Moisture Control Secrets: 7 Hacks for Perfect Soil!
Table of Contents
- Moisture Control: Why It Matters in Soil, Agriculture & Forestry
- Understanding Soil Moisture Dynamics
- 7 Moisture Control Hacks for Agriculture
- Moisture Control Techniques in Forestry
- Advanced Techniques & Smart Technologies
- Comparative Techniques Effectiveness Table
- Challenges and Key Considerations
- Farmonaut: Smart Soil Moisture Management Solutions
- Farmonaut Subscription Pricing
- FAQ: Moisture Control & Soil Management
- Conclusion
Moisture Control: Why It Matters in Soil, Agriculture & Forestry
Moisture control is the foundation of successful agriculture, farming, and forestry. Water availability and effective soil moisture management dictate plant health, crop yields, and forest vitality. Whether we’re focused on maximizing food production or sustaining natural forests, maintaining the right water levels in soil is absolutely essential. Too much water (waterlogging) leads to root damage, while too little causes drought stress, stunting growth and ruining yields.
Our goal, then, is clear: ensure plants and trees receive adequate, but not excessive, water by applying effective moisture control techniques. We’ll dive deep into the latest practices in soil water retention, mulching for agriculture, cover crops for soil health, rainwater harvesting, drip irrigation systems, soil moisture sensors, and more.
Whether we’re large-scale farmers, smallholders, or forest managers, understanding the dynamics of soil moisture is the first step toward sustainable, high-yield, and healthy crop or tree systems. And with advances in technology—especially platforms like Farmonaut—we now have unprecedented tools to optimize moisture control across every field and forest.
Understanding Soil Moisture Dynamics: The Science Behind Moisture Control
Soil moisture refers to the amount of water present in soil pores at any given time. It’s a complex interplay between soil type, organic matter content, weather, crop/root uptake, and farm management practices.
- Absorption: Plants absorb water from the root zone; available water depends on soil structure and moisture retention capacity.
- Evaporation: Water evaporates from both soil (surface evaporation) and transpiration through plant leaves (evapotranspiration).
- Percolation & Drainage: Excess water moves downward; if drainage is poor, waterlogging can occur, harming roots.
Key Factors that Influence Soil Moisture:
- Soil Type: Sandy soils drain quickly (low retention), while clay-rich soils hold more moisture but may cause waterlogging.
- Organic Matter (e.g., compost, mulch): Increases water retention, supports soil structure, and sustains microbial growth.
- Weather Conditions: Rainfall, temperature, humidity, and wind affect evaporation and plant water demand.
- Land Management Practices: Tillage, mulching, and cropping choices impact moisture control.
Achieving **optimal** soil moisture depends on routine assessment, adaptive irrigation, and proactive soil care. In the next sections, we’ll present the **7 best hacks for moisture control** using the most effective, science-backed approaches.
Soil Moisture Management: 7 Moisture Control Hacks for Agriculture
Let’s explore the most impactful moisture control techniques for agricultural fields. By adopting these soil management practices, we can significantly increase water-use efficiency, boost crop yields, and make our farming operations more resilient to changing weather.
“Drip irrigation systems use up to 50% less water than traditional methods, optimizing soil moisture with precision technology.”
1. Conservation Tillage Practices
Conservation tillage involves reducing or eliminating soil disturbance. By leaving previous crop residues (leaves, stems, stalks) on the soil surface, we create a protective layer that:
- Minimizes soil erosion by wind and rain
- Improves organic matter content and soil structure
- Enhances soil water retention—less water lost to evaporation
- Reduces rapid runoff and promotes rain infiltration
This practice is especially valuable on sloped fields or in regions exposed to heavy rainfall. By reducing tillage passes, we also cut fuel and labor costs, making it a sustainable and cost-effective approach to maintaining adequate soil moisture and health.
Learn more about conservation tillage techniques here.
2. Cover Crops for Soil Health
Cover crops—like clover, rye, or vetch—are grown during off-season periods or between main crops:
- They form a living mulch that prevents soil erosion and reduces water runoff
- Improves organic matter as roots and residues decompose, enriching soil structure
- Acts as a physical barrier, lowering surface evaporation and suppressing weed growth
- Boosts soil fertility by fixing nitrogen (especially leguminous cover crops), reducing the need for chemical inputs
Cover crops are an essential part of sustainable and effective soil moisture management because they enhance water retention and build resilience against both droughts and heavy rains.
Explore more about cover crops and their benefits here.
3. Mulching for Agriculture
Mulching involves spreading a layer of organic or inorganic material (straw, wood chips, leaves, even plastic sheeting) over the soil surface. This simple but powerful technique:
- Reduces evaporation by shielding soil from direct sun and wind
- Maintains moisture levels more consistently in root zones
- Regulates soil temperature, keeping soil cooler in summer and warmer in winter
- Suppresses weed growth and, as organic mulch breaks down, adds valuable organic matter
- Improves water infiltration and decreases soil crusting after rains
Scientific studies have shown mulching can decrease soil moisture loss by up to 25%, which directly improves crop yields and reduces irrigation needs.
Read more about mulching for agriculture and its impact on soil moisture.
4. Crop Rotation for Soil Moisture Dynamics
Crop rotation is the practice of growing different crops in sequence on the same plot. For instance, alternating between deep-rooted and shallow-rooted crops means:
- Roots access water from different soil depths, making optimal use of available moisture
- Improves soil structure and increases water-holding capacity
- Reduces risk of soil depletion and pests associated with monoculture
This dynamic, adaptive rotation leads to a healthier soil ecosystem and aids in both drought mitigation and waterlogging prevention.
5. Rainwater Harvesting in Farming
Rainwater harvesting is about capturing and storing rainfall for future irrigation— rather than allowing it to run off our fields. This practice:
- Ensures a consistent water supply during dry periods or drought
- Reduces dependency on groundwater or external water sources
- Helps maintain adequate moisture in remote or rain-fed regions
Typical systems range from simple barrels and tanks under roof gutters to advanced field-scale catchment ponds linked to drip irrigation systems.
Learn more about effective rainwater harvesting here.
6. Drip Irrigation Systems
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the plant roots through a network of pipes and emitters. Here’s why it’s a game-changer for soil moisture control:
- Minimizes evaporation—only target root zones get wet, saving up to 50% water compared to surface irrigation
- Avoids waterlogging and runoff (critical for clay soils)
- Reduces weed growth by keeping inter-row areas dry
- Easy to automate for consistent moisture, even on large fields or greenhouses
Drip irrigation is ideal for row crops, vegetables, orchards, and in regions facing scarce water supply.
Want to integrate drip irrigation into a larger smart farming system? Explore Farmonaut’s API to access soil and crop health data for precise irrigation scheduling.
7. Soil Moisture Sensors—Smart Water Management
Soil moisture sensors are technology-enabled devices that measure the real-time water content of soils. They empower us to:
- Precisely monitor soil moisture levels across different field sections
- Schedule irrigation only when and where it’s needed
- Avoid both overwatering (risk of waterlogging) and underwatering (drought stress)
- Integrate with advanced farm management platforms for optimization
When paired with satellite imagery and AI, as seen in Farmonaut’s platform, soil moisture sensors transform everyday farming. With these tools, we optimize crop water use, reduce costs, and promote truly sustainable water management.
Learn more about latest Farmonaut AI-based advisory tools for moisture management using the apps here.
Moisture Control Techniques Effectiveness Table: Comparative Overview
| Technique | How It Works | Estimated Water Savings (%) |
Suitable Crop Types | Ease of Implementation | Relative Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conservation Tillage | Leaves crop residues on soil surface, reduces erosion & evaporation | 15–30% | All major grains, pulses, oilseeds | Moderate | Low–Medium |
| Cover Crops | Plants like rye/clover are grown in off-season to cover and enhance soil | 10–25% | Cereals, veg, orchards, pulses | Moderate | Low |
| Mulching | Applies organic/inorganic materials to soil surface, preserving moisture | 20–50% | Vegetables, fruit trees, ornamentals | Easy | Low–Medium |
| Crop Rotation | Alternates crop types over seasons; roots access varying depths | 10–20% | All crops | Easy | Low |
| Rainwater Harvesting | Captures/stores rain for irrigation; prevents runoff | Variable, up to 30% |
All rain-fed crops | Moderate–Advanced | Medium–High |
| Drip Irrigation Systems | Delivers water directly to roots via pipes/emmiters | 30–50% | Veg, orchards, row crops |
Advanced | Medium–High |
| Soil Moisture Sensors | Monitors soil water with electronic sensors for precision control | 10–40% | All field crops, greenhouses |
Moderate–Advanced | Medium |
Moisture Control in Forestry: Specific Techniques for Forest & Tree Management
Forestry presents unique challenges for moisture management due to the diversity of tree species, forest floor layers, and micro-environments. Here are essential practices for maintaining optimal soil moisture and forest health.
Forest Floor Management Techniques
A well-managed forest floor, rich in leaf litter and organic matter, acts like a sponge:
- Absorbs rainfall, storing moisture near root zones
- Reduces runoff and mitigates drought effects
- Promotes slow releasing of water to trees
By maintaining this organic layer, especially in semi-arid regions, we greatly improve water retention and forest resilience.
Selective Thinning
Thinning out dense stands allows remaining trees to access more soil moisture (less competition for water and nutrients). This is crucial for:
- Boosting tree growth rates and stand vitality
- Helping forests survive dry periods and drought stress
- Maintaining healthy undergrowth, which also aids moisture retention
This is especially impactful during the reforestation or post-logging recovery phases.
Establishing Riparian Buffer Zones
Buffer zones—strips of native trees and plants along streams and rivers—fulfill several vital functions:
- Regulate water flow into forest areas, preventing erosion
- Absorb excess water during storms, releasing it during dry spells
- Preserve water quality for forest and wildlife health
These natural sponges are invaluable for strategic moisture control in forestry.
Soil Erosion Control in Forest Areas
Implementing erosion control measures—such as planting ground covers or using silt fences—helps:
- Prevent soil loss after heavy rains
- Maintain soil structure that is critical for water retention capacity
- Reduce surface runoff and non-point source pollution
Combined with other moisture control practices, this supports the overall health and vitality of forests.
Advanced Moisture Management: Integrating Technology, Control Systems & Smart Farming
Modern farming and forestry increasingly rely on technological advances to achieve effective soil moisture management. Let’s look at some advanced solutions and their applications:
- Subsurface Drainage Systems: In humid or high rainfall regions, installing tile drainage pipes or tiles helps remove excess water, reduce waterlogging, and maintain optimal aerobic conditions for roots.
- Automated Drip Irrigation: Coupled with weather forecasts and soil moisture sensors, it ensures each plant receives just enough water.
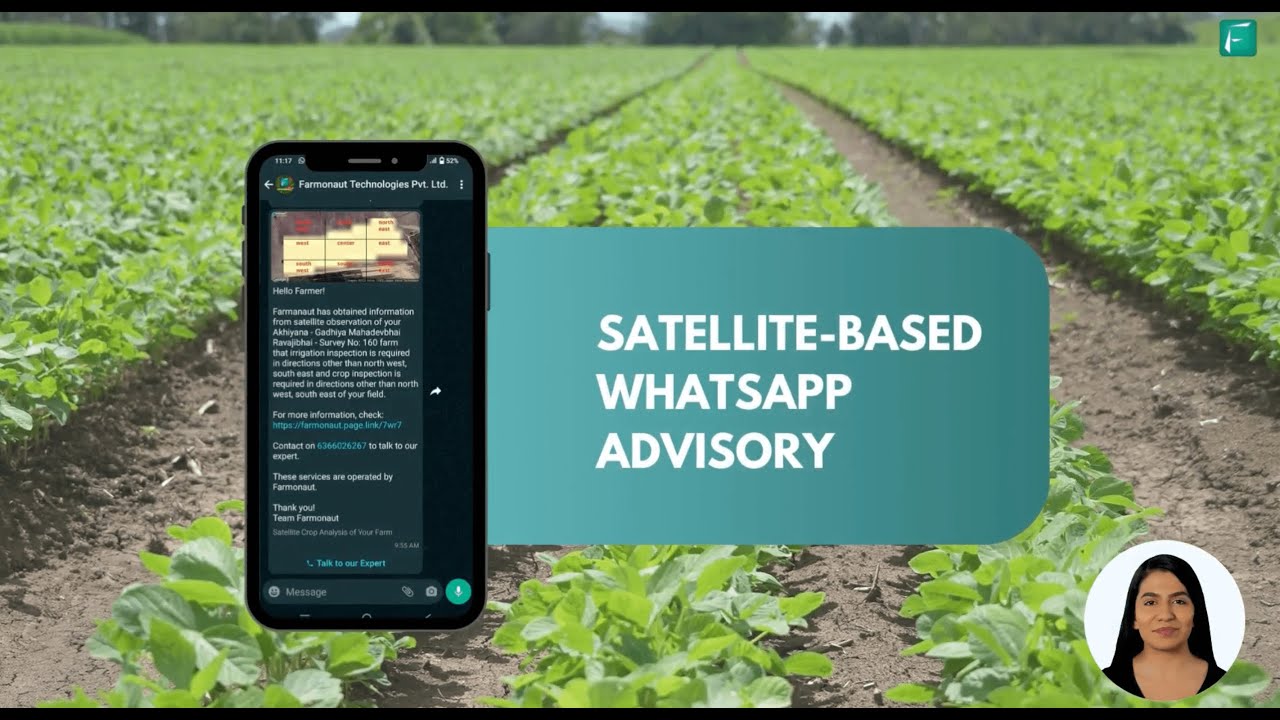
- Remote Sensing & Satellite Monitoring: Platforms like Farmonaut provide real-time data on soil moisture content, crop health, and weather patterns, allowing us to adapt moisture control strategies dynamically.
- Blockchain Traceability: For industries demanding proof of sustainable water use, Farmonaut’s traceability platform gives auditable records of every moisture control input and harvest, promoting trust and transparency in agricultural supply chains.
- Carbon Footprinting: Efficient soil moisture management also reduces energy consumption (e.g., from irrigation pumps). Track your fields’ environmental impact using Farmonaut’s carbon tracking solutions to make farming operations even more sustainable.
If you’re interested in integrating data-driven technology for moisture control and overall farm management, Farmonaut’s Large Scale Farm Management solution is tailored for cooperatives, agribusinesses, and landowners.
Moisture Control Challenges & Considerations: What to Watch Out For
Implementing advanced moisture control and soil management techniques is not one-size-fits-all. Here are some important factors and challenges:
- Soil Type Matters: Sandy soils benefit most from mulching and irrigation; clay soils need careful drainage to avoid waterlogging.
- Climate Variability: Extreme weather (heatwaves or storms) can abruptly change moisture needs and stress crops or trees.
- Initial Costs: Advanced systems (drip irrigation, drainage, sensors) may require upfront investment, but usually offer strong long-term returns via resource savings and higher yields.
- Labor & Knowledge: Techniques like conservation tillage may call for farmer training and more careful equipment use.
- Crop and Species Selection: Drought-tolerant varieties or deep-rooted trees are better suited for low-rainfall regions.
- Monitoring & Adaptation: Ongoing monitoring, such as with Farmonaut’s satellite data, is necessary to keep up with changing field conditions.
The most effective approach is always tailored. We must assess the specific characteristics of our land, crops, climate, and resources—then implement, monitor, and fine-tune the best moisture control techniques for our operation.
Farmonaut: Smart Moisture Control for Sustainable Agriculture & Forestry
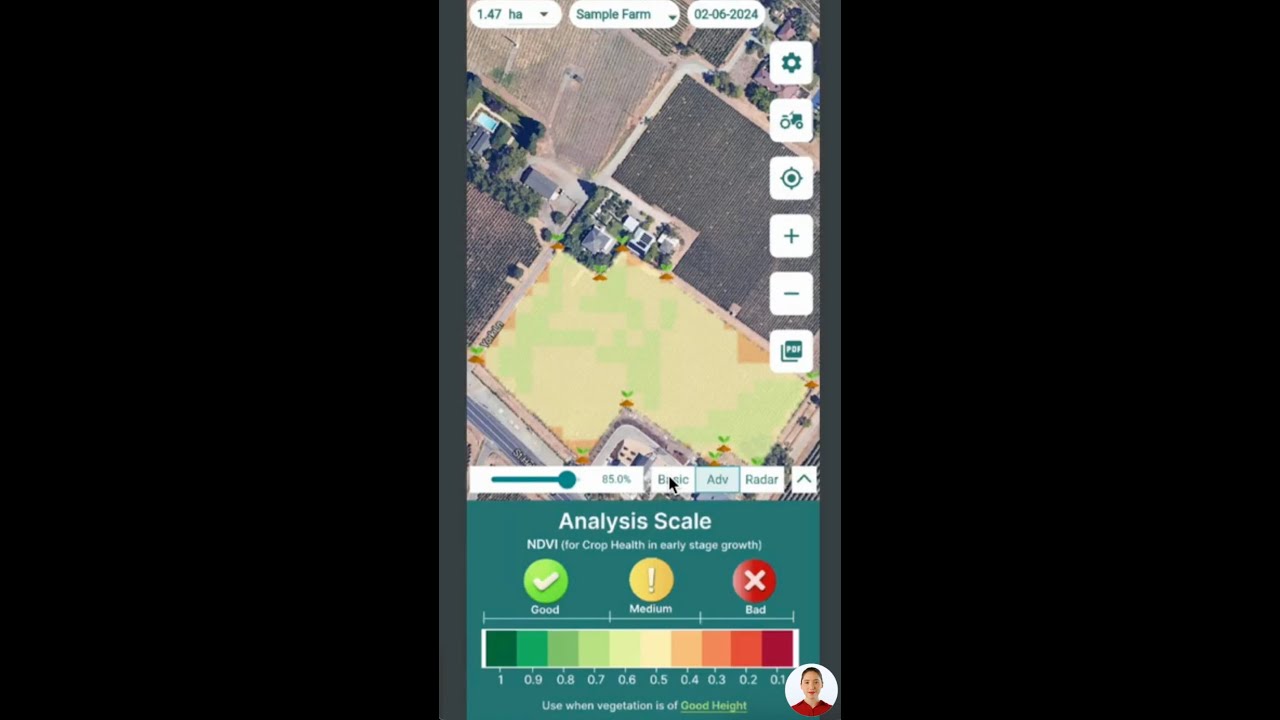
At Farmonaut, our mission is to bring precision agriculture and smart moisture management within reach of every farmer, forester, and agribusiness. Our platform leverages satellite imagery, AI, and real-time data to help you:
- Assess soil moisture content across your farms or forests from your smartphone or desktop
- Monitor crop health using NDVI and other advanced vegetation indices
- Get AI-powered advisory (via Jeevn AI) on when to irrigate, when to harvest, and how to optimize yields
- Automate reporting and integrate with fleets, weather forecasts, and traceability solutions
- Track carbon footprint for climate-smart, sustainable farming
Our technology empowers everyone—from smallholder farmers to large-scale forestry managers—to maximize yields, conserve water, save costs, and improve long-term land health.
Interested in farm loans or insurance? Farmonaut’s crop loan and insurance verification uses satellite data to streamline and secure access to financing, reducing fraud and speeding up approvals for agri-professionals.
To integrate Farmonaut’s satellite data, API access is available for developers and agri-businesses: Access the Farmonaut API here or view the developer documentation.
Ready to transform your farm or forestry operations with affordable, cutting-edge technology?
Farmonaut Subscriptions: Flexible, Scalable, and Accessible
With Farmonaut’s tier-based subscriptions, choose what’s right for you—be it a small plot or thousands of hectares. Our pricing is designed for scalability, flexibility, and maximum impact.
Check the live subscription pricing below and select the ideal package for your crops, forests, or agribusiness needs:
Frequently Asked Questions: Moisture Control, Soil Management & Farmonaut
-
Q1: Which soil moisture management technique offers the greatest water savings?
A: Drip irrigation systems and mulching for agriculture stand out. Drip systems can save up to 50% water, while mulching reduces evaporation by 20–50% depending on material and climate. -
Q2: Can I use Farmonaut’s services for forestry management as well?
A: Yes! Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring and advisory tools track moisture, health, and environmental trends in forests in addition to conventional farms. -
Q3: What is the easiest moisture control hack for small-scale farmers?
A: Mulching and cover crop planting. Both require minimal investment and deliver significant improvements in soil moisture retention and weed suppression. -
Q4: Are moisture control technologies suitable for all soil types?
A: Yes, but different soils benefit most from different techniques. Sandy soils require more water retention methods (mulch, organic matter), while clay soils often need drainage. -
Q5: What is the importance of soil moisture sensors?
A: Soil moisture sensors supply accurate data, preventing both over- and under-watering. They help automate smart irrigation and save resources, especially on large-scale farms. -
Q6: How does technology improve moisture management?
A: By using remote sensing, satellite monitoring, and AI-advisory tools (like those in Farmonaut apps), we can precisely track soil conditions, weather, and respond faster to risks—maximizing yields and sustainability. -
Q7: Where can I download the Farmonaut app?
A: Farmonaut’s mobile apps are available for Android and iOS. The web version works on any browser.
Conclusion: Mastering Soil Moisture for Resilient, Productive Farms & Forests
Moisture control is the cornerstone for healthy, productive agriculture and forestry. By using strategic soil moisture management techniques—from mulching, conservation tillage, and cover crops to advanced drip irrigation and monitoring systems—we ensure that each plant and tree receives the right amount of water at the right time.
The challenges of climate variability, drought, and resource scarcity make adopting these best practices not just desirable, but essential. Integrating technology—like Farmonaut’s data-driven platform, real-time crop/soil monitoring, blockchain traceability, and carbon footprinting tools—unleashes extraordinary potential for sustainable yields and forest vitality.
We’re all stewards of our soil and water, whether managing a smallholder farm, a commercial field, or a vast forest. By embracing innovative moisture control techniques, we protect our land for generations and set the foundation for a more resilient agricultural future.
Ready to go from knowledge to action? Optimize your irrigation, reduce costs, and watch your yields soar.
Get Started with Farmonaut now!
For comprehensive, affordable, and sustainable soil moisture management, Farmonaut empowers us at every step. Explore, manage, and thrive.