Comprehensive Guide to Land Classification: LULC, Terrain, and Landscape Analysis for Agriculture
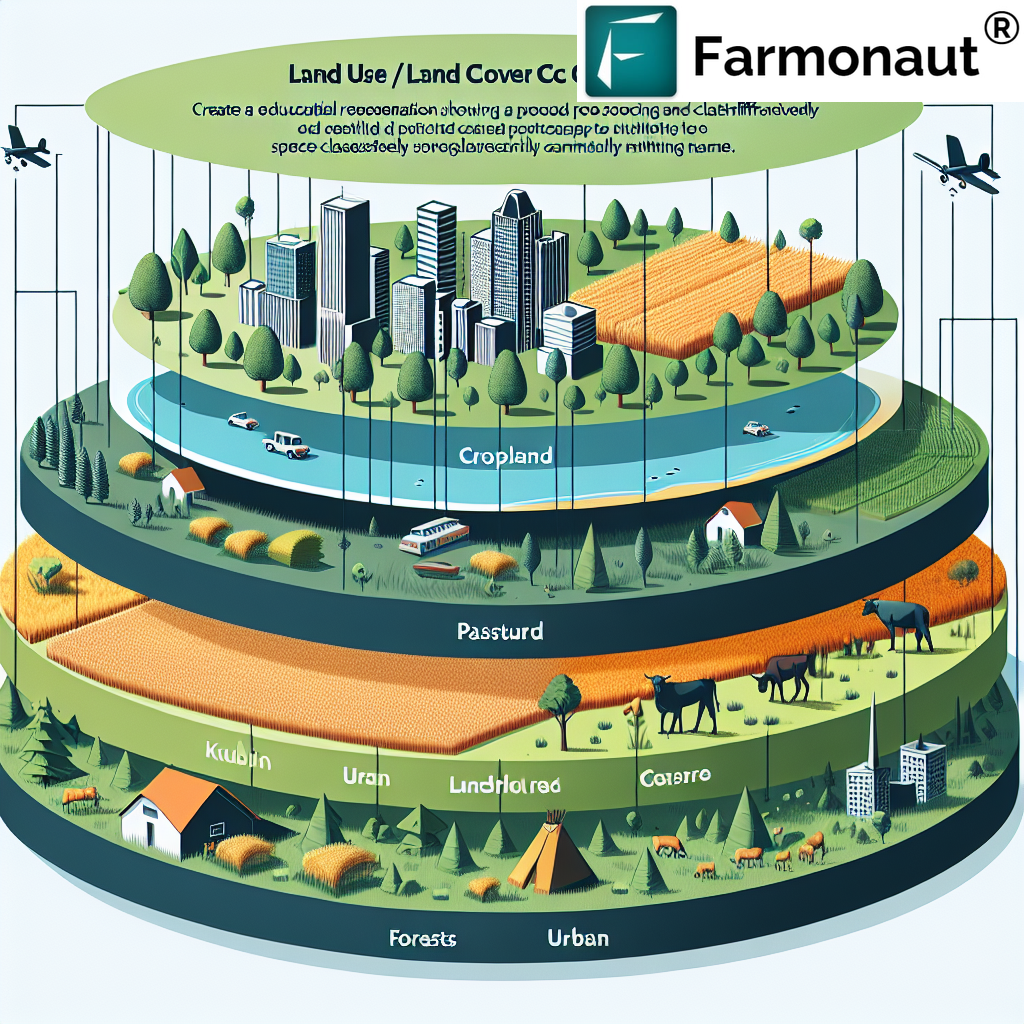
In the ever-evolving world of agriculture and environmental management, understanding the intricacies of land classification is crucial. At Farmonaut, we recognize the importance of this knowledge in optimizing agricultural practices and promoting sustainable land use. This comprehensive guide delves into various aspects of land classification, including Land Use and Land Cover (LULC) classification, terrain classification, and landscape classification. Our goal is to provide you with in-depth insights that can help enhance your agricultural practices and environmental stewardship.
1. Introduction to Land Classification
Land classification is a fundamental process in understanding and managing our planet’s resources. It involves categorizing land areas based on various characteristics such as vegetation cover, soil type, topography, and human use. This classification serves as a crucial tool for decision-makers, urban planners, agriculturists, and environmental scientists.
At Farmonaut, we leverage advanced satellite technology and AI to provide precise land classification data, enabling our clients to make informed decisions about land use and management. Our satellite-based crop health monitoring system, accessible through our mobile app, offers real-time insights into vegetation health and soil conditions.
2. Understanding LULC Classification
Land Use and Land Cover (LULC) classification is a critical component of land classification. It provides a comprehensive view of how land is being utilized and what natural or artificial cover exists on the Earth’s surface.
What is LULC Classification?
LULC classification categorizes land based on its use (human activities) and cover (physical characteristics). This classification helps in understanding the dynamics of land use changes, urban sprawl, deforestation, and agricultural expansion.
LULC Classification Levels
LULC classification is typically organized into hierarchical levels, each providing more detailed information:
- Level I: Broad categories such as Urban, Agricultural, Forest, Water, etc.
- Level II: More detailed categories like Residential, Commercial, Cropland, Deciduous Forest, etc.
- Level III: Highly specific categories such as Single-family Residential, Row Crops, Oak-Hickory Forest, etc.
- Level IV: The most detailed level, often customized for specific regional needs.
At Farmonaut, our satellite imagery analysis can provide LULC classification up to Level III, offering our clients detailed insights into their land resources. This information is crucial for precision agriculture, land use planning, and environmental monitoring.
Importance of LULC Classification in Agriculture
For the agricultural sector, LULC classification offers several benefits:
- Identifying suitable areas for specific crops
- Monitoring changes in agricultural land use over time
- Assessing the impact of urbanization on farmland
- Planning for sustainable land use practices
Our Jeevn AI Advisory System utilizes LULC data to provide tailored recommendations for crop management, helping farmers optimize their land use for maximum productivity and sustainability.
3. Terrain Classification: Unraveling Earth’s Topography
Terrain classification is another crucial aspect of land classification, focusing on the physical features of the Earth’s surface. It involves categorizing land based on elevation, slope, aspect, and other topographical characteristics.
Key Elements of Terrain Classification
- Elevation: The height of land above sea level
- Slope: The steepness or gradient of the land
- Aspect: The direction that a slope faces
- Roughness: The variability of the terrain surface
- Landforms: Distinct physical features like mountains, valleys, plains, etc.
At Farmonaut, we integrate terrain classification data into our satellite-based monitoring system. This information helps farmers understand how topography affects their land’s suitability for different crops and agricultural practices.
Applications of Terrain Classification in Agriculture
- Identifying areas prone to soil erosion
- Planning irrigation systems based on slope and drainage patterns
- Determining suitable areas for specific crops based on elevation and aspect
- Assessing potential flood risks in agricultural areas
Our platform combines terrain classification data with real-time satellite imagery to provide comprehensive insights for farm management. This integration allows for more precise decision-making in agricultural practices.
4. Landscape Classification: A Holistic Approach
Landscape classification takes a broader view, considering the interaction between natural and human-influenced elements in an area. It encompasses both LULC and terrain classification, providing a holistic understanding of the land.
Components of Landscape Classification
- Natural elements (vegetation, water bodies, landforms)
- Human-influenced elements (urban areas, agricultural fields, infrastructure)
- Ecological processes and interactions
- Cultural and historical aspects of land use
Farmonaut’s advanced satellite imagery analysis incorporates landscape classification to offer a comprehensive view of agricultural regions. This approach helps in understanding the broader context in which farming activities take place.
Benefits of Landscape Classification for Agriculture
- Ecosystem-based farm management
- Identification of potential wildlife corridors and buffer zones
- Assessment of landscape connectivity for biodiversity conservation
- Planning for sustainable agricultural landscapes
Our blockchain-based traceability solution leverages landscape classification data to provide consumers with a comprehensive understanding of where their food comes from, enhancing transparency in the agricultural supply chain.
5. The Role of Remote Sensing in Land Classification
Remote sensing technology plays a pivotal role in modern land classification methods. At Farmonaut, we harness the power of satellite imagery and advanced AI algorithms to provide accurate and up-to-date land classification data.
Advantages of Remote Sensing in Land Classification
- Large area coverage
- Regular and consistent data collection
- Multi-spectral imaging capabilities
- Cost-effective compared to traditional ground surveys
- Ability to monitor changes over time
Our satellite-based crop health monitoring system utilizes multi-spectral imagery to provide detailed LULC classification, helping farmers make informed decisions about crop management and resource allocation.
Remote Sensing Techniques Used in Land Classification
- Optical Remote Sensing: Uses visible and near-infrared light to classify land cover types
- Radar Remote Sensing: Useful for terrain classification and detecting surface roughness
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): Provides high-resolution elevation data for detailed terrain classification
- Hyperspectral Imaging: Offers detailed spectral information for precise LULC classification
Farmonaut’s platform integrates data from multiple remote sensing sources to provide comprehensive land classification information. Our API allows developers to access this data for custom applications.
6. Farmonaut’s Approach to Land Classification
At Farmonaut, we have developed a sophisticated approach to land classification that combines cutting-edge technology with agricultural expertise. Our method integrates satellite imagery, AI, and machine learning to provide accurate and actionable land classification data.
Key Features of Farmonaut’s Land Classification System
- High-resolution satellite imagery analysis
- AI-powered LULC classification
- Terrain analysis using advanced digital elevation models
- Integration of historical and real-time data
- Customizable classification schemes for specific agricultural needs
Our system is accessible through our user-friendly mobile apps, available for both Android and iOS platforms.
How Farmonaut’s System Compares to Traditional Methods
| Feature | Farmonaut Satellite System | Drone-based Monitoring | IoT-based Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coverage Area | Large (Global) | Limited (Local) | Very Limited (Field-level) |
| Data Collection Frequency | Daily to Weekly | On-demand | Continuous |
| Cost-effectiveness | High | Medium | Low |
| Data Processing Time | Fast (AI-powered) | Medium | Real-time |
| Scalability | Highly Scalable | Moderately Scalable | Limited Scalability |
| Weather Independence | High | Low | Medium |
Our satellite-based system offers unparalleled coverage and cost-effectiveness, making it an ideal solution for large-scale agricultural operations and precision farming.
7. Applications of Land Classification in Agriculture
Land classification plays a crucial role in various aspects of agriculture. At Farmonaut, we help our clients leverage this information for improved farm management and sustainable practices.
Key Applications
- Crop Suitability Analysis: Using LULC and terrain data to determine optimal crops for specific areas
- Precision Agriculture: Tailoring farming practices based on detailed land classification data
- Soil Conservation: Identifying areas prone to erosion and planning conservation measures
- Water Management: Planning irrigation systems and water conservation strategies
- Yield Prediction: Combining land classification with weather data for accurate yield forecasts
- Land Use Planning: Guiding decisions on agricultural expansion and land preservation
Our Jeevn AI Advisory System integrates these applications to provide personalized recommendations for farm management, accessible through our mobile app.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Land Classification in Agriculture
While we don’t include specific case studies, our clients have reported significant improvements in crop yields, resource efficiency, and sustainability after implementing our land classification-based solutions.
8. Challenges and Future Trends in Land Classification
As technology advances, the field of land classification continues to evolve. At Farmonaut, we stay at the forefront of these developments to provide our clients with the most accurate and useful data.
Current Challenges
- Handling big data from multiple satellite sources
- Improving classification accuracy in complex landscapes
- Integrating multi-temporal data for change detection
- Balancing spatial resolution with coverage area
Future Trends
- AI and Deep Learning: Enhanced classification algorithms for more accurate results
- Hyperspectral Imaging: More detailed spectral information for precise classification
- Integration with IoT: Combining satellite data with ground-based sensors for comprehensive monitoring
- Real-time Classification: Faster processing for near-instantaneous land classification updates
- 3D Land Classification: Incorporating LiDAR data for detailed 3D landscape models
Farmonaut is actively working on these trends, with ongoing research and development to enhance our land classification capabilities. Our API documentation is regularly updated to reflect these advancements.
9. FAQs
- Q: What is the difference between land use and land cover?
A: Land use refers to how humans utilize the land (e.g., agriculture, urban development), while land cover describes the physical material on the Earth’s surface (e.g., vegetation, water, bare soil). - Q: How often should land classification be updated?
A: The frequency of updates depends on the rate of change in the area. In rapidly changing regions, annual updates may be necessary, while in stable areas, updates every 3-5 years may suffice. - Q: Can Farmonaut’s land classification system be used for small farms?
A: Yes, our system is scalable and can be used for farms of all sizes, from small holdings to large commercial operations. - Q: How accurate is satellite-based land classification?
A: With advanced AI algorithms and high-resolution imagery, our system achieves accuracy levels of up to 95% for broad LULC categories, and 85-90% for more detailed classifications. - Q: How does terrain classification help in agricultural planning?
A: Terrain classification provides insights into slope, aspect, and elevation, which are crucial for planning irrigation systems, selecting suitable crops, and implementing soil conservation measures.
For more information on how Farmonaut’s land classification solutions can benefit your agricultural operations, please visit our website or contact our support team.
Subscribe to Farmonaut
Ready to leverage the power of advanced land classification for your agricultural needs? Subscribe to Farmonaut’s services now:
By subscribing to Farmonaut, you gain access to our comprehensive suite of land classification tools and agricultural management solutions. Join us in revolutionizing agriculture through advanced technology and data-driven insights.
In conclusion, land classification is a vital tool in modern agriculture and environmental management. At Farmonaut, we’re committed to providing cutting-edge solutions that make this powerful technology accessible and actionable for farmers, agribusinesses, and policymakers worldwide. By harnessing the power of satellite imagery, AI, and advanced analytics, we’re helping to shape a more sustainable and productive future for agriculture.










