutionizing how farmers grow food, manage resources, and secure their future. From optimizing irrigation and fertilization to real-time crop health monitoring and precision livestock management, the possibilities of IoT farming sensors are limitless.
This technology does not replace the knowledge and dedication of farmers—it amplifies their capacity, making each decision smarter and each harvest more abundant. With scalable, affordable solutions from technologies like Farmonaut, the benefits of the IoT in farming are within everyone’s reach—driving a future where agriculture is efficient, sustainable, and capable of feeding a changing world.