Hydroponic Farming Model: Urban Hydroponics Cost & Working (2025 Guide)
“Hydroponic systems use up to 90% less water than traditional soil farming methods in urban environments.”
Table of Contents
- Summary: Hydroponic Farming Revolutionizing Agriculture for the Future
- Hydroponic Trivia
- Understanding the Hydroponic Farming Model
- Working Models of Hydroponic Farming
- How Hydroponic Systems Work: The Science Behind Growth
- Hydroponics in Urban Environments: The Urban Farming Revolution
- Hydroponic Farming Cost Analysis: Is it Worth the Investment?
- Hydroponic vs Traditional Farming: Cost & Efficiency Comparison Table
- Advancing Farming Technology in 2025: Efficiency, Traceability, and Sustainability
- Farmonaut: Satellite Tools for 21st Century Farms
- Hydroponic Farming Model: Frequently Asked Questions
Summary: Hydroponic Farming – Revolutionizing Agriculture for the Future
Hydroponic farming is emerging as a pivotal approach to sustainable food production and urban agriculture as the global population and urbanization trends accelerate. This hydroponic farming model bypasses the limitations of arable land and water scarcity by growing plants in a soilless, nutrient-rich solution. By 2025, the hydroponic farming working model will help cities and regions meet critical food security needs, offering minimal water consumption, year-round crop growth, and unmatched resource efficiency.
Hydroponic urban farming leverages innovative technology both inside and outside city limits. The cost of hydroponics is steadily falling as adoption rises, while the benefits—including higher yields, reduced carbon footprint, and environmental sustainability—are driving global interest in this transformative model.
“Hydroponic systems use up to 90% less water than traditional soil farming methods in urban environments.”
“Urban hydroponic farms can produce crops up to 3 times faster than conventional agriculture using advanced technology.”
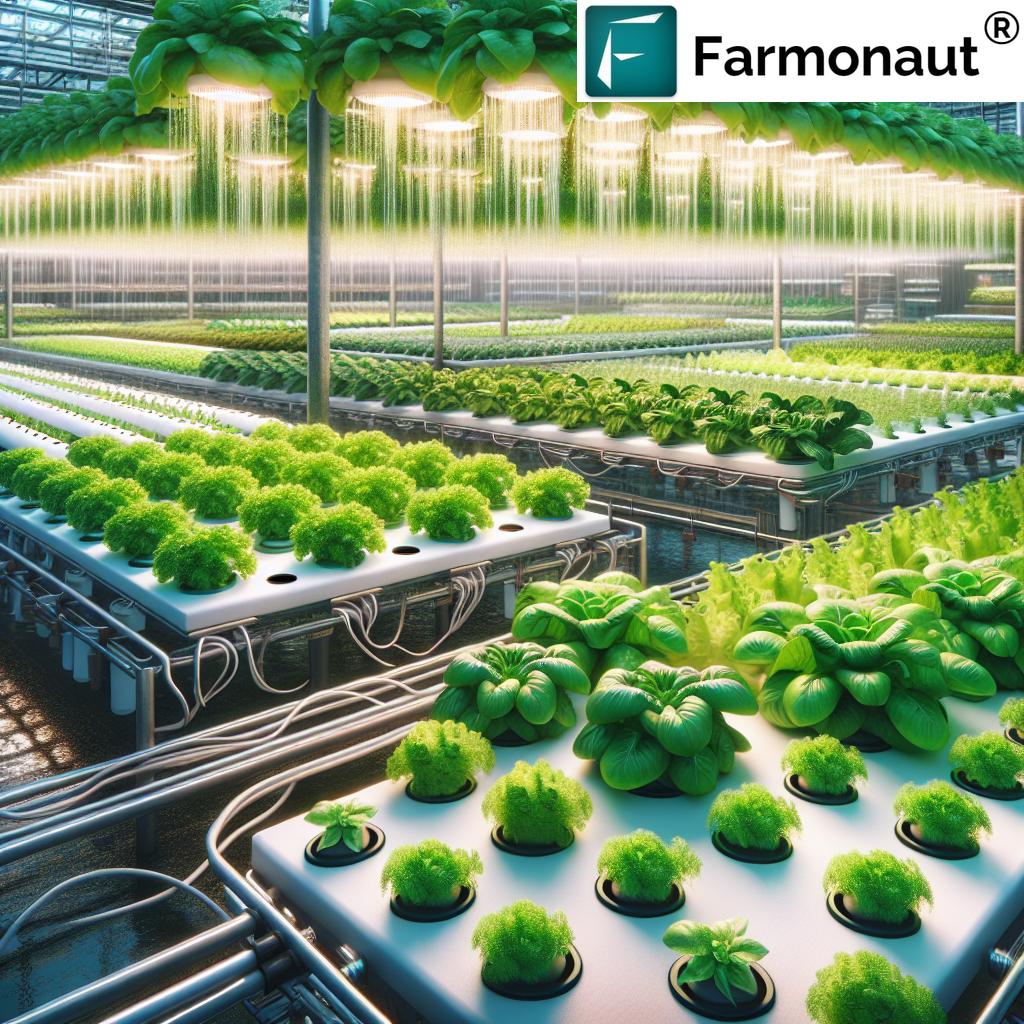
Understanding the Hydroponic Farming Model
The hydroponic farming model represents an innovative approach to modern agriculture, particularly in urban areas where space, water, and arable land are in short supply. Unlike traditional farming, which depends on fertile soil, weather, and consistent rainfall, farming hydroponics enables plants to thrive in a controlled environment.
At its core, the model is simple: plants are grown without soil. Instead, roots are submerged in or misted with a carefully balanced solution containing essential nutrients. This technique—adaptable across various system configurations—grants growers precise control over nutrient levels, pH, light, temperature, and humidity. Such control optimizes growth and maximizes yields in any environment.
Key Features of the Hydroponic Farming Model:
- Soilless Cultivation– Direct delivery of nutrients via water increases uptake efficiency and minimizes waste.
- Closed Circuit Irrigation– Unlike soil-based systems, hydroponic setups recycle water, saving up to 90% compared to conventional farming.
- Space-Efficient Setups– Customizable systems allow vertical, rooftop, and even mobile farms, making them ideal for urban application.
- Year-Round Production– Controlled environments are not subject to seasonal weather variations, ensuring continuous crop production and higher yields.
Hydroponic farming systems come in several configurations—each with unique advantages and suitability for specific crops, production scales, and urban environments. Let’s explore their workings in detail.
Working Models of Hydroponic Farming: Exploring Technology & Method
The hydroponic farming working model encompasses a variety of methods, each designed to meet specific space requirements and optimize plant growth.
- Nutrient Film Technique (NFT): A thin film of nutrient solution flows continuously over plant roots, which are suspended in a channel. This method is space-saving and ideal for leafy greens.
- Deep Water Culture (DWC): Plants float on rafts in a deep reservoir of oxygenated nutrient solution. Roots remain submerged, receiving a constant supply of water and nutrients.
- Aeroponics: Roots are suspended in air and misted with nutrient-rich water, increasing oxygen availability and promoting rapid growth.
- Drip Systems: Controlled drippers deliver precise amounts of solution to each plant’s root zone, making this model highly scalable for both small and large urban hydroponic farms.
Each hydroponic system leverages closed circuit design, enabling water recycling and reducing evaporation loss—a critical advantage in regions with mounting water scarcity and unpredictable climate variability.
These systems can be set up in:
- Rooftops – Utilizing underused urban spaces for food production
- Abandoned warehouses – Repurposed into vertical or horizontal farms
- Custom modular installations – Flexible solutions for commercial agriculture or individual entrepreneurs
How Hydroponic Systems Work: The Science Behind Growth
At its base, the hydroponic farming working model operates on a simple, innovative principle: grow plants by immersing their roots in a nutrient solution instead of soil.
Key Elements of a Hydroponic System Include:
- Nutrient Solution: A precisely balanced mix of macronutrients (Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium) and micronutrients required by the specific crop.
- Water Reservoir: Stores and recirculates the nutrient solution through the system, ensuring minimal consumption and water efficiency.
- Pumps and Aeration: Keep the solution moving (and oxygenated) to deliver nutrients and avoid stagnation.
- Growing Structures: Channels, net pots, rafts, or vertical columns support plant roots and provide maximum exposure to the nutrient solution.
- Lighting and Climate Control: LED lights and HVAC controls regulate light, temperature, and humidity—enabling consistent, rapid growth cycles regardless of season or external weather.
The controlled environment enables urban farmers to optimize plant growth by adjusting variables to meet the precise requirements of each crop:
- Regulate pH: Fine-tune solution acidity/alkalinity for nutrient uptake.
- Nutrient Levels: Directly influence growth stage and productivity.
- Humidity & Temperature: Ensure optimal photosynthesis and transpiration.
This hydroponic model is critical for enabling year-round farming in urban spaces, especially as traditional agriculture faces mounting challenges of land scarcity and climate unpredictability.
Hydroponics in Urban Environments: The Urban Farming Revolution
Hydroponic urban farming is transforming cities into food production hubs. This evolution is powered by technological innovation and propelled forward by shifting demographics: By 2025, the urban population will exceed 60% globally, further accelerating the need for sustainable urban food systems.
Key Advantages of Urban Hydroponics:
- Localized Food Production: Produce is grown closer to consumers (house to plate), reducing transportation costs, spoilage, and overall carbon footprint.
- Repurposing Space: Rooftops, abandoned warehouses, and unused urban lots are transformed into high-yield, vertical farms.
- Jobs & Education: Urban hydroponics fosters new employment, entrepreneurship, and sustainability learning opportunities within cities.
- Food Security: Empowered urban communities gain reliable year-round access to fresh produce, mitigating impacts from supply chain disruption or climate variability.
Technological integration further enhances hydroponic farming efficiency:
- IoT sensors & automation: Enable real-time monitoring of crop health, predict maintenance needs, and automate nutrient delivery.
- AI and Satellite-driven analytics: Further optimize resource use, detect plant stress early, and maximize overall system performance.
By bringing hydroponic farming directly to cities, we are enabling sustainable, resilient, and scalable food production for the 21st century.
Hydroponic Farming Cost Analysis: Is it Worth the Investment?
One of the most common questions is about hydroponic farming cost. While hydroponic systems require greater upfront investment due to technology, infrastructure, and energy needs, they often deliver superior returns over time by maximizing space efficiency, yield, and resource conservation.
Main Hydroponic Cost Categories:
- Initial Setup Cost: Infrastructure (frames, tanks, growing beds), climate control, lighting, and automation hardware.
- Operational Expenses: Energy (lighting, pumps), water, nutrients, labor, and periodic maintenance.
- Consumables: Seedlings, plant nutrition, replacement membranes/filters, and growing media (rockwool, coconut coir, clay balls, etc.).
Recent innovations are driving costs down:
- Affordable LED Lighting: Energy-efficient, long-life LED technology is transforming operating expenses.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Solar, wind, and battery storage are increasingly used to offset power consumption.
- Modular Systems: Allow for scaling up or down as needed, minimizing initial expenditures.
Hydroponic farming models boast:
- Higher yields per sq ft – You can grow more crops in less space with hydroponics.
- Faster crop cycles – Rapid growth results in more crop cycles per year, increasing profits.
- Reduced pesticide use – Controlled environments minimize the need for chemical intervention.
- Minimal land use – Ideal for urban agriculture and non-arable lands.
These factors—combined with growing consumer demand for pesticide-free produce and government incentives—are steadily improving the overall economic viability of hydroponic farming.
Hydroponic vs Traditional Farming: Cost & Efficiency Comparison Table
| Parameter | Hydroponic Model (Estimated Values) | Traditional Soil-based Model (Estimated Values) | Comparative Insight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Setup Cost (USD/sq ft) | $20–$80 (urban, advanced tech) | $2–$6 (basic infrastructure) | Hydroponics is higher upfront, but pays off over time with increased productivity and efficiency. |
| Water Usage per Crop Cycle (litres) | 10–20 (uses up to 90% less water) | 100–200 | Hydroponic farming is far more water efficient, making it ideal for water-scarce urban environments. |
| Average Yield per sq ft (per annum) | 12–25 kg | 4–7 kg | Hydroponics achieves 2–4x higher yields in less space via optimized growth conditions. |
| Crop Growth Time (days) | 21–28 (leafy greens; faster cycles) | 45–65 | Hydroponic crops grow up to 3x faster, boosting production cycles per year. |
| Space Requirement | Compact, vertical possible | Sprawling, horizontal | Hydroponic systems maximize yield per area, ideal for urban settings with limited land. |
| Labor Cost | Moderate (automatable) | High (manual labor) | Automation & controlled environments can reduce hydroponic labor costs over time. |
Advancing Farming Technology in 2025: Efficiency, Traceability, and Sustainability
As we stride into 2025 and beyond, the intersection of hydroponics and digital agritech solutions is revolutionizing how we grow food. Satellite monitoring, AI-driven crop advisory, and blockchain traceability play critical roles in supporting hydroponic farms to maximize crop yields and embrace sustainable practices.
Traceability has also become a key requirement for future-ready hydroponic food production. Using solutions such as blockchain-based product traceability from Farmonaut, growers can guarantee the authenticity and purity of their produce. This direct transparency fosters consumer trust and helps monitor food safety within urban hydroponic supply chains.
As carbon regulations and sustainability policies intensify, tracking resource consumption and emission has never been more important. Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting tools enable both urban and commercial hydroponic farms to monitor, manage, and demonstrate their environmental impact in real time, aligning with global efforts to reduce carbon output.
Farmonaut: Satellite Tools for 21st Century Farms
At Farmonaut, we understand that modern hydroponic farming and urban agriculture require more than just advanced growing systems—they need real-time, data-driven decision support. Our satellite-based monitoring platform provides actionable insights on vegetation health, crop stress, water management, and resource allocation, without needing expensive hardware installations.
You can access Farmonaut’s crop health analytics and visualizations via our web app, Android, and iOS—anywhere, anytime—allowing both small urban farms and large agricultural operations to thrive. For those needing in-depth customization, the Farmonaut API and its developer documentation enable seamless cloud integration of our data streams into your own farm management system.

Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI delivers predictive advice and operational strategies for hydroponic farms, increasing yields, reducing costs, and optimizing nutrient schedules. Our fleet management platform helps track vehicle and equipment utilization efficiently—essential for scaling up automated urban agriculture and indoor farming logistics.
To support the future of global agricultural finance and insurance, we offer satellite-based crop loan and insurance verification services. By lowering fraud risk and making satellite verification accessible, we help urban and commercial hydroponic farmers access much-needed funding quickly and securely.
Explore our large-scale farm management app to scale operations for both indoor vertical setups and horizontal hydroponic installations—empowering you to monitor, analyze, and optimize multiple growing sites, whether in the city or countryside.
With an unwavering commitment to cost reduction, transparency, and sustainability, we at Farmonaut believe that technology-driven hydroponics is the cornerstone of resilient urban food systems and global food security in 2025 and beyond.
Hydroponic Farming Model: Frequently Asked Questions
What is the hydroponic farming model?
The hydroponic farming model is a method of growing plants without soil by directly supplying roots with a nutrient-rich water solution. It’s highly efficient, minimizes water usage, and allows precise control over plant growth variables.
How does hydroponic urban farming reduce resource consumption?
Hydroponic urban farming uses a closed water circuit, recycling up to 90% of the water, and eliminates significant losses to soil evaporation. It also requires less space, less land, and reduces the need for chemical pesticides.
What are the main working models of hydroponic farming?
Common models include Nutrient Film Technique (NFT), Deep Water Culture (DWC), aeroponics, and drip systems—each tailored to space, crop, and yield requirements.
What is the average cost of setting up a hydroponic farm in urban areas?
Costs range from $20-80 per sq ft for advanced urban hydroponic setups, higher than traditional, but are offset by much greater yields, water savings, and automation potential.
What are the environmental benefits of adopting hydroponic farming in cities?
Hydroponics dramatically reduces water and land use, minimizes carbon footprint (through local food production), and supports sustainable diet diversity in urban regions.
How does Farmonaut support modern hydroponic agriculture?
Farmonaut provides satellite-based crop health and resource monitoring, AI advisories, blockchain product traceability, real-time data insights, and tools for operational optimization suitable for hydroponic and all farming models.
Conclusion: Hydroponic Farming Model Shaping Urban Agriculture of the Future
The hydroponic farming model stands as a beacon of agricultural innovation—especially as urbanization accelerates and traditional agriculture faces new challenges. By 2025 and beyond, hydroponic farms will play a pivotal role within urban food systems—reducing costs, minimizing environmental impact, and enabling sustainable, resilient food production. Technology-led farming hydroponics will empower cities to meet growing food needs and adapt to climate variability, while providing scalable solutions for regions with limited arable land or water scarcity.
With advancements in satellite monitoring, AI, and blockchain-enabled traceability, the future of hydroponic urban farming is not just about increased yields—it’s about creating a transparent, secure, and resource-efficient food system for all.
Ready to harness the power of technology-driven hydroponics? Discover how Farmonaut’s data platforms and real-time insights are transforming the possibilities for hydroponic farming in cities, commercial farms, and beyond.