GIS in Agriculture: 7 Ways GIS is Used in Farming 2025
“Over 70% of precision agriculture operations in 2025 will rely on GIS for mapping and yield analysis.”
The use of GIS in agriculture has fundamentally redefined how we approach crop production, environmental stewardship, and food security. In recent years, advances in geographic information systems (GIS) have revolutionized modern farming and forestry by offering farmers, agronomists, and environmental professionals powerful tools for real-time management, smart decision-making, and actionable insights. Heading into 2025, the role of GIS in farming is not just growing—it’s becoming integral to sustainable, precision agriculture and our strategies for feeding a growing population while protecting our planet.
What is GIS in Agriculture?
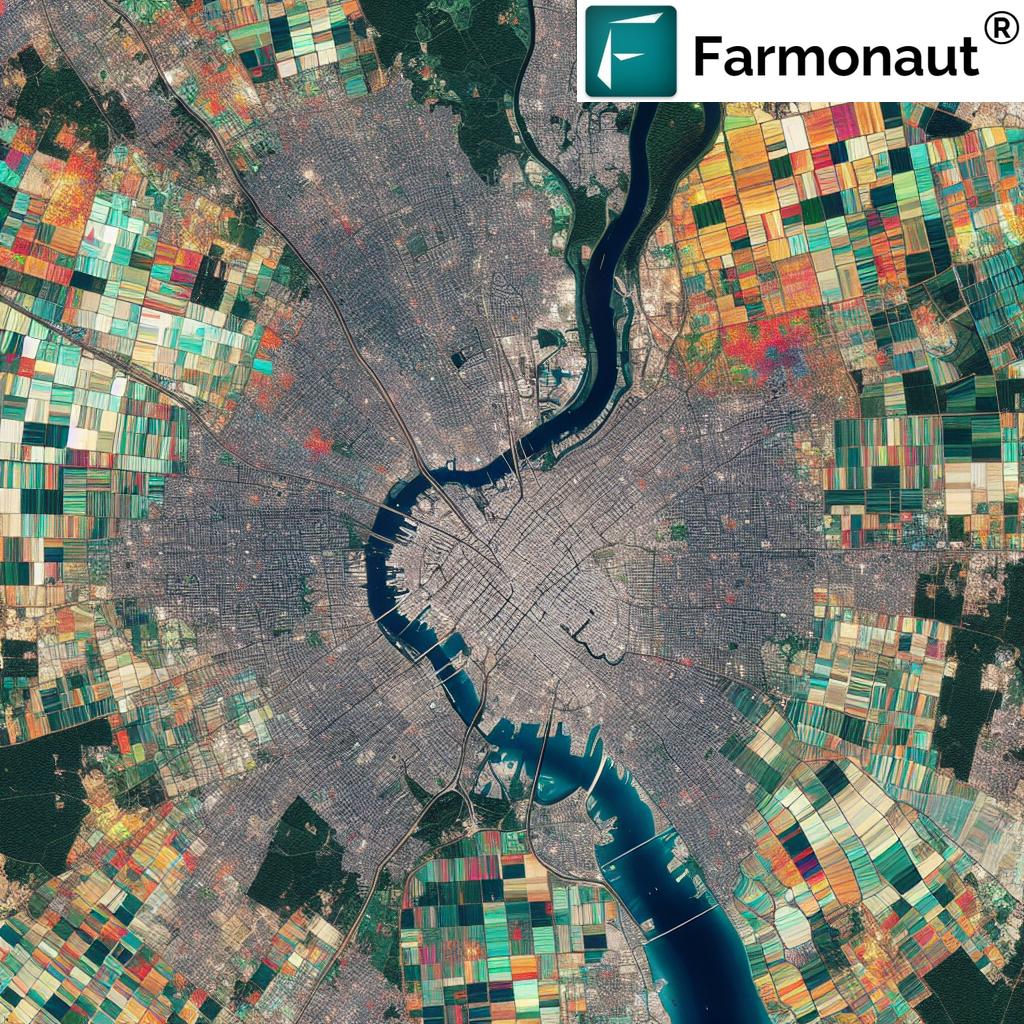
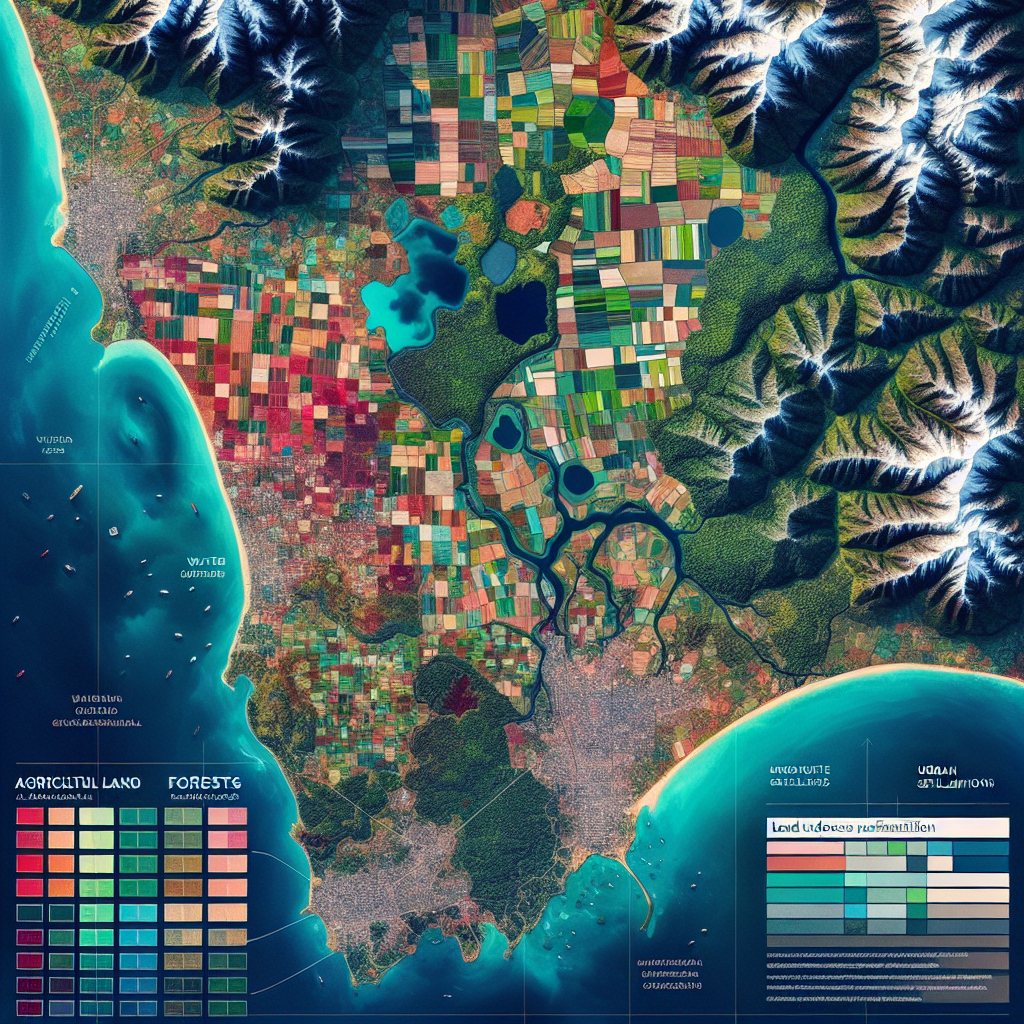
GIS in agriculture refers to the use of spatial mapping and geo-data technologies to analyze, manage, and optimize farming operations. At its core, a GIS combines layers of spatial information—such as soil types, crop health, weather patterns, water availability, and land use—with powerful data visualization and analytics tools. This approach enables stakeholders—from smallholder farmers to large agribusinesses—to visualize relationships and patterns across their farm fields, supporting more informed decisions about planting, irrigation, nutrient management, pest control, and sustainability.
The essence of GIS use in agriculture lies in its ability to collect, store, and manipulate vast quantities of geographic data. These systems help farmers and agricultural professionals map fields, track crop performance, assess environmental impact, and align operations with both current field conditions and future predictions. This data-driven approach is at the heart of precision agriculture, minimizing waste and maximizing yield while supporting sustainable resource management.
Benefits of GIS in Agriculture
The impact of GIS use in agriculture extends to nearly every facet of the agricultural value chain—from individual field practices to large-scale environmental resource management. Here are some of the standout advantages:
- Enhanced Efficiency: GIS enables precision farming techniques that reduce input costs, optimize resource utilization, and make every drop of water or gram of fertilizer count.
- Improved Decision-Making: Spatial analysis yields actionable insights for field management, pest control, and regulatory compliance.
- Sustainability: By supporting environmentally responsible farming—minimizing chemical use, conserving water, protecting soil health—GIS helps move agriculture toward a sustainable future.
- Risk Mitigation: Real-time monitoring of weather, pests, disease, and changing conditions reduces crop loss risk and increases farm resilience to climate change.
- Yield Optimization: Insights from GIS yield mapping allow farmers to target high and low-performing zones within a field, boosting data-driven productivity every season.
“GIS technology can reduce fertilizer use by up to 30% through targeted application in modern farming.”
GIS in Agriculture: 7 Ways GIS is Used in Farming 2025
Let’s explore the focused applications that demonstrate exactly how GIS is used in agriculture in 2025, helping agriculture progress toward greater efficiency, resilience, and sustainability.
-
Precision Farming and Mapping
Leading-edge GIS platforms enable farmers to collect and analyze granular spatial data about their fields, such as soil composition, nutrient levels, and moisture content. Using GPS-guided machinery integrated with GIS, inputs like seeds, fertilizers, and pesticides are applied variably and precisely—technology called Variable Rate Application (VRA).
- This targeted input approach maximizes yields while minimizing waste and environmental impact.
- It solves the problem of resource underuse or overuse across different field zones, directly influencing crop health and profitability.
- Farmonaut’s platform, for instance, offers satellite-based precision mapping that is affordable and accessible to all farm sizes worldwide.
Learn how GIS-powered carbon footprinting improves precision and sustainability in agriculture.
-
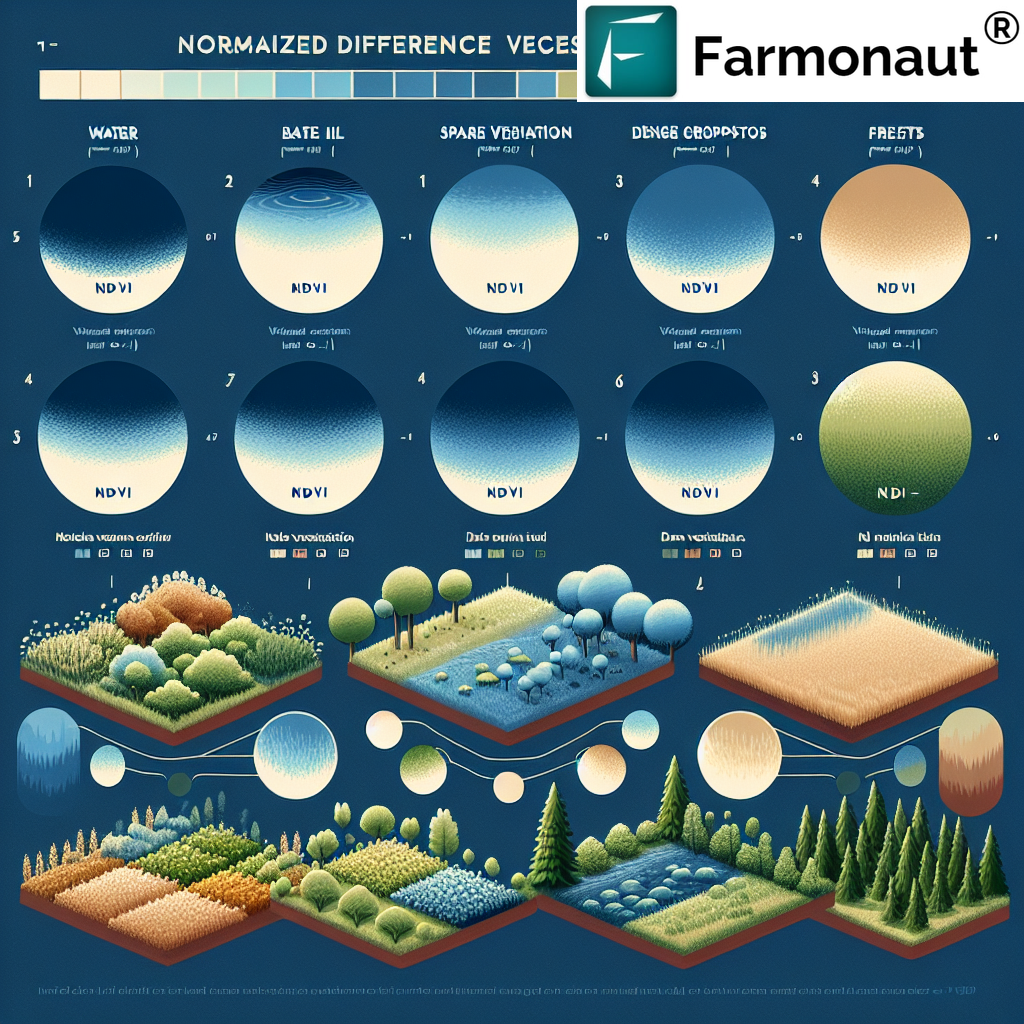
Crop Health Monitoring and Management
Using satellite imagery, drones, and AI-powered analytics, GIS platforms provide up-to-date information on crop conditions, detect pest infestations, and disease outbreaks early. This application is especially critical to minimize yield loss.
- Real-time image analysis highlights unhealthy zones due to stress, pest, or disease.
- Allows for the early detection of issues and precise intervention (such as targeted spraying) that reduces losses and optimizes the use of agrochemicals.
- Our Farmonaut platform offers real-time monitoring and AI-based advisory—enabling actionable, location-specific recommendations for farmers everywhere.
Try Farmonaut’s live satellite-based crop health monitoring for your farm (Web, Android, iOS).
-
Soil and Water Management
GIS in farming helps to map soil types, monitor moisture levels, and plan irrigation scheduling. This is critical for optimizing water use efficiency and conserving finite water resources—an accelerating challenge in light of climate change and water scarcity.
- Better understanding of spatial soil variability supports adoption of appropriate tillage and cropping practices.
- Reduces runoff, soil erosion, and ensures optimal plant growth by matching irrigation and nutrient delivery to actual needs.
- Farmonaut incorporates real-time soil moisture analytics—helping users optimize irrigation and reduce wastage.
-
Yield Prediction and Mapping
GIS analyzes historical crop yield data, environmental factors, and weather records to model and predict future outputs. Yield maps generated after each harvest enable the identification of both high-yielding and problematic zones within fields.
- This supports data-driven improvements in subsequent planting cycles and helps target interventions for maximum productivity.
- Agro-businesses and governments use GIS-based yield mapping for regional food security planning.
- Farmonaut supports yield prediction and mapping across all user segments, making these insights accessible everywhere.
-
Land Use Planning and Farm Management
For both small and large-scale agriculture, GIS mapping is vital for land parcel delineation, boundary verification, and zoning. These capabilities support crop rotation planning, plantation establishment, and efficient land allocation.
- GIS helps agribusinesses keep precise digital records of property and field boundaries—improving both governance and operational efficiency.
- Governments utilize GIS data for policy making, subsidy distribution, and land use conservation.
- Our Farmonaut Large Scale Farm Management platform delivers advanced spatial tools tailored for enterprise-scale land planning and administration.
Discover Farmonaut’s enterprise GIS features for land use planning and efficient field management.
-
Climate Impact Analysis & Risk Management
As climate patterns shift, GIS helps agriculture adapt. GIS tools assess the effects of climate change on agricultural landscapes—guiding farmers to shift planting dates, select resilient crops, and refine risk management strategies.
- Early warnings and simulation models enable anticipation and mitigation of risks related to drought, flooding, and extreme weather events.
- The integration of satellite monitoring and weather data within platforms like Farmonaut is central to modern risk management approaches.
-
Blockchain-Based Product Traceability
A critical innovation for agriculture supply chains, blockchain integration with GIS enhances traceability and transparency. Stakeholders can track products from farm to table, secure in the knowledge that every stage—harvest, storage, transport—is timestamped and geo-referenced.
- Enhances food safety, reduces fraud, and fosters consumer trust—all vital to the future of agriculture.
- Farmonaut offers end-to-end blockchain-based traceability solutions for food and raw material supply chains.
Read more about product traceability and how GIS-secured blockchain builds food supply chain trust.
How Farmonaut Leverages GIS for Sustainable, Precision Farming
We at Farmonaut are dedicated to transforming agricultural operations through access to affordable, satellite-powered GIS tools. Our technology suite enables everyone in the agricultural value chain—from individual farmers to large agribusinesses and government agencies—to harness real-time crop health monitoring, resource allocation, and risk management capabilities.
By leveraging the latest advancements in satellite imagery, AI, blockchain, and machine learning, we help farmers:
- Monitor vegetation health (NDVI) and detect problems like nutrient deficiency, water stress, or pests across every corner of their field.
- Receive AI-powered advisory on weather, irrigation, and nutrient application for each field zone via our Jeevn AI system.
- Enhance supply chain transparency with blockchain-backed traceability.
- Efficiently manage logistics, machinery, and fleet operations for maximum productivity and minimal environmental impact.
- Track and minimize their carbon footprint for a truly sustainable agricultural future.
Comparative Table: GIS Applications and Their Benefits
| GIS Application | Estimated Impact on Yield (%) | Sustainability Benefit | Key Technologies Used |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precision Mapping & Variable Rate Input | 5-20% | Reduces waste, minimizes environmental impact | Satellite imagery, GPS, VRA sensors |
| Crop Health Monitoring & Disease Detection | 5-15% | Early intervention, reduces chemical use | Drones, Satellite imagery, AI analytics |
| Soil & Water Resource Management | 3-12% | Conserves water, improves soil health | Soil sensors, Remote sensing, GIS analytics |
| Yield Prediction & Mapping | 5-10% | Informs input planning, reduces risk | Historical data, Statistical GIS models |
| Land Use Planning & Farm Management | 5-25% | Reduces land misuse, supports biodiversity | GIS mapping, Satellite & drone imaging |
| Climate Impact Analysis & Risk Management | 5-18% | Mitigates crop loss, increases resilience | Climate models, Real-time satellite data |
| Blockchain Product Traceability | 2-8% | Builds consumer trust, reduces fraud | Blockchain, GIS tagging |
The Future of GIS in Agriculture & Forestry: 2025 and Beyond
By 2025, the role of GIS in agriculture and forestry will only become more increasingly integral as precision agriculture, digital innovation, and sustainability take center stage in tackling the challenges of our era—climate change, resource scarcity, and mounting food demand. Key trends for the future include:
- Wider accessibility: As cloud-based GIS platforms and mobile apps proliferate, farmers worldwide—even in remote regions—gain real-time access to rich satellite and weather data.
- Integration with AI and machine learning: Automated decision support will become smarter, offering ever more precise yield predictions, adaptive spraying, and dynamic risk mitigation.
- Expansion of IoT (Internet of Things) and sensors: Combining GIS with in-field sensors, drones, UAVs, and remote sensing enhances the accuracy of monitoring and interventions—giving a more complete picture than ever before.
- Sustainability mandates: With pressure mounting to meet net-zero emissions goals, GIS will underpin carbon footprint tracking and environmental compliance for both small and large farm operations.
At the vanguard of these changes, Farmonaut continues to make precision agriculture affordable, scalable, and impact-driven for all.
GIS in Forestry: Resource Management and Conservation
GIS isn’t just for cropping systems; it’s equally critical in forestry. Key roles of GIS in forestry include:
- Forest Inventory Management: Accurately map tree species, age, health, and biomass.
- Risk Assessment: Pinpoint zones at risk of fire, pest infestations, or illegal logging.
- Biodiversity Protection: Geographically track wildlife, conserve critical habitats, and plan corridors for species movement.
- Reforestation and Sustainable Harvest Planning: Use spatial data to schedule optimal replanting and minimize environmental disturbance.
We at Farmonaut support these forestry applications by delivering powerful remote sensing and management tools for governments, conservationists, and plantation enterprises.
Farmonaut: Technology Options and Seamless Access
- Web, Android & iOS app: Access live farm monitoring from any device. All core features can be managed on the go, making data-driven farming possible everywhere.
- API Access: For agritech developers and businesses, you can integrate Farmonaut’s crop, soil, and weather data into your own products or research systems. View our public API here and explore the API developer documentation.
-
Subscription Options: Choose scalable subscription plans below to suit farm sizes and business needs:
- Specialty services: From traceability to fleet management and carbon footprinting, Farmonaut offers a comprehensive suite of GIS-powered agritech solutions.
FAQ on GIS Use in Agriculture
What is GIS in agriculture?
GIS in agriculture refers to the application of Geographic Information Systems—a framework for gathering, managing, and analyzing spatial and geographic data—specifically for farm and food system operations, from mapping fields to monitoring crop health and optimizing resource use.
How is GIS used in agriculture in 2025?
In 2025, GIS is used in agriculture for precision field mapping, targeted fertilizer application, monitoring crop growth with satellite/drone imagery, managing water and soil resources, predicting yield, planning land use, and enhancing supply chain traceability. The technology enables smarter, more sustainable decision-making at every level.
What are the major benefits of GIS in farming?
Major benefits include reduced waste, lower input costs, maximized crop yields, improved environmental sustainability, early detection of pest or disease outbreaks, optimized irrigation, and stronger climate resilience.
How does GIS enhance sustainability in agriculture?
By supporting data-driven, targeted interventions, GIS ensures only the right amount of resources—water, fertilizer, pesticide—is used exactly where needed. This minimizes environmental impact, helps conserve biodiversity, and supports sustainable farming for future generations.
Can smallholder farmers benefit from GIS?
Yes. Platforms like Farmonaut are designed to be affordable and require no special hardware, making sophisticated GIS tools available even to smallholders and individual farmers.
What technologies are integrated within modern GIS for agriculture?
Modern GIS solutions for agriculture combine satellite imagery, drone and remote sensing, soil and climate data, artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain for traceability.
How does GIS support climate risk management in farming?
GIS enables ongoing monitoring of weather, soil moisture, and crop health; it supports scenario modeling to predict the impact of drought, floods, or other extremes; and it helps farmers plan resilient cropping patterns to adapt to the realities of climate change.
Conclusion: GIS in Agriculture Driving the Future of Sustainable Food Production
As we move through 2025, GIS in agriculture continues to break new ground—propelling global farming into an era of precision, sustainability, and resiliency. By harnessing spatial information, leveraging innovations in satellite monitoring, AI, and blockchain, and making data-driven decisions, we can optimize yields, minimize environmental harm, and ensure food security for future generations. The question for agriculture is no longer if GIS will be used—but how fast we can scale its benefits to reach everyone, everywhere.
We at Farmonaut are proud to stand at the forefront of this movement—offering feature-rich, scalable GIS tools that empower farmers, agribusinesses, and governments worldwide.
Start your GIS-powered farming journey with Farmonaut today!