Sugar Cane Farming 2026: Smart Advances Shaping Production
Advancements and Trends in Sugar Cane Farming and Production in 2025–2026
- Introduction: The Global Role of Sugar Cane Farming
- Modern Sugar Cane Farming Practices (2025–2026)
- Precision Agriculture & Remote Sensing in Sugar Cane Production
- The Role of Smart Sugar Cane Harvesters
- Sugar Cane Production and Processing Technology Trends
- Comparison Table: Smart Technologies in Sugar Cane Farming (2025–2026)
- Sustainability and the Circular Economy in Sugar Cane
- Blockchain Traceability: Ensuring Transparency in the Sugar Cane Chain
- Challenges, Climate Resilience & the Future of Sugar Cane Farming
- Empowering Sugar Cane Farmers: Farmonaut’s Satellite Solutions
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Introduction: The Global Role of Sugar Cane Farming
Sugar cane farming remains one of the world’s most important agricultural industries, forming the backbone of rural economies in tropical and subtropical regions. As we move into 2026, the evolution of modern sugar cane farms is accelerating, driven by technological innovations, changing market dynamics, and ambitious sustainability goals. This article explores the state of advanced sugar cane farming, the integration of smart practices in the production and processing chain, and the future prospects for farmers searching for a sugar cane farm near me.
With over 1.9 billion tonnes harvested annually, sugar cane is not only essential for sugar production but also plays a critical role in the agricultural economy, supporting food security, energy (bioethanol), and sustainable practices worldwide. Let us delve into the latest advancements shaping sugar cane farming in 2025–2026 and beyond.
Modern Sugar Cane Farming Practices (2025–2026)
Modern sugar cane farming as we approach 2026 is defined by the adoption of smart, sustainable, and efficient cultivation methods. Farmers are increasingly utilizing a symphony of precision agriculture tools—powered by satellite imagery, drones, and soil sensors—to optimize every step, from land preparation to irrigation and fertilization.
- Precision Planting: Automated equipment ensures uniform seed placement and density, maximizing sunlight usage and yields.
- Crop Rotation & Intercropping: Sugar cane farms now implement rotation with legumes or other crops to maintain soil fertility, prevent disease outbreaks, and enhance biodiversity.
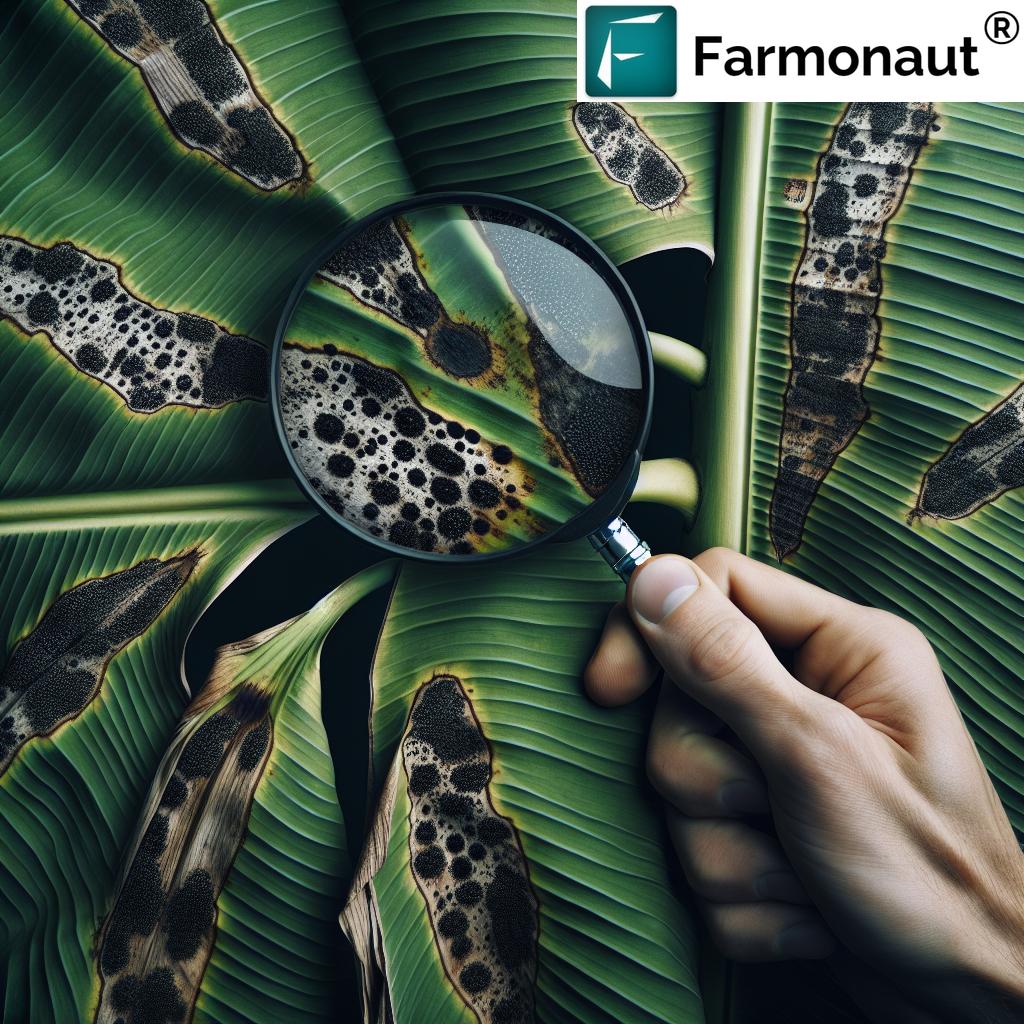
- Biological Pest Management: Farmers are shifting to integrated pest management (IPM) that combines targeted chemical use with natural predators to reduce environmental impact.
- Resilient Varieties: High-yield, drought-resistant sugar cane varieties—developed via advanced breeding and biotechnology—are common on farms, enhancing resilience to climate variability and maximizing output in harsher conditions.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Sensors, drones, and satellite platforms are leveraged to catch early warning signs of pest or disease outbreaks and address issues proactively.
The essence of modern sugar cane cultivation is maximizing resource use while minimizing negative environmental impact—a key consideration for the entire production chain from 2025 onwards.
Precision Agriculture & Remote Sensing in Sugar Cane Production
Leveraging Satellite Technology, Sensors & AI for Future-Ready Sugar Cane Farming
Precision agriculture is reshaping the way farmers manage sugar cane farming. With remote sensing innovations and data-driven analysis, farms achieve higher operational efficiency, reduce input costs, and improve yields while safeguarding soil health.
- Satellite Imagery: Regular multispectral images from satellites allow farmers to monitor crop health, evaluate soil moisture, and optimize resource use at the field level—often via mobile apps.
- AI & Machine Learning: Algorithms trained on historical and live crop data predict potential outbreaks (disease, pests), weather anomalies, and provide actionable insights for farm management.
- IoT Sensors: Connected field sensors monitor temperature, moisture, and nutrient levels—helping farms deliver just the right amount of water and fertilizer.
- Drones: Drones improve pest management, crop scouting, and can even facilitate targeted application of agrochemicals or biofertilizers, reducing waste and environmental impacts.
- Blockchain Integration: Blockchain ensures traceability—from farm to processing mills—documenting every stage in the chain for quality, safety, and consumer trust.
These advances in technology are set to define sugar cane farming well into the future, emphasizing not only productivity but also sustainability and transparency in the entire supply chain.
The Role of Smart Sugar Cane Harvesters
Automated Harvesting: Speed, Precision, and Data-Driven Gains in 2025–2026
The sugar cane harvester landscape has transformed in 2025 with the entrance of GPS-incorporated, AI-driven, and sensor-equipped harvesters. What was once a labor-intensive phase now capitalizes on robotized machines that selectively cut mature cane, minimizing damage to stalks and soil while maximizing both speed and harvest efficiency.
- GPS Navigation Systems: Modern harvesters are guided by real-time GPS, traversing fields with pinpoint accuracy for uniform cutting and optimal row coverage.
- Onboard Sensors: Smart harvesters utilize visual and NIR (near-infrared) sensors to analyze cane maturity and quality, ensuring only the best mature stalks are harvested.
- Real-Time Data Transmission: Data on crop quality and volume is transmitted instantly to mills, allowing better planning and optimization of the processing chain.
- Eco-Friendly Mechanization: Electric and hybrid harvester models are emerging to reduce carbon emissions and lower operational costs.
These advancements ensure that modern sugar cane harvesters play a crucial role in increasing productivity and sustainability across sugar cane farms worldwide.
Sugar Cane Production and Processing Technology Trends
Optimizing the Entire Sugar Cane Processing Chain for 2025 and Beyond
Once harvested, speed and quality are paramount—sugar cane rapidly loses sucrose if not processed promptly. In 2026, mills are seamlessly linked with farm data to enhance supply chain transparency and efficiency.
- Real-Time Linkage: Digital integration connects harvested crop data directly with processing mills, ensuring tracking, inventory management, and quality control.
- Efficient Extraction: Automated presses allow for higher recovery rates from cane, reducing both labor and time.
- Bagasse Utilization: Bagasse—the leftover plant fiber—serves as a renewable biofuel, supplying mills with energy for processing.
- Specialty Sugars & By-Products: Technological advancements allow for production of organic, low-glycemic, or specialty sugars, while by-products like molasses and bioethanol further diversify income streams.
- Water Recycling: Advanced filtration and recycling units reduce water usage in the production process, further optimizing sustainability.
These steps position leading sugar cane farms near major markets at the forefront of sustainable agriculture and efficient sugar cane production.
Comparison Table: Smart Technologies in Sugar Cane Farming (2025–2026)
Below is a detailed table comparing the pivotal technological innovations in modern sugar cane farming and processing for 2025–2026. This handy guide helps farmers, agribusiness professionals, and researchers rapidly assess impacts on yield, costs, and sustainability across major technologies.
| Technology Name | Main Function/Feature | Estimated Increased Yield (%) | Estimated Cost Savings (%) | Sustainability Impact | Projected Adoption Rate (2026, %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPS-Guided Smart Sugar Cane Harvester | Precision harvesting using GPS & AI sensors for selective cutting, transmitting real-time data to mills | 12–15% | 18–22% | High (Lower fuel use & post-harvest loss) | 68% |
| Satellite-Based Crop Monitoring | Real-time remote sensing, detecting stress & optimizing irrigation/fertilization via mobile/web apps | 11–13% | 13–19% | High (Water use down, input efficiency up) | 76% |
| AI Predictive Analytics | Forecasts yield, pest risks, and climate impact using historical and real-time data | 8–10% | 9–12% | Medium–High (Early interventions reduce losses) | 59% |
| Precision Irrigation System | Soil moisture sensors automate and optimize water scheduling for minimal waste | 10–14% | 18–21% | High (Optional drip integration) | 61% |
| Automated Extraction & Processing Equipment | Significantly reduces cane-to-sugar process time, increases recovery ratio | 10–12% | 20–27% | Medium–High (Supports biofuel/bagasse use) | 55% |
| Blockchain-Based Traceability | Full farm-to-market traceability for sustainability, safety, and compliance | Varied (mainly quality assurance) | up to 7% | High (Promotes ethical & sustainable supply chains) | 28% |
| Drones for Crop Scouting & Input Delivery | Monitor fields, map health, and perform precision agrochemical sprays | 5–7% | 6–8% | Medium (Reduces chemical drift/waste) | 34% |
Sustainability and the Circular Economy in Sugar Cane
The future of sugar cane farming is inseparable from sustainability. Circular economy models are increasingly adopted—reusing by-products, cutting emissions, and driving resource efficiency.
- Bagasse Power Generation: Residual biomass powers mills, supplying energy for processing while reducing dependency on fossil fuels.
- Bioethanol Production: Sourced from both molasses and direct cane juice, bioethanol contributes to renewable energy goals while opening new markets for producers.
- Carbon Footprinting: Leading farms use digital tools to monitor and manage emissions. Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting platform offers satellite-driven solutions to track, report, and reduce carbon impact in sugar cane production.
- Water & Nutrient Cycling: Closed-loop systems recycle water throughout processing; some fields implement leachate recapture from runoff to retain nutrients.
All these practices aim to improve resilience, protect soil and water, and prepare sugar cane farms for a climate-driven future.
Blockchain Traceability: Ensuring Transparency in the Sugar Cane Chain
As market expectations increase for transparency and compliance, blockchain-based traceability is becoming pivotal in the sugar cane supply chain. This technology guarantees a tamper-proof ledger for every step—from farm to mill to consumer.
- Authenticates the origin and sustainability of sugar cane farms near critical markets.
- Prevents fraudulent substitutions or mislabeling along the chain.
- Supports premium product claims—such as organic or fair-trade certifications—improving market access for farmers and mills.
- Consumers increasingly demand transparency, pushing adoption of platforms like Farmonaut’s agriculture traceability solution for the sugar cane processing industry.
Challenges, Climate Resilience & the Future of Sugar Cane Farming
2026 and Beyond: Evolving Practices for Resilience and Market Shifts
Despite remarkable advancements, sugar cane farming faces looming challenges in the coming years. Changing climate conditions, labor shortages, market volatility, and regulatory demands all necessitate constant adaptation.
- Climate Change: Irregular rainfall and rising temperatures prompt urgent development of enhanced and resilient varieties.
- Labor Dynamics: The shift towards mechanization (especially smart harvesters) mitigates labor supply risks, but also requires digital upskilling of rural workforces.
- Water Scarcity: Precision irrigation and soil sensors help farms reduce water use and adapt to variability.
- Regulatory & Compliance: From environmental to consumer safety standards—especially for bioethanol—digital traceability and audit platforms are key for mills and exporters.
The future is about continuous innovation, adoption of smart technologies, and an unwavering commitment to sustainable sugar cane farming—ensuring the crop remains one of the world’s most important and resilient crops globally.
Empowering Sugar Cane Farmers: Farmonaut’s Satellite Solutions
As Farmonaut, our mission is to democratize satellite technology for accessibility and affordability in modern agriculture. Our satellite-based solutions enable farmers, mills, and agribusinesses to monitor sugar cane crop health, soil status, and resource use with precision—from planting to processing.
- Real-Time Satellite Crop Health Monitoring: Farmers receive regular NDVI and soil data, supporting evidence-based interventions to prevent losses in sugar cane production.
- AI Advisory: Our Jeevn AI System delivers timely, tailored strategies for field operations (weather, irrigation, pest alerts), optimizing for local climate, soil conditions, and market dynamics.
- Resource and Fleet Management: Our Fleet Management platform streamlines logistics for machines and vehicles across multiple sugar cane farms, reducing downtime and operational costs.
- Blockchain Integration: Enabling traceability through our traceability solution—supporting quality assurance and regulatory compliance throughout the entire chain.
- Environmental Impact Monitoring: Our carbon footprint monitoring service helps farms and mills track emissions (CO2, water use), supporting sustainability certifications and operational improvements.
- Scalable Farm Management: From smallholder to enterprise, our Large Scale Farm Management platform provides customizable dashboards for multi-farm operations, ensuring seamless crop, soil, and resource management.
- Access to APIs: For advanced analytics and integration, visit our API page or consult the developer documentation.
- Benefit from our real-time crop health and soil monitoring, ensuring the best yield and quality for your sugar cane fields.
- Use our Jeevn AI for dynamic field-specific advisory on irrigation, pests, and harvest timing—ideal for maximizing efficiency in varying climates
- Leverage our APIs for integrating satellite intelligence into your existing farm management or enterprise resource platforms.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Sugar Cane Farming 2025–2026
-
What are the main innovations transforming sugar cane farming in 2026?
Modern sugar cane farming is shaped by smart harvesters, satellite-based crop health monitoring, precision irrigation, blockchain traceability, and advanced resource management—each helping optimize yields, costs, and sustainability. -
How do smart harvesters outperform traditional manual harvesting?
Smart harvesters selectively cut mature cane with minimum damage, utilize GPS navigation, analyze maturity, and transmit real-time data, boosting yield by up to 15% and significantly reducing losses. -
Why is satellite monitoring critical for efficient sugar cane farms?
Satellites provide frequent, large-scale imagery to assess soil health, crop vigor, and detect risks early—enabling farmers to act swiftly, conserve resources, and maximize returns, whether you are running a sugar cane farm near me or on another continent. -
How does digital traceability add value to sugar cane supply chains in 2025–2026?
Blockchain-led solutions ensure end-to-end visibility, authenticate origin, and support sustainability and compliance—giving mills and exporters a competitive advantage and building consumer trust. -
Can sugar cane farming be profitable and sustainable in the future?
Absolutely. The adoption of precision farming, renewable energy practices, carbon tracking tools, and specialty by-product markets is helping farmers balance profitability and sustainability, even as climate challenges intensify. -
Is Farmonaut an online marketplace, regulations platform, or farm machinery manufacturer?
No. Farmonaut provides data-driven, satellite technology-based solutions for monitoring, advisory, traceability, and environmental impact—not hardware, regulatory services, or farm input e-commerce. -
How can I access Farmonaut’s services for my sugar cane farm?
Download the Farmonaut app on Android or iOS, or access our web platform. API and integration details are available for developers looking to incorporate our solutions.
Conclusion: The Future of Sugar Cane Farming and Production
Sugar cane farming is undergoing a dynamic shift as we approach 2026, embracing smart technologies, sustainability, and data-driven decision-making. The fusion of precision agriculture, AI-enabled harvesters, blockchain traceability, and environmental monitoring ensures that the entire production chain can continue to evolve—maximizing yields, reducing costs, and advancing both market and societal sustainability goals.
Those seeking a “sugar cane farm near me” in today’s world will find enterprises that not only deliver high-quality, responsibly produced sugar, but also serve as models for future-ready agriculture. By embracing the latest innovations in sugar cane production and processing, the industry stands poised for a vibrant and sustainable future.
Discover the smart solutions powering tomorrow’s agriculture, and join the movement to a more sustainable and efficient global food economy.